J Korean Soc Radiol.
2018 Sep;79(3):139-151. 10.3348/jksr.2018.79.3.139.
Pulmonary Comorbidities of Lung Emphysema
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Cheonan Hospital, Cheonan, Korea. ytokim@schmc.ac.kr
- KMID: 2418655
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2018.79.3.139
Abstract
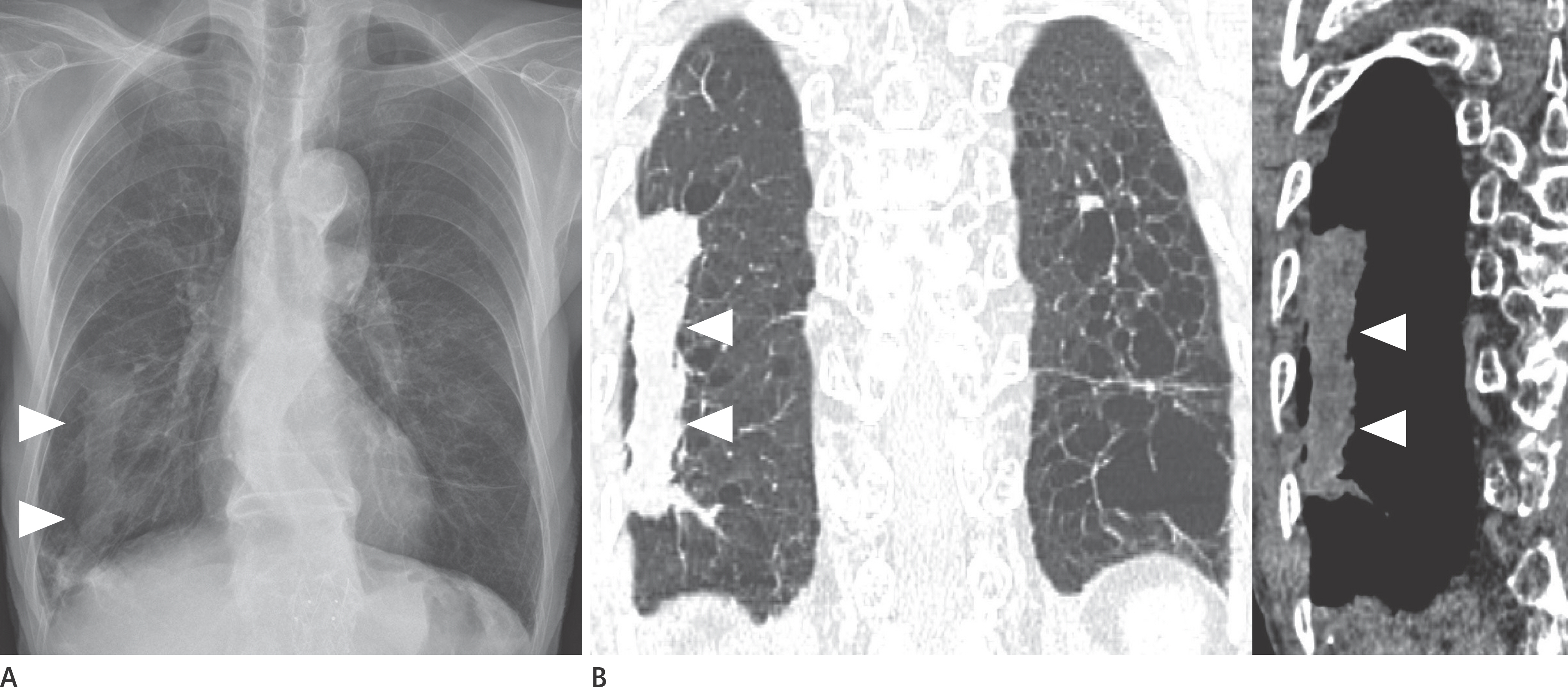
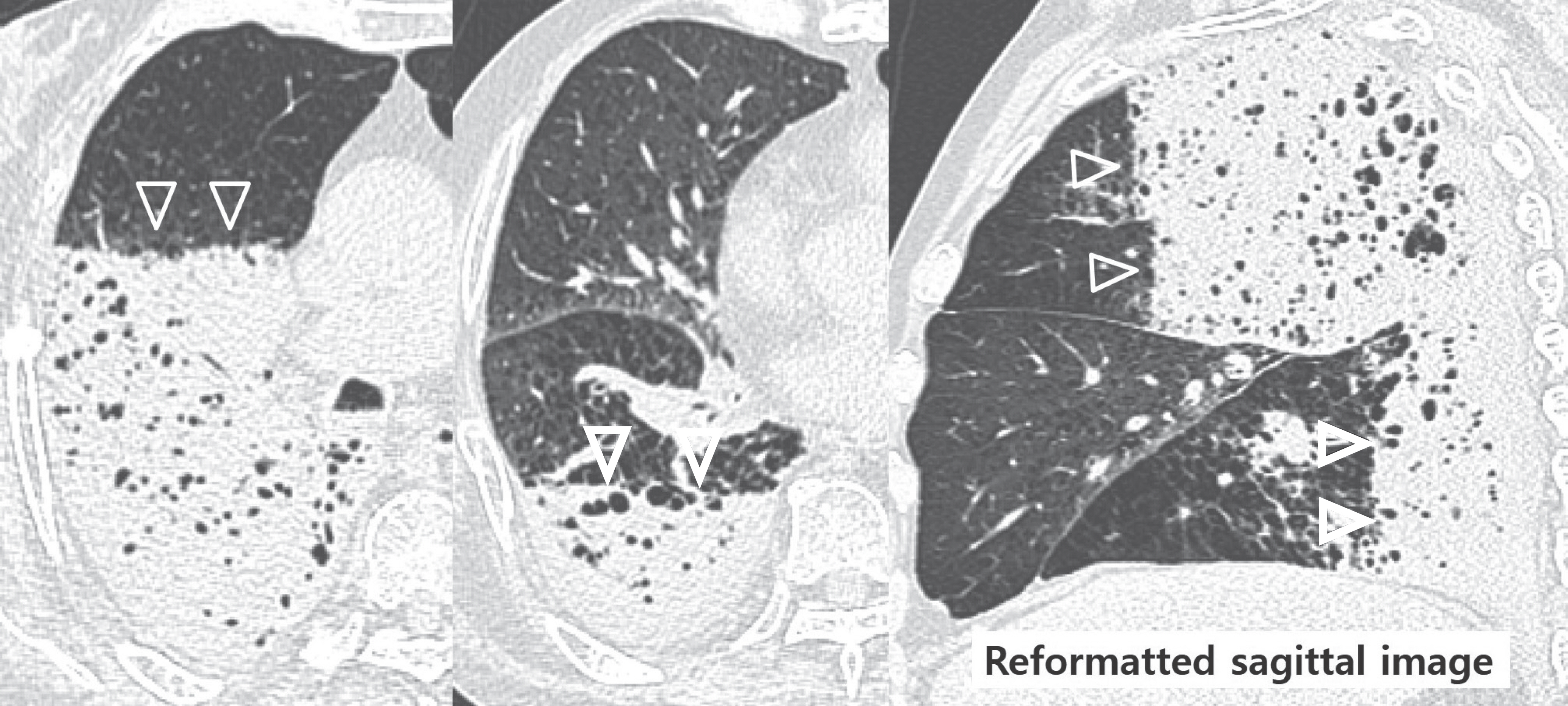
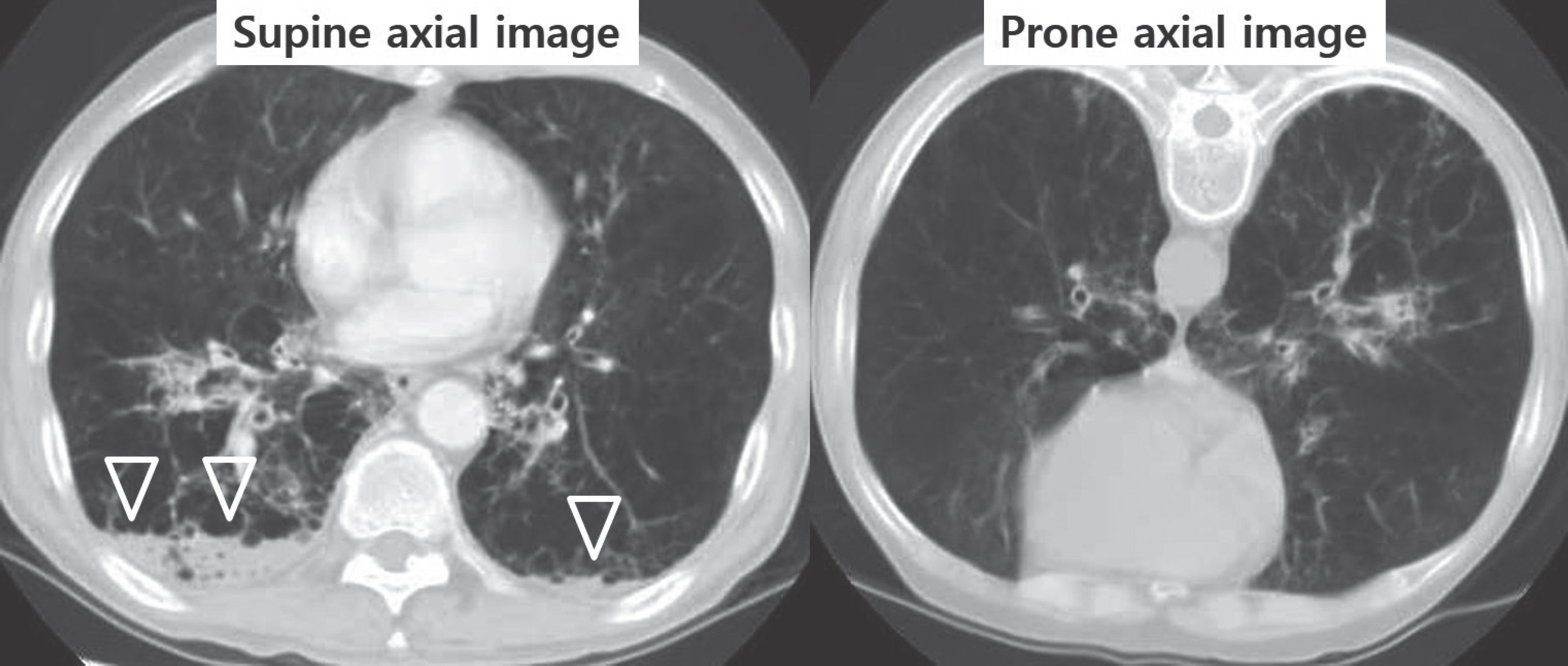
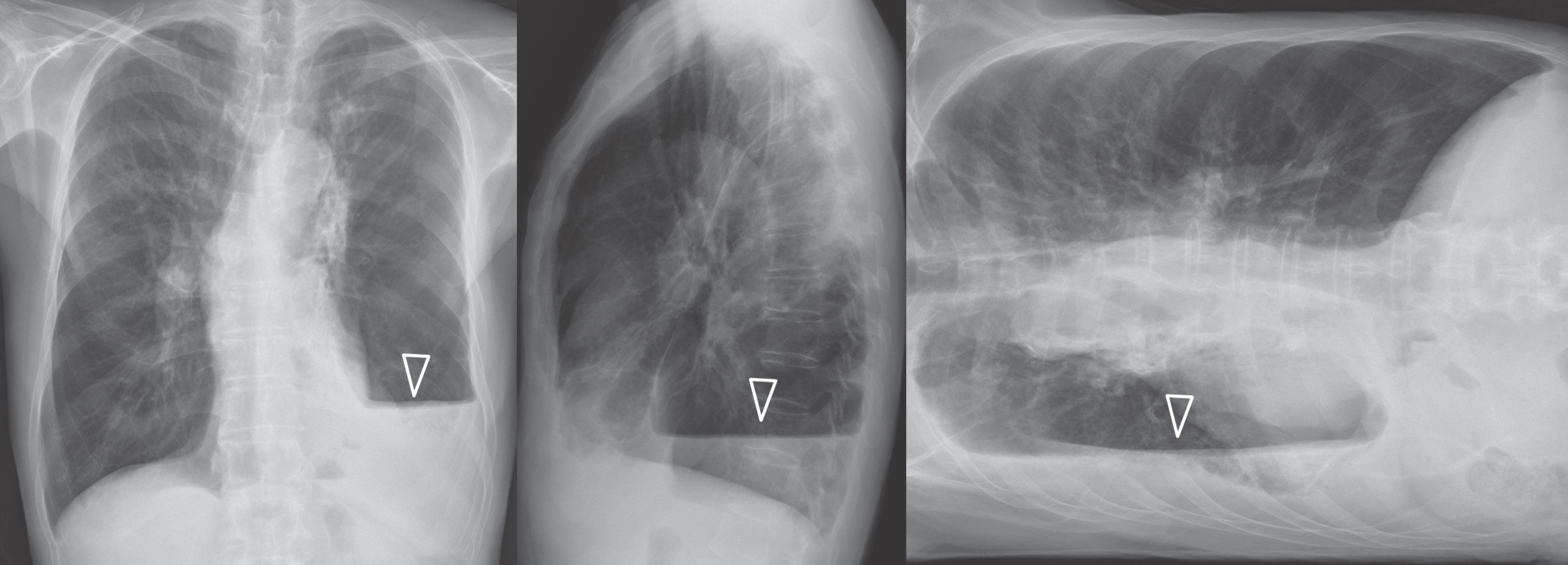
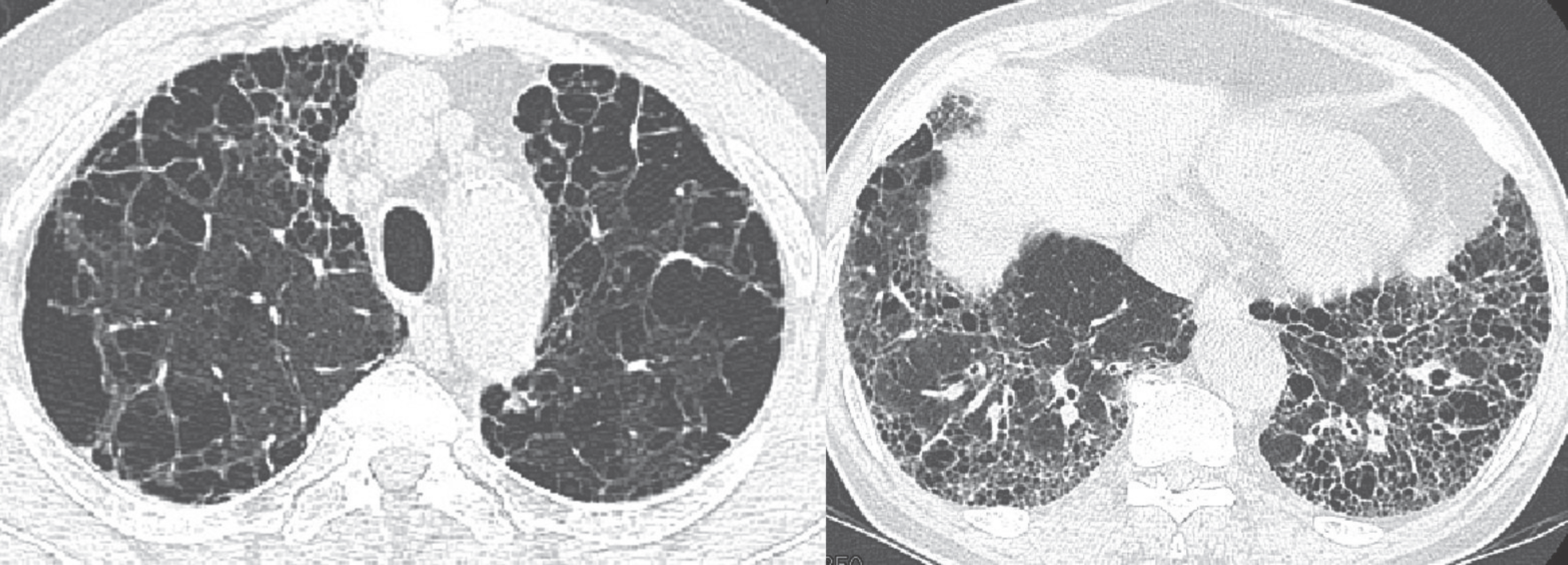
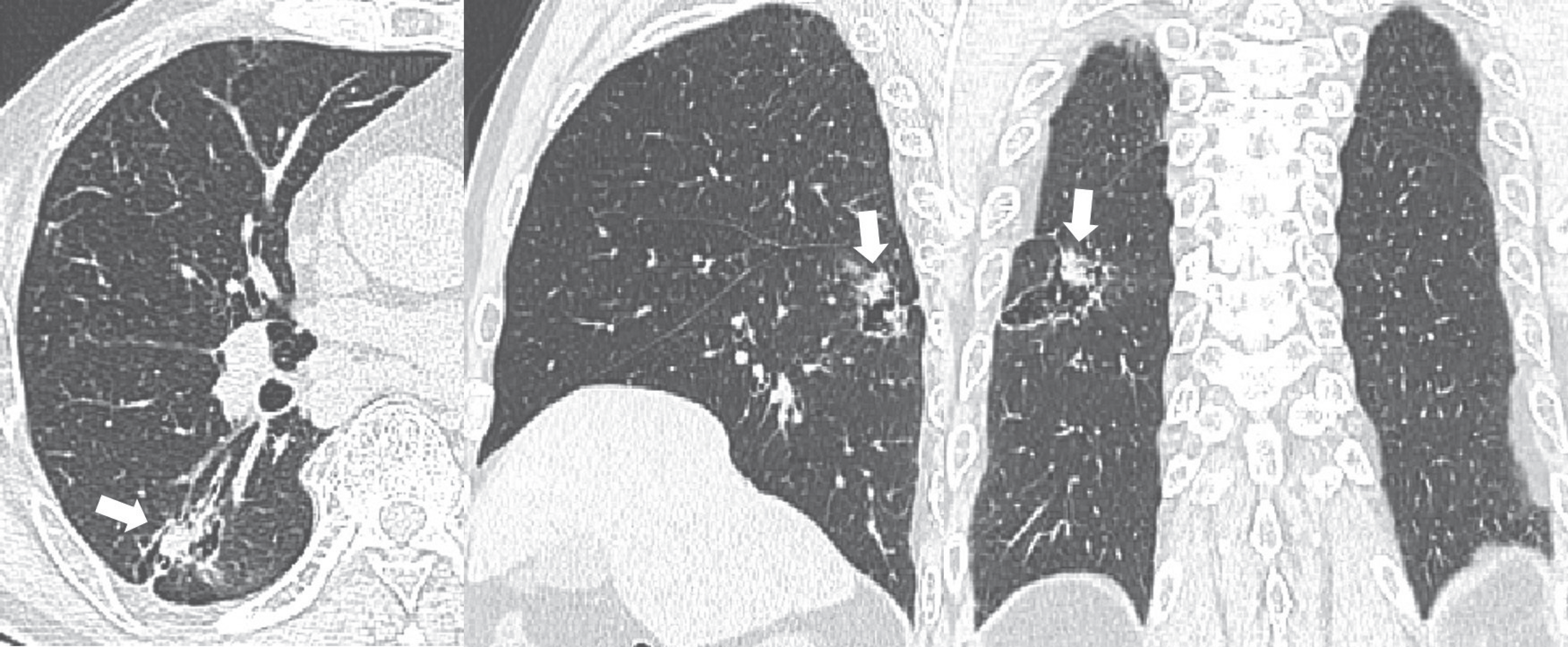
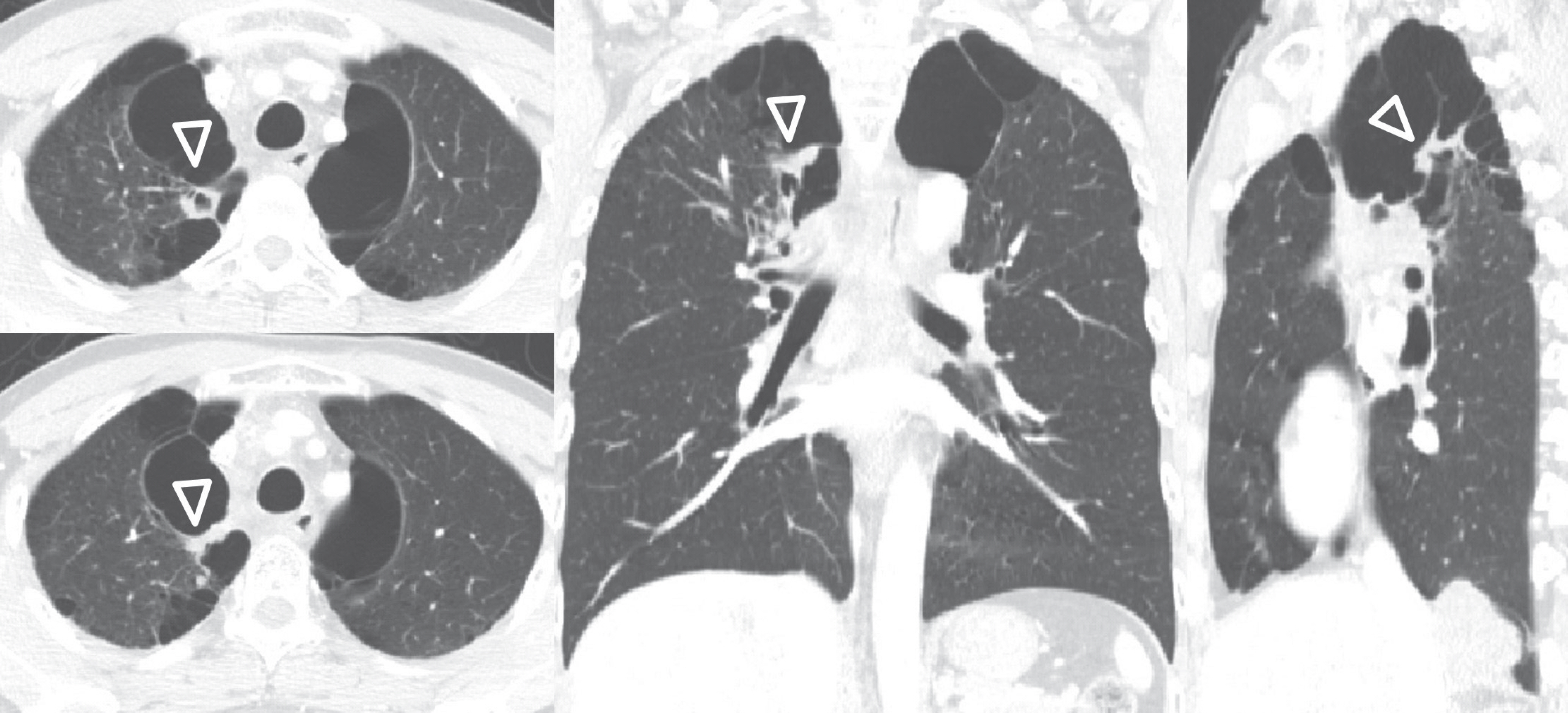
