J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2018 May;61(3):292-301. 10.3340/jkns.2018.0028.
Medulloblastoma in the Molecular Era
- Affiliations
-
- 1Developmental & Stem Cell Biology Program, The Hospital for Sick Children, Toronto, Canada. mdtaylor@sickkids.ca
- 2The Arthur and Sonia Labatt Brain Tumour Research Centre, The Hospital for Sick Children, Toronto, Canada.
- 3Department of Surgery, University of Toronto, Toronto, Canada.
- 4Department of Laboratory Medicine and Pathobiology, University of Toronto, Toronto, Canada.
- 5Division of Neurosurgery, University of Toronto, Toronto, Canada.
- KMID: 2417354
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2018.0028
Abstract
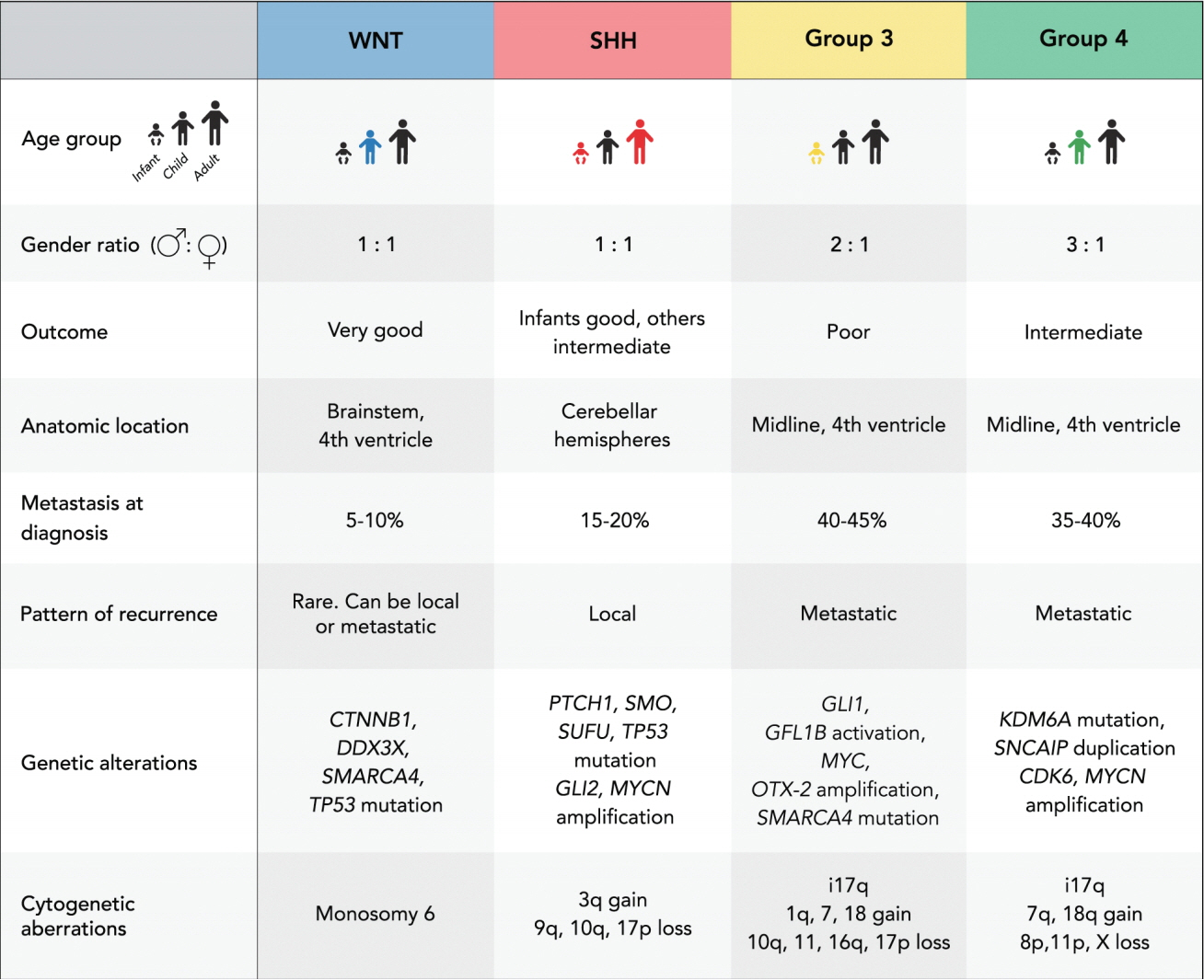
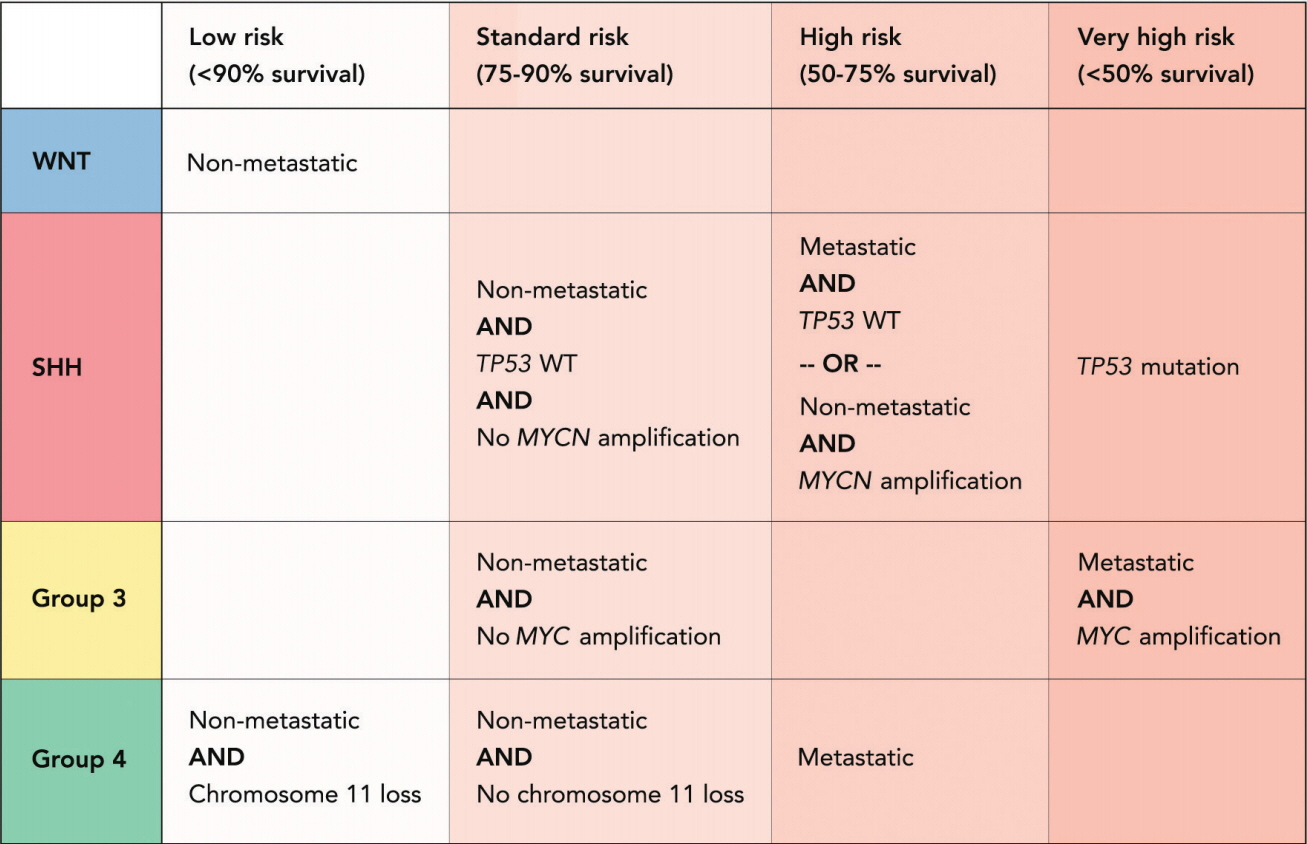
- Medulloblastoma is the most common malignant brain tumor of childhood and remains a major cause of cancer related mortality in children. Significant scientific advancements have transformed the understanding of medulloblastoma, leading to the recognition of four distinct clinical and molecular subgroups, namely wingless (WNT), sonic hedgehog, group 3, and group 4. Subgroup classification combined with the recognition of subgroup specific molecular alterations has also led to major changes in risk stratification of medulloblastoma patients and these changes have begun to alter clinical trial design, in which the newly recognized subgroups are being incorporated as individualized treatment arms. Despite these recent advancements, identification of effective targeted therapies remains a challenge for several reasons. First, significant molecular heterogeneity exists within the four subgroups, meaning this classification system alone may not be sufficient to predict response to a particular therapy. Second, the majority of novel agents are currently tested at the time of recurrence, after which significant selective pressures have been exerted by radiation and chemotherapy. Recent studies demonstrate selection of tumor sub-clones that exhibit genetic divergence from the primary tumor, exist within metastatic and recurrent tumor populations. Therefore, tumor resampling at the time of recurrence may become necessary to accurately select patients for personalized therapy.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Brain Tumor Classification by Methylation Profile
Jin Woo Park, Kwanghoon Lee, Eric Eunshik Kim, Seong-Ik Kim, Sung-Hye Park
J Korean Med Sci. 2023;38(43):e356. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2023.38.e356.
