Kosin Med J.
2018 Jun;33(1):96-104. 10.7180/kmj.2018.33.1.96.
Fatal neurological complication after liver transplantation in acute hepatic failure patient with hepatic encephalopathy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesia and Pain Medicine, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Yangsan, Korea. johnri@naver.com
- KMID: 2415845
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7180/kmj.2018.33.1.96
Abstract
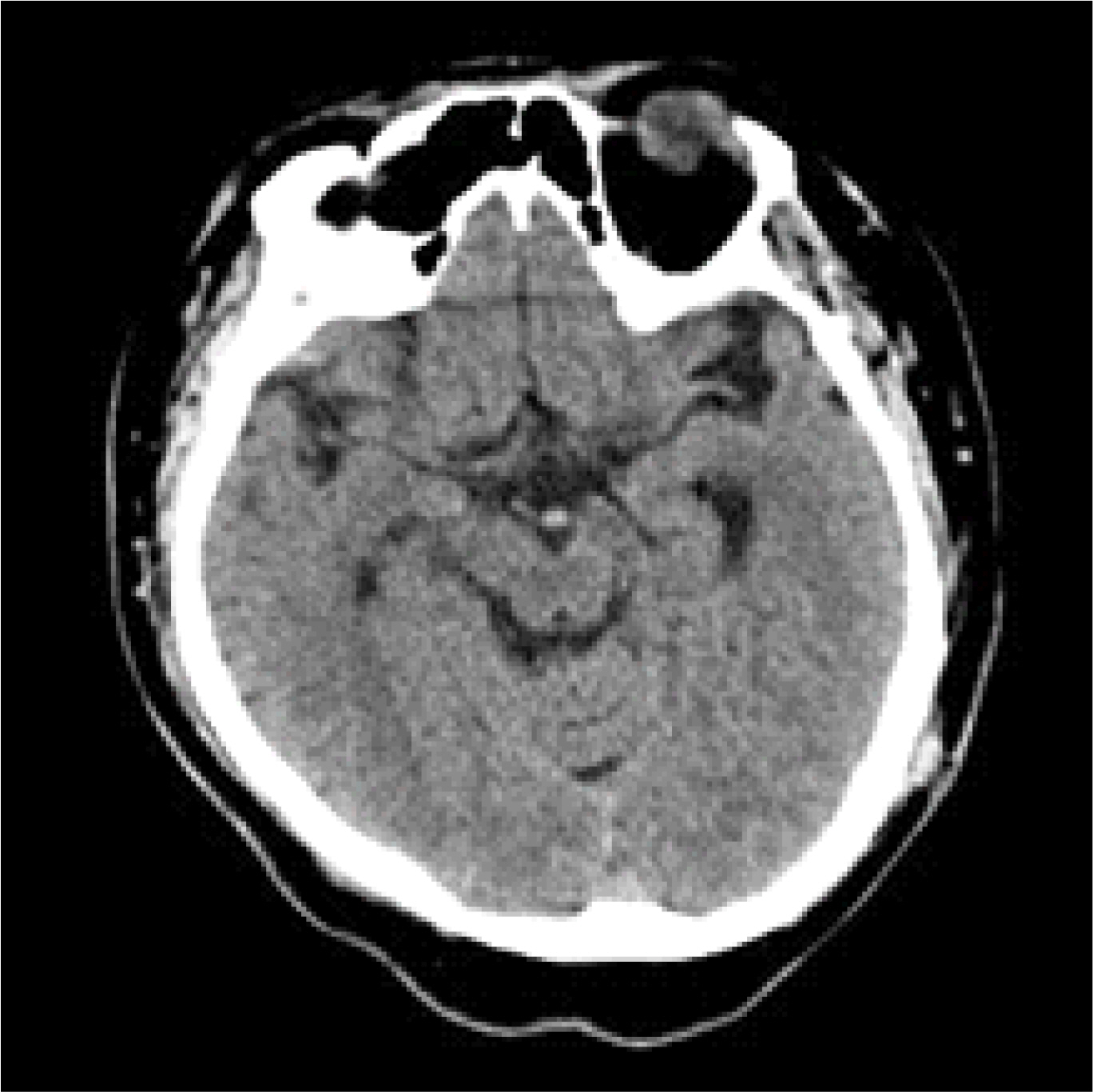
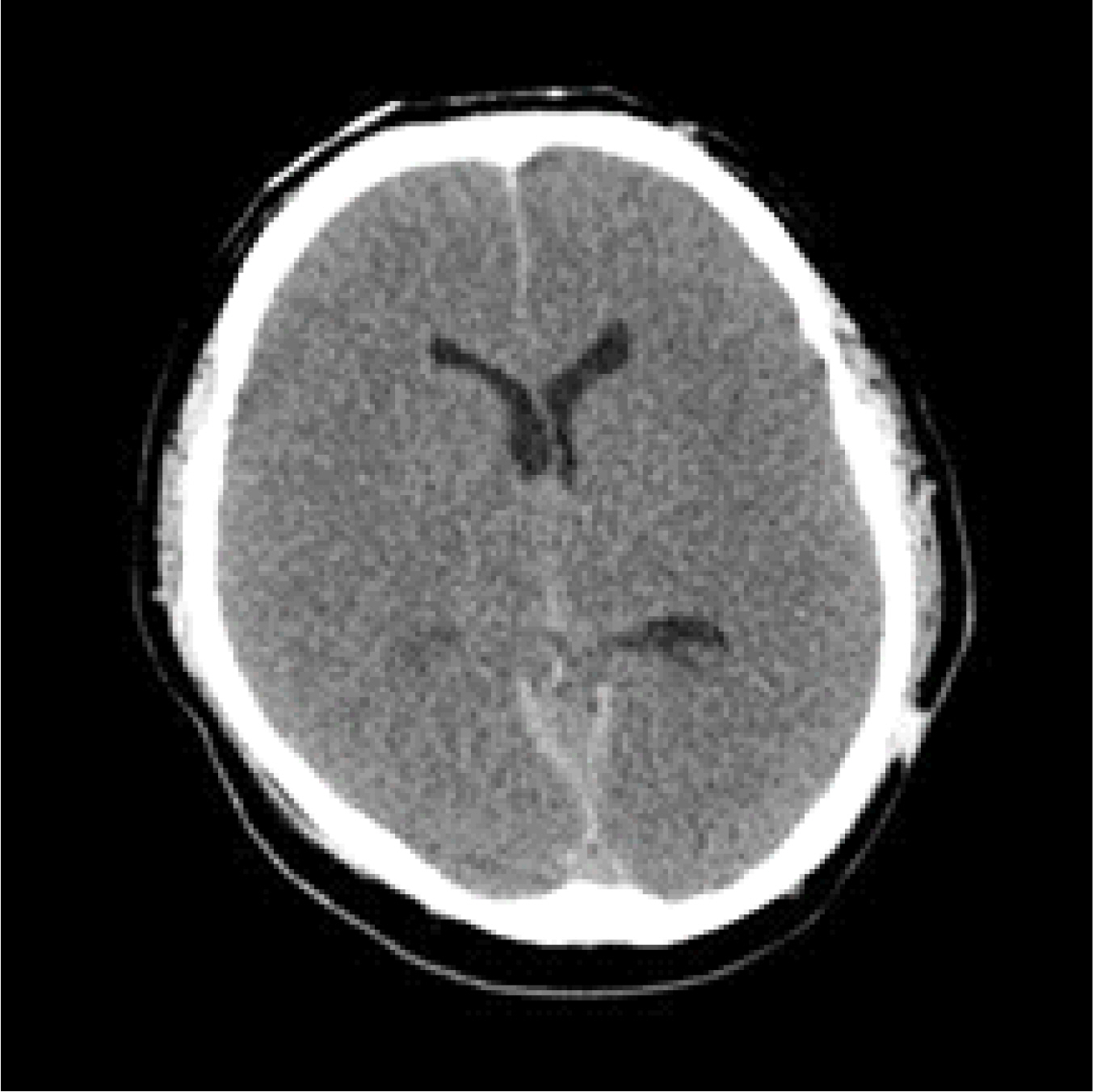
- Liver transplantation is a current definitive treatment for those with end-stage liver disease. Hepatic encephalopathy is a common complication of hepatic failure, which can be improved and aggravated by various causes. It is important to differentiate hepatic encephalopathy from other diseases causing brain dysfunction such as cerebral hemorrhage, which is also related to high mortality after liver transplant surgery. A 37-year-old patient was presented with acute liver failure and high ammonia levels and seizure-like symptoms. Computed tomography (CT) of his brain showed mild brain atrophy, regarded as a symptom of hepatic encephalopathy, and treated to decrease blood ammonia level. Deceased donor liver transplantation was performed and liver function and ammonia level normalized after surgery, but the patient showed symptoms of involuntary muscle contraction and showed loss of pupil reflex and fixation without recovery of consciousness. Brain CT showed brain edema and bilateral cerebral infarction, and the patient died after a few days. The purpose of this case report is to emphasize the importance of preoperative neurological evaluation, careful transplantation decision, and proper perioperative management of liver transplantation in patients with acute hepatic encephalopathy.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1.Saner FH., Gensicke J., Olde Damink SW., Pavlaković G., Treckmann J., Kaiser GM, et al. Neurologic complications in adult living donor liver transplant patients: an underestimated factor? J Neurol. 2010. 257:253–8.