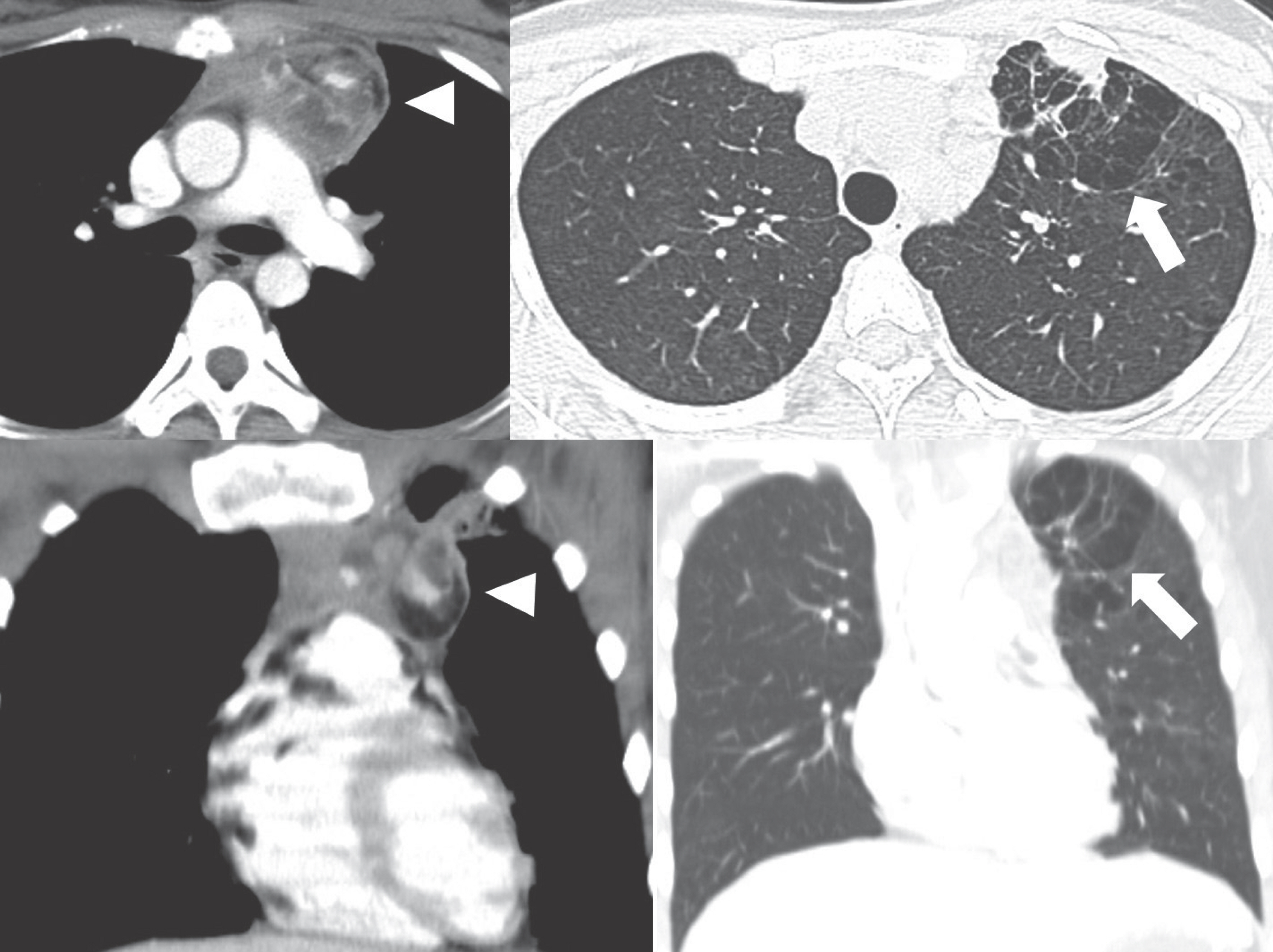
- Pulmonary emphysema is defined as the "abnormal permanent enlargement of the airspaces distal to the terminal bronchioles accompanied by destruction of the alveolar wall and without obvious fibrosis." Pulmonary emphysema could result in various complications or comorbidities, many of which are interrelated. Pulmonary emphysema can result in a number of interrelated complications and comorbidities. When pulmonary emphysema is accompanied by comorbidities, it may exhibit different and unique radiologic findings, depending on the