Reference
-
References
1. Alimova I, Venkataraman S, Harris P, Marquez VE, Northcott PA, Dubuc A, et al. Targeting the enhancer of zeste homologue 2 in medulloblastoma. Int J Cancer. 131:1800–1809. 2012.
Article2. Badodi S, Dubuc A, Zhang X, Rosser G, Da Cunha Jaeger M, Kameda-Smith MM, et al. Convergence of BMI1 and CHD7 on ERK signaling in medulloblastoma. Cell Rep. 21:2772–2784. 2017.
Article3. Bandopadhayay P, Bergthold G, Nguyen B, Schubert S, Gholamin S, Tang Y, et al. BET bromodomain inhibition of MYC-amplified medulloblastoma. Clin Cancer Res. 20:912–925. 2014.
Article4. Berman DM, Karhadkar SS, Hallahan AR, Pritchard JI, Eberhart CG, Watkins DN, et al. Medulloblastoma growth inhibition by hedgehog pathway blockade. Science. 297:1559–1561. 2002.
Article5. Buonamici S, Williams J, Morrissey M, Wang A, Guo R, Vattay A, et al. Interfering with resistance to smoothened antagonists by inhibition of the PI3K pathway in medulloblastoma. Sci Transl Med. 2:51ra70. 2010.
Article6. Cavalli FMG, Remke M, Rampasek L, Peacock J, Shih DJH, Luu B, et al. Intertumoral heterogeneity within medulloblastoma subgroups. Cancer Cell. 31:737–754.e6. 2017.7. Cohen BH, Geyer JR, Miller DC, Curran JG, Zhou T, Holmes E, et al. Pilot study of intensive chemotherapy with peripheral hematopoietic cell support for children less than 3 years of age with malignant brain tumors, the CCG-99703 phase I/II study. a report from the Children’s Oncology Group. Pediatr Neurol. 53:31–46. 2015.
Article8. Dubuc AM, Northcott PA, Kenney AM, Taylor MD. Calculating a cure for cancer: managing medulloblastoma MATH1-ematically. Expert Rev Neurother. 10:1489–1492. 2010.
Article9. Dubuc AM, Remke M, Korshunov A, Northcott PA, Zhan SH, Mendez- Lago M, et al. Aberrant patterns of H3K4 and H3K27 histone lysine methylation occur across subgroups in medulloblastoma. Acta Neuropathol. 125:373–384. 2013.
Article10. Faria CC, Agnihotri S, Mack SC, Golbourn BJ, Diaz RJ, Olsen S, et al. Identification of alsterpaullone as a novel small molecule inhibitor to target group 3 medulloblastoma. Oncotarget. 6:21718–21729. 2015.
Article11. Faria CC, Golbourn BJ, Dubuc AM, Remke M, Diaz RJ, Agnihotri S, et al. Foretinib is effective therapy for metastatic sonic hedgehog medulloblastoma. Cancer Res. 75:134–146. 2015.
Article12. Gajjar A, Pfister SM, Taylor MD, Gilbertson RJ. Molecular insights into pediatric brain tumors have the potential to transform therapy. Clin Cancer Res. 20:5630–5640. 2014.
Article13. Gajjar A, Pizer B. Role of high-dose chemotherapy for recurrent medulloblastoma and other CNS primitive neuroectodermal tumors. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 54:649–651. 2010.
