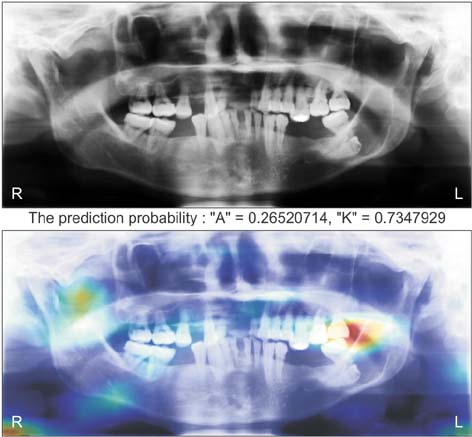
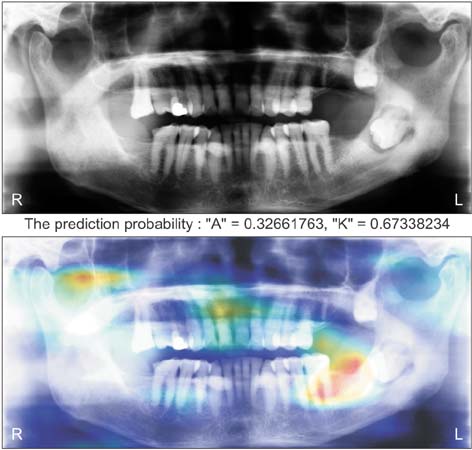
Healthc Inform Res.
2018 Jul;24(3):236-241. 10.4258/hir.2018.24.3.236.
Application of Convolutional Neural Network in the Diagnosis of Jaw Tumors
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Faculty of Dentistry, Trisakti University, Jakarta, Indonesia.
- 2Faculty of Dentistry, Thammasat University, Pathumthani, Thailand. siriwan.suebnukarn@gmail.com
- KMID: 2418173
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4258/hir.2018.24.3.236
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
Ameloblastomas and keratocystic odontogenic tumors (KCOTs) are important odontogenic tumors of the jaw. While their radiological findings are similar, the behaviors of these two types of tumors are different. Precise preoperative diagnosis of these tumors can help oral and maxillofacial surgeons plan appropriate treatment. In this study, we created a convolutional neural network (CNN) for the detection of ameloblastomas and KCOTs.
METHODS
Five hundred digital panoramic images of ameloblastomas and KCOTs were retrospectively collected from a hospital information system, whose patient information could not be identified, and preprocessed by inverse logarithm and histogram equalization. To overcome the imbalance of data entry, we focused our study on 2 tumors with equal distributions of input data. We implemented a transfer learning strategy to overcome the problem of limited patient data. Transfer learning used a 16-layer CNN (VGG-16) of the large sample dataset and was refined with our secondary training dataset comprising 400 images. A separate test dataset comprising 100 images was evaluated to compare the performance of CNN with diagnosis results produced by oral and maxillofacial specialists.
RESULTS
The sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, and diagnostic time were 81.8%, 83.3%, 83.0%, and 38 seconds, respectively, for the CNN. These values for the oral and maxillofacial specialist were 81.1%, 83.2%, 82.9%, and 23.1 minutes, respectively.
CONCLUSIONS
Ameloblastomas and KCOTs could be detected based on digital panoramic radiographic images using CNN with accuracy comparable to that of manual diagnosis by oral maxillofacial specialists. These results demonstrate that CNN may aid in screening for ameloblastomas and KCOTs in a substantially shorter time.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Apajalahti S, Kelppe J, Kontio R, Hagstrom J. Imaging characteristics of ameloblastomas and diagnostic value of computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging in a series of 26 patients. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2015; 120(2):e118–e130.
Article2. Jaeger F, de Noronha MS, Silva ML, Amaral MB, Grossmann SM, Horta MC, et al. Prevalence profile of odontogenic cysts and tumors on Brazilian sample after the reclassification of odontogenic keratocyst. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2017; 45(2):267–270.
