Yonsei Med J.
2018 Jan;59(1):113-118. 10.3349/ymj.2018.59.1.113.
Clinical Outcomes of Low-Dose Methotrexate Therapy as a Second-Line Drug for Intravenous Immunoglobulin-Resistant Kawasaki Disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Severance Children's Hospital, Seoul, Korea. dskim6634@yuhs.ac
- KMID: 2418857
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2018.59.1.113
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) is the standard treatment for Kawasaki disease (KD). However, there is still no standard treatment for IVIG-resistant KD. This study aimed to evaluate the efficacy of low-dose methotrexate (MTX) as a treatment for IVIG-resistant KD.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We retrospectively analyzed 10-year data for patients with IVIG-resistant KD who were administered MTX at Severance Children's Hospital.
RESULTS
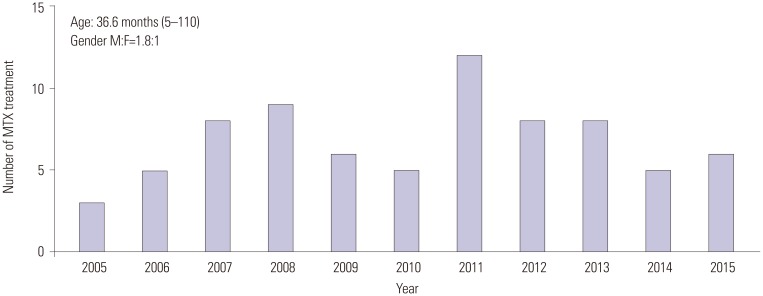
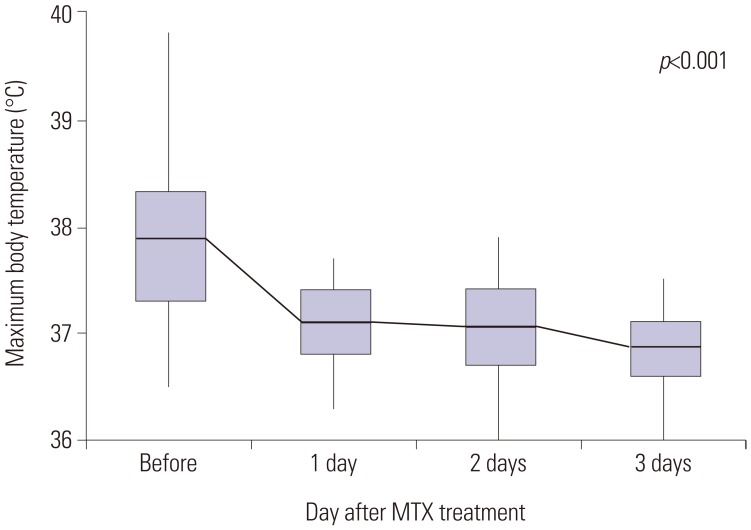
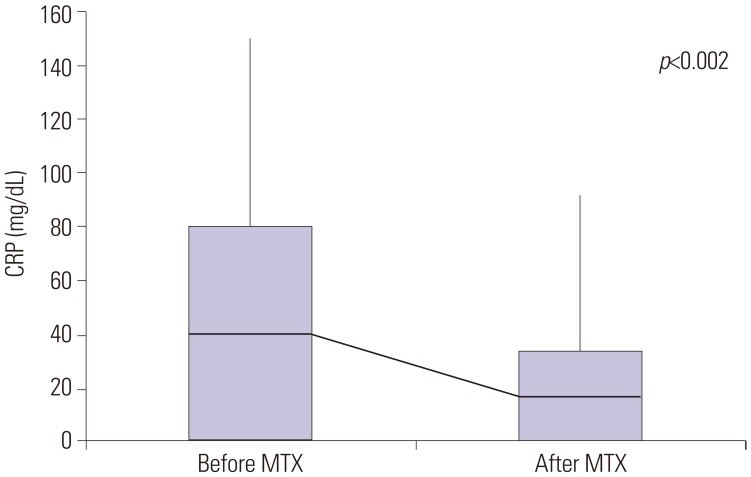
The subjects included 75 patients with KD aged 5 months to 9.2 years who had been administered MTX. Their maximum body temperatures decreased significantly within 24 h of therapy. The patients' C-reactive protein levels were significantly lower 1 week after administering the first dose of MTX than those before treatment. No adverse effect for MTX was observed.