underlying lung condition. The purpose of this article was to review radiologic findings that have been reported in patients with underlying emphysema, as well as localized pulmonary comorbidities including infection, fibrosis, primary lung cancer, hemorrhage, and other rare conditions.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1.Chatila WM., Thomashow BM., Minai OA., Criner GJ., Make BJ. Comorbidities in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2008. 5:549–555.
Article2.Cavaillès A., Brinchault-Rabin G., Dixmier A., Goupil F., Gut-Gobert C., Marchand-Adam S, et al. Comorbidities of COPD. Eur Respir Rev. 2013. 22:454–475.3.Cleverley JR., Müller NL. Advances in radiologic assessment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Clin Chest Med. 2000. 21:653–663.
Article4.Friedman PJ. Imaging studies in emphysema. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2008. 5:494–500.
Article5.Takasugi JE., Godwin JD. Radiology of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Radiol Clin North Am. 1998. 36:29–55.
Article6.Sethi S. Infection as a comorbidity of COPD. Eur Respir J. 2010. 35:1209–1215.
Article7.Juhl KS., Bendstrup E., Rasmussen F., Hilberg O. Emphysema mimicking interstitial lung disease: two case reports. Respir Med Case Rep. 2015. 15:24–26.
Article8.Nambu A., Ozawa K., Kobayashi N., Tago M. Imaging of community-acquired pneumonia: roles of imaging examinations, imaging diagnosis of specific pathogens and discrimination from noninfectious diseases. World J Radiol. 2014. 6:779–793.
Article9.Ziskind MM., Schwarz MI., George RB., Weill H., Shames JM., Herbert SJ, et al. Incomplete consolidation in pneumococcal lobar pneumonia complicating pulmonary emphysema. Ann Intern Med. 1970. 72:835–839.