Article14. Gajjar AJ, Robinson GW. Medulloblastoma-translating discoveries from the bench to the bedside. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 11:714–722. 2014.
Article15. Geyer JR, Sposto R, Jennings M, Boyett JM, Axtell RA, Breiger D, et al. Multiagent chemotherapy and deferred radiotherapy in infants with malignant brain tumors: a report from the Children’s Cancer Group. J Clin Oncol. 23:7621–7631. 2005.
Article16. Gibson P, Tong Y, Robinson G, Thompson MC, Currle DS, Eden C, et al. Subtypes of medulloblastoma have distinct developmental origins. Nature. 468:1095–1099. 2010.
Article17. Grill J, Sainte-Rose C, Jouvet A, Gentet JC, Lejars O, Frappaz D, et al. Treatment of medulloblastoma with postoperative chemotherapy alone: an SFOP prospective trial in young children. Lancet Oncol. 6:573–580. 2005.
Article18. Guerreiro Stucklin AS, Ramaswamy V, Daniels C, Taylor MD. Review of molecular classification and treatment implications of pediatric brain tumors. Curr Opin Pediatr. 30:3–9. 2018.
Article19. Henrich N, Marra CA, Gastonguay L, Mabbott D, Malkin D, Fryer C, et al. De-escalation of therapy for pediatric medulloblastoma: trade-offs between quality of life and survival. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 61:1300–1304. 2014.
Article20. Hoff von K, Hinkes B, Gerber NU, Deinlein F, Mittler U, Urban C, et al. Long-term outcome and clinical prognostic factors in children with medulloblastoma treated in the prospective randomised multicentre trial HIT’91. Eur J Cancer. 45:1209–1217. 2009.
Article21. Holgado BL, Guerreiro Stucklin A, Garzia L, Daniels C, Taylor MD. Tailoring medulloblastoma treatment through genomics: making a change, one subgroup at a time. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 18:143–166. 2017.
Article22. Hovestadt V, Jones DT, Picelli S, Wang W, Kool M, Northcott PA, et al. Decoding the regulatory landscape of medulloblastoma using DNA methylation sequencing. Nature. 510:537–541. 2014.
Article23. Johansson G, Andersson U, Melin B. Recent developments in brain tumor predisposing syndromes. Acta Oncol. 55:401–411. 2016.
Article24. Jones DTW, Jäger N, Kool M, Zichner T, Hutter B, Sultan M, et al. Dissecting the genomic complexity underlying medulloblastoma. Nature. 488:100–105. 2012.25. Kim J, Aftab BT, Tang JY, Kim D, Lee AH, Rezaee M, et al. Itraconazole and arsenic trioxide inhibit hedgehog pathway activation and tumor growth associated with acquired resistance to smoothened antagonists. Cancer Cell. 23:23–34. 2013.
Article26. Kool M, Jones DT, Jäger N, Northcott PA, Pugh TJ, Hovestadt V, et al. Genome sequencing of SHH medulloblastoma predicts genotype-related response to smoothened inhibition. Cancer Cell. 25:393–405. 2014.
Article27. Kool M, Korshunov A, Remke M, Jones DT, Schlanstein M, Northcott PA, et al. Molecular subgroups of medulloblastoma: an international metaanalysis of transcriptome, genetic aberrations, and clinical data of WNT, SHH, group 3, and group 4 medulloblastomas. Acta Neuropathol. 123:473–484. 2012.
Article28. Korshunov A, Remke M, Kool M, Hielscher T, Northcott PA, Williamson D, et al. Biological and clinical heterogeneity of MYCN-amplified medulloblastoma. Acta Neuropathol. 123:515–527. 2012.
Article29. Kuzan-Fischer CM, Guerreiro Stucklin AS, Taylor MD. Advances in genomics explain medulloblastoma behavior at the bedside. Neurosurgery. 64(CN_suppl_1):21–26. 2017.
Article30. Lafay-Cousin L, Smith A, Chi SN, Wells E, Madden J, Margol A, et al. Clinical, pathological, and molecular characterization of infant medulloblastomas treated with sequential high-dose chemotherapy. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 63:1527–1534. 2016.