Article3. Ariji Y, Morita M, Katsumata A, Sugita Y, Naitoh M, Goto M, et al. Imaging features contributing to the diagnosis of ameloblastomas and keratocystic odontogenic tumours: logistic regression analysis. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2011; 40(3):133–140.
Article4. Hayashi K, Tozaki M, Sugisaki M, Yoshida N, Fukuda K, Tanabe H. Dynamic multislice helical CT of ameloblastoma and odontogenic keratocyst: correlation between contrast enhancement and angiogenesis. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2002; 26(6):922–926.
Article5. Minami M, Kaneda T, Ozawa K, Yamamoto H, Itai Y, Ozawa M, et al. Cystic lesions of the maxillomandibular region: MR imaging distinction of odontogenic keratocysts and ameloblastomas from other cysts. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1996; 166(4):943–949.
Article6. Min S, Lee B, Yoon S. Deep learning in bioinformatics. Brief Bioinform. 2017; 18(5):851–869.
Article7. Shichijo S, Nomura S, Aoyama K, Nishikawa Y, Miura M, Shinagawa T, et al. Application of convolutional neural networks in the diagnosis of helicobacter pylori infection based on endoscopic images. EBioMedicine. 2017; 25:106–111.
Article8. Shin HC, Roth HR, Gao M, Lu L, Xu Z, Nogues I, et al. Deep convolutional neural networks for computer-aided detection: CNN architectures, dataset characteristics and transfer learning. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2016; 35(5):1285–1298.
Article9. Simonyan K, Zisserman A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition [Internet]. Ithaca (NY): arXiv.org;c2015. cited at 2018 Jul 15. Available from: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1409.1556.pdf.10. Russakovsky O, Deng J, Su H, Krause J, Satheesh S, Ma S, et al. ImageNet large scale visual recognition challenge. Int J Comput Vis. 2015; 115(3):211–252.
Article11. Sturm I, Lapuschkin S, Samek W, Muller KR. Interpretable deep neural networks for single-trial EEG classification. J Neurosci Methods. 2016; 274:141–145.
Article12. Oh S, Lee MS, Zhang BT. Ensemble learning with active example selection for imbalanced biomedical data classification. IEEE/ACM Trans Comput Biol Bioinform. 2011; 8(2):316–325.
Article13. Malin BA, Emam KE, O'Keefe CM. Biomedical data privacy: problems, perspectives, and recent advances. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2013; 20(1):2–6.
Article14. Erhan D, Bengio Y, Courville A, Manzagol PA, Vincent P, Bengio S. Why does unsupervised pre-training help deep learning? J Mach Learn Res. 2010; 11:625–660.15. Greenspan H, Van Ginneken B, Summers RM. Guest editorial deep learning in medical imaging: overview and future promise of an exciting new technique. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2016; 35(5):1153–1159.
Article16. Bar Y, Diamant I, Wolf L, Greenspan H. Deep learning with non-medical training used for chest pathology identification. Medical imaging 2015: computer-aided diagnosis (Proceedings of SPIE 9414). Bellingham (WA): International Society for Optics and Photonics;2015.17. Raoof S, Feigin D, Sung A, Raoof S, Irugulpati L, Rosenow EC 3rd. Interpretation of plain chest roentgenogram. Chest. 2012; 141(2):545–558.
Article18. Berbaum K, Franken EA Jr, Smith WL. The effect of comparison films upon resident interpretation of pediatric chest radiographs. Invest Radiol. 1985; 20(2):124–128.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Lesion-Based Convolutional Neural Network in Diagnosis of Early Gastric Cancer
- Convolutional Neural Network Based Sinogram Extrapolation for Truncated CT: Preliminary Study
- The Future of Capsule Endoscopy: The Role of Artificial Intelligence and Other Technical Advancements
- Deep learning convolutional neural network algorithms for the early detection and diagnosis of dental caries on periapical radiographs: A systematic review
- A Narrative Review on the Application of Artificial Intelligence on the Diagnosis and Outcome Prediction for Spinal Diseases