CONCLUSION
MTX treatment of IVIG-resistant KD resulted in rapid defervescence, improvement of clinical symptoms, and normalization of acute-phase reactants in all patients. Thus, MTX could be a candidate treatment for IVIG-resistant KD.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
C-Reactive Protein/analysis
Child
Child, Preschool
Coronary Vessels/pathology
Demography
Dose-Response Relationship, Drug
Drug Therapy, Combination
Female
Humans
Immunoglobulins, Intravenous/*therapeutic use
Infant
Male
Methotrexate/administration & dosage/*therapeutic use
Mucocutaneous Lymph Node Syndrome/blood/*drug therapy
Retrospective Studies
Steroids/therapeutic use
Treatment Outcome
Immunoglobulins, Intravenous
Steroids
C-Reactive Protein
Methotrexate
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Infliximab Treatment for Intravenous Immunoglobulin-resistant Kawasaki Disease: a Multicenter Study in Korea
Gyu Hur, Min Seob Song, Sejung Sohn, Hyoung Doo Lee, Gi Beom Kim, Hwa Jin Cho, Kyung Lim Yoon, Chan Uhng Joo, Myung Chul Hyun, Chul Ho Kim
Korean Circ J. 2019;49(2):183-191. doi: 10.4070/kcj.2018.0214.
Reference
-
1. Dimitriades VR, Brown AG, Gedalia A. Kawasaki disease: pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, and management. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2014; 16:423. PMID: 24744086.
Article2. Fukushige J, Takahashi N, Ueda K, Hijii T, Igarashi H, Ohshima A. Long-term outcome of coronary abnormalities in patients after Kawasaki disease. Pediatr Cardiol. 1996; 17:71–76. PMID: 8833489.
Article3. Rashid AK, Kamal SM, Ashrafuzzaman M, Mustafa KG. Kawasaki disease and its treatment - an update. Curr Rheumatol Rev. 2014; 10:109–116. PMID: 25599679.
Article4. Shulman ST. Intravenous immunoglobulin for the treatment of Kawasaki disease. Pediatr Ann. 2017; 46:e25–e28. PMID: 28079915.
Article5. Egami K, Muta H, Ishii M, Suda K, Sugahara Y, Iemura M, et al. Prediction of resistance to intravenous immunoglobulin treatment in patients with Kawasaki disease. J Pediatr. 2006; 149:237–240. PMID: 16887442.
Article6. Zhu BH, Lv HT, Sun L, Zhang JM, Cao L, Jia HL, et al. A meta-analysis on the effect of corticosteroid therapy in Kawasaki disease. Eur J Pediatr. 2012; 171:571–578. PMID: 22057683.
Article7. Lee MS, An SY, Jang GC, Kim DS. A case of intravenous immunoglobulin-resistant Kawasaki disease treated with methotrexate. Yonsei Med J. 2002; 43:527–532. PMID: 12205742.
Article8. Ahn SY, Kim DS. Treatment of intravenous immunoglobulin-resistant Kawasaki disease with methotrexate. Scand J Rheumatol. 2005; 34:136–139. PMID: 16095010.9. Lee TJ, Kim KH, Chun JK, Kim DS. Low-dose methotrexate therapy for intravenous immunoglobulin-resistant Kawasaki disease. Yonsei Med J. 2008; 49:714–718. PMID: 18972590.
Article10. Fischer P, Uttenreuther-Fischer MM, Naoe S, Gaedicke G. Kawasaki disease: update on diagnosis, treatment, and a still controversial etiology. Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 1996; 13:487–501. PMID: 8940732.
Article11. Rowley AH, Shulman ST. Pathogenesis and management of Kawasaki disease. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2010; 8:197–203. PMID: 20109049.
Article12. Burns JC, Shimizu C, Shike H, Newburger JW, Sundel RP, Baker AL, et al. Family-based association analysis implicates IL-4 in susceptibility to Kawasaki disease. Genes Immun. 2005; 6:438–444. PMID: 15889128.
Article13. Lee TJ, Chun JK, Yeon SI, Shin JS, Kim DS. Increased serum levels of macrophage migration inhibitory factor in patients with Kawasaki disease. Scand J Rheumatol. 2007; 36:222–225. PMID: 17657678.