Article31. Lau J, Schmidt C, Markant SL, Taylor MD, Wechsler-Reya RJ, Weiss WA. Matching mice to malignancy: molecular subgroups and models of medulloblastoma. Childs Nerv Syst. 28:521–532. 2012.
Article32. Law N, Smith ML, Greenberg M, Bouffet E, Taylor MD, Laughlin S, et al. Executive function in paediatric medulloblastoma: the role of cerebrocerebellar connections. J Neuropsychol. 11:174–200. 2017.
Article33. MacDonald TJ, Aguilera D, Castellino RC. The rationale for targeted therapies in medulloblastoma. Neuro Oncol. 16:9–20. 2014.
Article34. Marino S. Medulloblastoma: developmental mechanisms out of control. Trends Mol Med. 11:17–22. 2005.
Article35. Milla LA, Arros A, Espinoza N, Remke M, Kool M, Taylor MD, et al. Neogenin1 is a sonic hedgehog target in medulloblastoma and is necessary for cell cycle progression. Int J Cancer. 134:21–31. 2014.
Article36. Mille F, Tamayo-Orrego L, Levesque M, Remke M, Korshunov A, Cardin J, et al. The Shh receptor Boc promotes progression of early medulloblastoma to advanced tumors. Dev Cell. 31:34–47. 2014.
Article37. Morrissy AS, Cavalli FMG, Remke M, Ramaswamy V, Shih DJH, Holgado BL, et al. Spatial heterogeneity in medulloblastoma. Nat Genet. 49:780–788. 2017.38. Morrissy AS, Garzia L, Shih DJ, Zuyderduyn S, Huang X, Skowron P, et al. Divergent clonal selection dominates medulloblastoma at recurrence. Nature. 529:351–357. 2016.39. Moxon-Emre I, Bouffet E, Taylor MD, Laperriere N, Scantlebury N, Law N, et al. Impact of craniospinal dose, boost volume, and neurologic complications on intellectual outcome in patients with medulloblastoma. J Clin Oncol. 32:1760–1768. 2014.
Article40. Moxon-Emre I, Taylor MD, Bouffet E, Hardy K, Campen CJ, Malkin D, et al. Intellectual outcome in molecular subgroups of medulloblastoma. J Clin Oncol. 34:4161–4170. 2016.
Article41. Mumert M, Dubuc A, Wu X, Northcott PA, Chin SS, Pedone CA, et al. Functional genomics identifies drivers of medulloblastoma dissemination. Cancer Res. 72:4944–4953. 2012.
Article42. Northcott PA, Buchhalter I, Morrissy AS, Hovestadt V, Weischenfeldt J, Ehrenberger T, et al. The whole-genome landscape of medulloblastoma subtypes. Nature. 547:311–317. 2017.
Article43. Northcott PA, Dubuc AM, Pfister S, Taylor MD. Molecular subgroups of medulloblastoma. Expert Rev Neurother. 12:871–884. 2012.
Article44. Northcott PA, Jones DT, Kool M, Robinson GW, Gilbertson RJ, Cho YJ, et al. Medulloblastomics: the end of the beginning. Nat Rev Cancer. 12:818–834. 2012.
Article45. Northcott PA, Korshunov A, Pfister SM, Taylor MD. The clinical implications of medulloblastoma subgroups. Nat Rev Neurol. 8:340–351. 2012.
Article46. Northcott PA, Korshunov A, Witt H, Hielscher T, Eberhart CG, Mack S, et al. Medulloblastoma comprises four distinct molecular variants. J Clin Oncol. 29:1408–1414. 2011.
Article47. Northcott PA, Lee C, Zichner T, Stütz AM, Erkek S, Kawauchi D, et al. Enhancer hijacking activates GFI1 family oncogenes in medulloblastoma. Nature. 511:428–434. 2014.48. Northcott PA, Nakahara Y, Wu X, Feuk L, Ellison DW, Croul S, et al. Multiple recurrent genetic events converge on control of histone lysine methylation in medulloblastoma. Nat Genet. 41:465–472. 2009.
Article49. Northcott PA, Shih DJ, Peacock J, Garzia L, Morrissy AS, Zichner T, et al. Subgroup-specific structural variation across 1,000 medulloblastoma genomes. Nature. 488:49–56. 2012.50. Northcott PA, Shih DJ, Remke M, Cho YJ, Kool M, Hawkins C, et al. Rapid, reliable, and reproducible molecular sub-grouping of clinical medulloblastoma samples. Acta Neuropathol. 123:615–626. 2012.