Article10.Chandra D., Rose SR., Carter RB., Musher DM., Hamill RJ. Fluid-containing emphysematous bullae: a spectrum of illness. Eur Respir J. 2008. 32:303–306.
Article11.Kim YT., Han KS., Kim YI. [Parenchymal air-fluid level in emphysematous lung: a report of two cases]. J Korean Radiol Soc. 1999. 40:713–715.12.Morgan MD., Edwards CW., Morris J., Matthews HR. Origin and behaviour of emphysematous bullae. Thorax. 1989. 44:533–538.
Article13.Boushy SF., Kohen R., Billig DM., Heiman MJ. Bullous emphysema: clinical, roentgenologic and physiologic study of 49 patients. Dis Chest. 1968. 54:327–334.
Article14.Bradshaw DA., Murray KM., Amundson DE. Spontaneous regression of a giant pulmonary bulla. Thorax. 1996. 51:549–550.
Article15.Byrd RP Jr., Roy TM. Spontaneous partial resolution of a giant pulmonary bulla. Austin J Pulm Respir Med. 2014. 1:1017–1020.16.Bonay M., Debray MP. Rapid improvement in pulmonary function after inflammatory autobullectomy. Eur J Intern Med. 2008. 19:e99–e100.
Article17.Worthy SA., Brown MJ., Müller NL. Technical report: cystic air spaces in the lung: change in size on expiratory high-resolution CT in 23 patients. Clin Radiol. 1998. 53:515–519.