Article14. Leung DY, Schlievert PM, Meissner HC. The immunopathogenesis and management of Kawasaki syndrome. Arthritis Rheum. 1998; 41:1538–1547. PMID: 9751085.
Article15. Kim KY, Kim DS. Recent advances in Kawasaki disease. Yonsei Med J. 2016; 57:15–21. PMID: 26632378.
Article16. Kitamura S, Kameda Y, Seki T, Kawachi K, Endo M, Takeuchi Y, et al. Long-term outcome of myocardial revascularization in patients with Kawasaki coronary artery disease. A multicenter cooperative study. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1994; 107:663–673. PMID: 8127095.17. Wong PH, White KM. Impact of immunoglobulin therapy in pediatric disease: a review of immune mechanisms. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2016; 51:303–314. PMID: 26142065.
Article18. Saneeymehri S, Baker K, So TY. Overview of pharmacological treatment options for pediatric patients with refractory Kawasaki disease. J Pediatr Pharmacol Ther. 2015; 20:163–177. PMID: 26170768.
Article19. Kuo HC, Yang KD, Chang WC, Ger LP, Hsieh KS. Kawasaki disease: an update on diagnosis and treatment. Pediatr Neonatol. 2012; 53:4–11. PMID: 22348488.
Article20. Miura M, Kohno K, Ohki H, Yoshiba S, Sugaya A, Satoh M. Effects of methylprednisolone pulse on cytokine levels in Kawasaki disease patients unresponsive to intravenous immunoglobulin. Eur J Pediatr. 2008; 167:1119–1123. PMID: 18175148.
Article21. Ogata S, Bando Y, Kimura S, Ando H, Nakahata Y, Ogihara Y, et al. The strategy of immune globulin resistant Kawasaki disease: a comparative study of additional immune globulin and steroid pulse therapy. J Cardiol. 2009; 53:15–19. PMID: 19167633.
Article22. Saji T, Takatsuki S, Kobayashi T. [Anti TNF-α (infliximab) treatment for intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) resistance patients with acute Kawasaki disease the effects of anticytokine therapy]. Nihon Rinsho. 2014; 72:1641–1649. PMID: 25518416.23. Bachlava E, Loukopoulou S, Karanasios E, Chrousos G, Michos A. Management of coronary artery aneurysms using abciximab in children with Kawasaki disease. Int J Cardiol. 2016; 220:65–69. PMID: 27372045.
Article24. Okada S, Azuma Y, Suzuki Y, Yamada H, Wakabayashi-Takahara M, Korenaga Y, et al. Adjunct cyclosporine therapy for refractory Kawasaki disease in a very young infant. Pediatr Int. 2016; 58:295–298. PMID: 26670024.
Article25. Suzuki H, Terai M, Hamada H, Honda T, Suenaga T, Takeuchi T, et al. Cyclosporin A treatment for Kawasaki disease refractory to initial and additional intravenous immunoglobulin. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2011; 30:871–876. PMID: 21587094.
Article26. Wessels JA, Huizinga TW, Guchelaar HJ. Recent insights in the pharmacological actions of methotrexate in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2008; 47:249–255. PMID: 18045808.
Article27. Dabkowska B, Dabkowski J. [Methotrexate–mechanism of action and application]. Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2001; 11:452–455. PMID: 11852822.28. Cronstein BN. Molecular mechanism of methotrexate action in inflammation. Inflammation. 1992; 16:411–423. PMID: 1428120.
Article29. Gülfe A, Sturfelt G. [Severe adverse effect of methotrexate in rheumatoid arthritis. Don't forget security routines in intercurrent disease!]. Lakartidningen. 1997; 94:1811–1812. PMID: 9190463.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Low-dose Methotrexate Therapy for Intravenous Immunoglobulin-resistant Kawasaki Disease
- A Case of Intravenous Immunoglobulin-Resistant Kawasaki Disease Treated with Methotrexate
- Predictors and management of intravenous immunoglobulin-resistant Kawasaki disease
- Efficacy of Dexamethasone Therapy for Coronary Lesion after Immunoglobulin-retreated Kawasaki Disease
- Treatment of Intravenous Immune-Globulin Resistant Kawasaki Disease with Corticosteroids