Article51. Pambid MR, Berns R, Adomat HH, Hu K, Triscott J, Maurer N, et al. Overcoming resistance to Sonic hedgehog inhibition by targeting p90 ribosomal S6 kinase in pediatric medulloblastoma. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 61:107–115. 2014.
Article52. Parsons DW, Li M, Zhang X, Jones S, Leary RJ, Lin JC, et al. The genetic landscape of the childhood cancer medulloblastoma. Science. 331:435–439. 2011.
Article53. Pei Y, Liu KW, Wang J, Garancher A, Tao R, Esparza LA, et al. HDAC and PI3K antagonists cooperate to inhibit growth of MYC-driven medulloblastoma. Cancer Cell. 29:311–323. 2016.
Article54. Perreault S, Ramaswamy V, Achrol AS, Chao K, Liu TT, Shih D, et al. MRI surrogates for molecular subgroups of medulloblastoma. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 35:1263–1269. 2014.
Article55. Pfaff E, Remke M, Sturm D, Benner A, Witt H, Milde T, et al. TP53 mutation is frequently associated with CTNNB1 mutation or MYCN amplification and is compatible with long-term survival in medulloblastoma. J Clin Oncol. 28:5188–5196. 2010.
Article56. Pietsch T, Schmidt R, Remke M, Korshunov A, Hovestadt V, Jones DT, et al. Prognostic significance of clinical, histopathological, and molecular characteristics of medulloblastomas in the prospective HIT2000 multicenter clinical trial cohort. Acta Neuropathol. 128:137–149. 2014.
Article57. Pugh TJ, Weeraratne SD, Archer TC, Pomeranz Krummel DA, Auclair D, Bochicchio J, et al. Medulloblastoma exome sequencing uncovers subtype-specific somatic mutations. Nature. 488:106–110. 2012.
Article58. Ramaswamy V, Nör C, Taylor MD. p53 and Meduloblastoma. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 6:a026278. 2015.59. Ramaswamy V, Northcott PA, Taylor MD. FISH and chips: the recipe for improved prognostication and outcomes for children with medulloblastoma. Cancer Genet. 204:577–588. 2011.
Article60. Ramaswamy V, Remke M, Adamski J, Bartels U, Tabori U, Wang X, et al. Medulloblastoma subgroup-specific outcomes in irradiated children: who are the true high-risk patients? . Neuro Oncol. 18:591–297. 2016.
Article61. Ramaswamy V, Remke M, Bouffet E, Bailey S, Clifford SC, Doz F, et al. Risk stratification of childhood medulloblastoma in the molecular era: the current consensus. Acta Neuropathol. 131:821–831. 2016.
Article62. Ramaswamy V, Remke M, Bouffet E, Faria CC, Perreault S, Cho YJ, et al. Recurrence patterns across medulloblastoma subgroups: an integrated clinical and molecular analysis. Lancet Oncol. 14:1200–1207. 2013.
Article63. Ramaswamy V, Remke M, Shih D, Wang X, Northcott PA, Faria CC, et al. Duration of the pre-diagnostic interval in medulloblastoma is subgroup dependent. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 61:1190–1194. 2014.
Article64. Ramaswamy V, Taylor MD. Medulloblastoma: from myth to molecular. J Clin Oncol. 35:2355–2363. 2017.
Article65. Rausch T, Jones DT, Zapatka M, Stütz AM, Zichner T, Weischenfeldt J, et al. Genome sequencing of pediatric medulloblastoma links catastrophic DNA rearrangements with TP53 mutations. Cell. 148:59–71. 2012.
Article66. Remke M, Hielscher T, Northcott PA, Witt H, Ryzhova M, Wittmann A, et al. Adult medulloblastoma comprises three major molecular variants. J Clin Oncol. 29:2717–2723. 2011.
Article67. Robinson G, Parker M, Kranenburg TA, Lu C, Chen X, Ding L, et al. Novel mutations target distinct subgroups of medulloblastoma. Nature. 488:43–48. 2012.