Article18.Nakajima J., Takamoto S., Tanaka M., Takeuchi E., Murakawa T. Thoracoscopic resection of the pulmonary aspergilloma: report of two cases. Chest. 2000. 118:1490–1492.19.Katzenstein AL., Mukhopadhyay S., Zanardi C., Dexter E. Clinically occult interstitial fibrosis in smokers: classification and significance of a surprisingly common finding in lobectomy specimens. Hum Pathol. 2010. 41:316–325.
Article20.Wright JL., Tazelaar HD., Churg A. Fibrosis with emphysema. Histopathology. 2011. 58:517–524.
Article21.Hiwatari N., Shimura S., Takishima T. Pulmonary emphysema followed by pulmonary fibrosis of undetermined cause. Respiration. 1993. 60:354–358.
Article22.Fujita J., Sato K., Irino S. Emphysematous modification of diffuse centrilobular lesions due to staphylococcal pneumonia. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1991. 156:1322–1323.
Article23.Papiris SA., Triantafillidou C., Manali ED., Kolilekas L., Baou K., Kagouridis K, et al. Combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema. Expert Rev Respir Med. 2013. 7:19–31. quiz 32.
Article24.Cottin V., Cordier JF. Combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema: an experimental and clinically relevant phenotype. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2005. 172:1605;author reply. 1605–1606.
Article25.Auerbach O., Garfinkel L., Hammond EC. Relation of smoking and age to findings in lung parenchyma: a microscopic study. Chest. 1974. 65:29–35.
Article26.Katzenstein AL. Smoking-related interstitial fibrosis (SRIF): pathologic findings and distinction from other chronic fibrosing lung diseases. J Clin Pathol. 2013. 66:882–887.
Article27.Kawabata Y., Hoshi E., Murai K., Ikeya T., Takahashi N., Saitou Y, et al. Smoking-related changes in the background lung of specimens resected for lung cancer: a semiquantitative study with correlation to postoperative course. Histopathology. 2008. 53:707–714.
Article28.Watanabe Y., Kawabata Y., Kanauchi T., Hoshi E., Kurashima K., Koyama S, et al. Multiple, thin-walled cysts are one of the HRCT features of airspace enlargement with fibrosis. Eur J Radiol. 2015. 84:986–992.
Article29.Goldstein MJ., Snider GL., Liberson M., Poske RM. Bronchogenic carcinoma and giant bullous disease. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1968. 97:1062–1070.30.Hanaoka N., Tanaka F., Otake Y., Yanagihara K., Nakagawa T., Kawano Y, et al. Primary lung carcinoma arising from emphysematous bullae. Lung Cancer. 2002. 38:185–191.
Article31.Stoloff IL., Kanofsky P., Magilner L. The risk of lung cancer in males with bullous disease of the lung. Arch Environ Health. 1971. 22:163–167.
Article32.Farooqi AO., Cham M., Zhang L., Beasley MB., Austin JH., Miller A, et al. Lung cancer associated with cystic airspaces. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2012. 199:781–786.
Article33.Ogawa D., Shiota Y., Marukawa M., Hiyama J., Mashiba H., Yu-noki K, et al. Lung cancer associated with pulmonary bulla. case report and review of literature. Respiration. 1999. 66:555–558.34.Maki D., Takahashi M., Murata K., Sawai S., Fujino S., Inoue S. Computed tomography appearances of bronchogenic carcinoma associated with bullous lung disease. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2006. 30:447–452.
Article35.Withey S., Tamimi A. Spontaneous pulmonary haemorrhage into an existing emphysematous bulla. BMJ Case Rep. 2016. 2016:bcr2015213144.
Article36.Lee EJ., Park SH., Park HH., Park SH., Lee JY., Lee WS, et al. Spontaneous pulmonary hematoma with no underlying causes: a case report. Tuberc Respir Dis (Seoul). 2015. 78:363–365.
Article37.Nakamura S., Kawaguchi K., Fukui T., Fukumoto K., Okasaka T., Yokoi K. The development of large-cell carcinoma in the wall of a giant bulla complicated by hemorrhage. Surg Case Rep. 2016. 2:22.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical use of chest CT in chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases
- Pulmonary Emphysema: Visual Interpretation and Quantitative Analysis
- The Single Lung Transplantation for End-Stage Emphysema by Functional Criteria
- A Case of Pulmonary Sequestration and Congenital Lobar Emphysema Presenting with Congestive Heart Failure and Pulmonary Hypertension
- Quantification of Emphysema with a Three-Dimensional Chest CT Scan: Correlation with the Visual Emphysema Scoring on Chest CT, Pulmonary Function Tests and Dyspnea Severity