Article2.Shawcross D., Jalan R. The pathophysiologic basis of hepatic encephalopathy: central role for ammonia and inflammation. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2005. 62:2295–304.
Article3.Schliess F., Gőrg B., Fischer R., Desjardins P., Bidmon HJ., Herrmann A, et al. Ammonia induces MK-801-sensitive nitration and phosphorylation of protein tyrosine residues in rat astrocytes. FASEB J. 2002. 16:739–41.
Article4.Lang EW., Mudaliar Y., Lagopoulos Y., Dorsch N., Yam N., Griffith J, et al. A review of cerebral autoregulation: assessment and measurements. Australasian Anaesthesia. 2005. 161–72.5.Horowitz ME., Schafer DF., Molnar P., Jones EA., Blasberg RG., Patlak CS, et al. Increased blood-brain transfer in a rabbit model of acute liver failure. Gastroenterology. 1983. 84:1003–11.
Article6.Larsen FS., Gottstein J., Blei AT. Cerebral hyperemia and nitric oxide synthase in rats with ammonia-induced brain edema. J Hepatol. 2001. 34:548–54.
Article7.Davies NA., Wright G., Ytrebø LM., Stadlbauer V., Fuskevåg OM., Zwingmann C, et al. L-ornithine and phenylacetate synergistically produce sustained reduction in ammonia and brain water in cirrhotic rats. Hepatology. 2009. 50:155–64.
Article8.Jiang Q., Jiang XH., Zheng MH., Jiang LM., Chen YP., Wang L. Rifaximin versus nonabsorbable disaccharides in the management of hepatic encephalopathy: a meta-analysis. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008. 20:1064–70.
Article9.Kircheis G. Current state of knowledge of hepatic encephalopathy (Part V): clinical efficacy of L-ornithine-L-aspartate in the management of HE. Metab Brain Dis. 2016. 31:1365–7.
Article10.Kircheis G., Wettstein M., Dahl SV., Häussinger D. Clinical efficacy of L-ornithine-L-aspartate in the management of hepatic encephalopathy. Metab Brain Dis. 2002. 17:453–62.11.Ytrebø LM., Kristiansen RG., Maehre H., Fuskevåg OM., Kalstad T., Revhaug A, et al. L-ornithine phenylacetate attenuates increased arterial and extracellular brain ammonia and prevents intracranial hypertension in pigs with acute liver failure. Hepatology. 2009. 50:165–74.
Article12.Munñoz SJ., Robinson M., Northrup B., Bell R., Moritz M., Jarrell B, et al. Elevated intracranial pressure and computed tomography of the brain in fulminant hepatocellular failure. Hepatology. 1991. 13:209–12.
Article13.Kumar R., Shalimar ., Sharma H., Goyal R., Kumar A., Khanal S, et al. Prospective derivation and validation of early dynamic model for predicting outcome in patients with acute liver failure. Gut. 2012. 61:1068–75.
Article14.Bhatia V., Batra Y., Acharya SK. Prophylactic phenytoin does not improve cerebral edema or survival in acute liver failure--a controlled clinical trial. J Hepatol. 2004. 41:89–96.
Article15.Rajajee V., Fontana RJ., Courey AJ., Patil PG. Protocol based invasive intracranial pressure monitoring in acute liver failure: Feasibility, safety and impact on management. Crit Care. 2017. 21:178,017-. 1762–6.
Article16.Jalan R., Olde Damink SW., Deutz NE., Hayes PC., Lee A. Moderate hypothermia in patients with acute liver failure and uncontrolled intracranial hypertension. Gastroenterology. 2004. 127:1338–46.
Article17.Stravitz RT., Larsen FS. Therapeutic hypothermia for acute liver failure. Crit Care Med. 2009. 37:S258–64.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Understanding Acute Liver Failure: A Basic Overview of Definition and Treatment
- Three Cases of Fulminant Hepatic Failure due to Congestive Heart Failure
- A Case of Fulminant Hepatic Failure Who Recovered during Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy
- Acute Hyperammonemic Encephalopathy with Features on Diffusion-Weighted Images: Report of Two Cases
- Acute Hepatic Failure after Spinal Surgery in Patient with Liver Cirrhosis: A case report