Article68. Robinson GW, Orr BA, Wu G, Gururangan S, Lin T, Qaddoumi I, et al. Vismodegib exerts targeted efficacy against recurrent sonic hedgehogsubgroup medulloblastoma: results from phase II Pediatric Brain Tumor Consortium studies PBTC-025B and PBTC-032. J Clin Oncol. 33:2646–2654. 2015.
Article69. Rudin CM, Hann CL, Laterra J, Yauch RL, Callahan CA, Fu L, et al. Treatment of medulloblastoma with hedgehog pathway inhibitor GDC-0449. N Engl J Med. 361:1173–1178. 2009.
Article70. Rusert JM, Wu X, Eberhart CG, Taylor MD, Wechsler-Reya RJ. SnapShot: medulloblastoma. Cancer Cell. 26:940–940.e1. 2014.
Article71. Rutkowski S, Bode U, Deinlein F, Ottensmeier H, Warmuth-Metz M, Soerensen N, et al. Treatment of early childhood medulloblastoma by postoperative chemotherapy alone. N Engl J Med. 352:978–986. 2005.
Article72. Sabel M, Fleischhack G, Tippelt S, Gustafsson G, Doz F, Kortmann R, et al. Relapse patterns and outcome after relapse in standard risk medulloblastoma: a report from the HIT-SIOP-PNET4 study. J Neurooncol. 129:515–524. 2016.
Article73. Schneider C, Ramaswamy V, Kulkarni AV, Rutka JT, Remke M, Tabori U, et al. Clinical implications of medulloblastoma subgroups: incidence of CSF diversion surgery. J Neurosurg Pediatr. 15:236–242. 2015.
Article74. Schwalbe EC, Lindsey JC, Nakjang S, Crosier S, Smith AJ, Hicks D, et al. Novel molecular subgroups for clinical classification and outcome prediction in childhood medulloblastoma: a cohort study. Lancet Oncol. 18:958–971. 2017.
Article75. Schwalbe EC, Williamson D, Lindsey JC, Hamilton D, Ryan SL, Megahed H, et al. DNA methylation profiling of medulloblastoma allows robust subclassification and improved outcome prediction using formalin-fixed biopsies. Acta Neuropathol. 125:359–371. 2013.
Article76. Shih DJ, Northcott PA, Remke M, Korshunov A, Ramaswamy V, Kool M, et al. Cytogenetic prognostication within medulloblastoma subgroups. J Clin Oncol. 32:886–896. 2014.77. Skowron P, Ramaswamy V, Taylor MD. Genetic and molecular alterations across medulloblastoma subgroups. J Mol Med (Berl). 93:1075–1084. 2015.
Article78. Suryo Rahmanto A, Savov V, Brunner A, Bolin S, Weishaupt H, Malyukova A, et al. FBW7 suppression leads to SOX9 stabilization and increased malignancy in medulloblastoma. Embo J. 35:2192–2212. 2016.
Article79. Swartling FJ, Grimmer MR, Hackett CS, Northcott PA, Fan QW, Goldenberg DD, et al. Pleiotropic role for MYCN in medulloblastoma. Genes Dev. 24:1059–1072. 2010.80. Tabori U, Baskin B, Shago M, Alon N, Taylor MD, Ray PN, et al. Universal poor survival in children with medulloblastoma harboring somatic TP53 mutations. J Clin Oncol. 28:1345–1350. 2010.
Article81. Taipale J, Chen JK, Cooper MK, Wang B, Mann RK, Milenkovic L, et al. Effects of oncogenic mutations in smoothened and patched can be reversed by cyclopamine. Nature. 406:1005–1009. 2000.
Article82. Taipale J, Cooper MK, Maiti T, Beachy PA. Patched acts catalytically to suppress the activity of smoothened. Nature. 418:892–897. 2002.
Article83. Tang Y, Gholamin S, Schubert S, Willardson MI, Lee A, Bandopadhayay P, et al. Epigenetic targeting of hedgehog pathway transcriptional output through BET bromodomain inhibition. Nat Med. 20:732–740. 2014.
Article84. Taylor MD, Liu L, Raffel C, Hui CC, Mainprize TG, Zhang X, et al. Mutations in SUFU predispose to medulloblastoma. Nat Genet. 31:306–310. 2002.
Article85. Taylor MD, Northcott PA, Korshunov A, Remke M, Cho YJ, Clifford SC, et al. Molecular subgroups of medulloblastoma: the current consensus. Acta Neuropathol. 123:465–472. 2012.
Article86. Taylor MD, Zhang X, Liu L, Hui CC, Mainprize TG, Scherer SW, et al. Failure of a medulloblastoma-derived mutant of SUFU to suppress WNT signaling. Oncogene. 23:4577–4583. 2004.
Article87. Taylor RE, Bailey CC, Robinson KJ, Weston CL, Walker DA, Ellison D, et al. Outcome for patients with metastatic (M2-3) medulloblastoma treated with SIOP/UKCCSG PNET-3 chemotherapy. Eur J Cancer. 41:727–734. 2005.
Article88. Thompson EM, Hielscher T, Bouffet E, Remke M, Luu B, Gururangan S, et al. Prognostic value of medulloblastoma extent of resection after accounting for molecular subgroup: a retrospective integrated clinical and molecular analysis. Lancet Oncol. 17:484–495. 2016.89. Thompson MC, Fuller C, Hogg TL, Dalton J, Finkelstein D, Lau CC, et al. Genomics identifies medulloblastoma subgroups that are enriched for specific genetic alterations. J Clin Oncol. 24:1924–1931. 2006.
Article90. Traenka C, Remke M, Korshunov A, Bender S, Hielscher T, Northcott PA, et al. Role of LIM and SH3 protein 1 (LASP1) in the metastatic dissemination of medulloblastoma. Cancer Res. 70:8003–8014. 2010.
Article91. Triscott J, Lee C, Foster C, Manoranjan B, Pambid MR, Berns R, et al. Personalizing the treatment of pediatric medulloblastoma: polo-like kinase 1 as a molecular target in high-risk children. Cancer Res. 73:6734–6744. 2013.
Article92. Venkataraman S, Alimova I, Balakrishnan I, Harris P, Birks DK, Griesinger A, et al. Inhibition of BRD4 attenuates tumor cell self-renewal and suppresses stem cell signaling in MYC driven medulloblastoma. Oncotarget. 5:2355–2371. 2014.
Article93. Wang X, Dubuc AM, Ramaswamy V, Mack S, Gendoo DMA, Remke M, et al. Medulloblastoma subgroups remain stable across primary and metastatic compartments. Acta Neuropathol. 129:449–457. 2015.
Article94. Wang X, Ramaswamy V, Remke M, Mack SC, Dubuc AM, Northcott PA, et al. Intertumoral and intratumoral heterogeneity as a barrier for effective treatment of medulloblastoma. Neurosurgery 60 Suppl. 1:57–63. 2013.
Article95. Whittier KL, Boese EA, Gibson-Corley KN, Kirby PA, Darbro BW, Qian Q, et al. G-protein coupled receptor expression patterns delineate medulloblastoma subgroups. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 1:66. 2013.
Article96. Wu X, Northcott PA, Dubuc A, Dupuy AJ, Shih DJ, Witt H, et al. Clonal selection drives genetic divergence of metastatic medulloblastoma. Nature. 482:529–533. 2012.
Article97. Yauch RL, Dijkgraaf GJP, Alicke B, Januario T, Ahn CP, Holcomb T, et al. Smoothened mutation confers resistance to a hedgehog pathway inhibitor in medulloblastoma. Science. 326:572–574. 2009.
Article98. Zapotocky M, Mata-Mbemba D, Sumerauer D, Liby P, Lassaletta A, Zamecnik J, et al. Differential patterns of metastatic dissemination across medulloblastoma subgroups. J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2017; [Epub ahead of print].
Article99. Zhou L, Picard D, Ra YS, Li M, Northcott PA, Hu Y, et al. Silencing of thrombospondin-1 is critical for myc-induced metastatic phenotypes in medulloblastoma. Cancer Res. 70:8199–8210. 2010.
Article100. Zhukova N, Ramaswamy V, Remke M, Martin DC, Castelo-Branco P, Zhang CH, et al. WNT activation by lithium abrogates TP53 mutation associated radiation resistance in medulloblastoma. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2:174. 2014.
Article101. Zhukova N, Ramaswamy V, Remke M, Pfaff E, Shih DJ, Martin DC, et al. Subgroup-specific prognostic implications of TP53 mutation in medulloblastoma. J Clin Oncol. 31:2927–2935. 2013.
Article