Determinants and outcomes of motivation in health professions education: a systematic review based on self-determination theory
- Affiliations
-
- 1Health Professions Education Programme, School of Medicine, College of Medical, Veterinary and Life Sciences, University of Glasgow, Glasgow, United Kingdom. corsini@fen.uchile.cl
- 2Teaching and Learning Centre, Faculty of Economics and Business, University of Chile, Santiago, Chile.
- 3Dental School, School of Medicine, College of Medical, Veterinary and Life Sciences, University of Glasgow, Glasgow, United Kingdom.
- 4Institute of Health and Wellbeing, School of Medicine, College of Medical, Veterinary and Life Sciences, University of Glasgow, Glasgow, United Kingdom.
- KMID: 2413768
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3352/jeehp.2016.13.19
Abstract
- PURPOSE
This study aimed at conducting a systematic review in health professions education of determinants, mediators and outcomes of students' motivation to engage in academic activities based on the self-determination theory's perspective.
METHODS
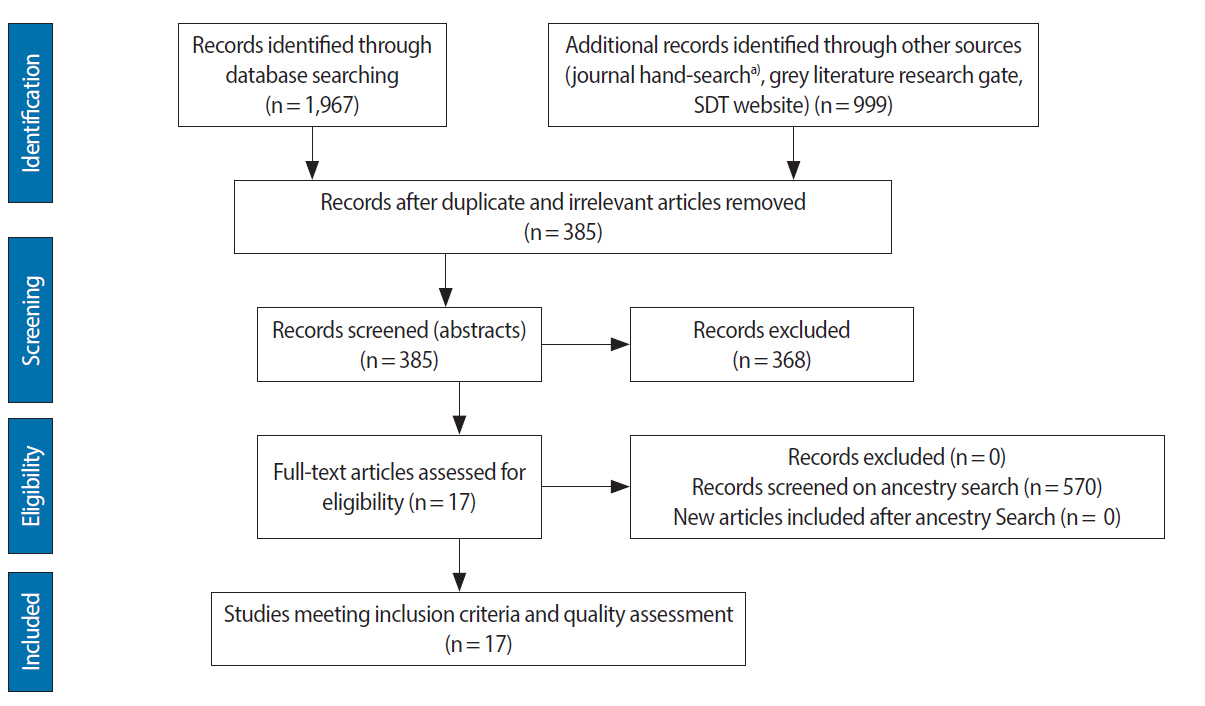
A search was conducted across databases (MEDLINE, CINHAL, EMBASE, PsycINFO, and ERIC databases), hand-search of relevant journals, grey literature, and published research profile of key authors. Quantitative and qualitative studies were included if they reported research in health professions education focused on determinants, mediators, and/or outcomes of motivation from the self-determination and if meeting the quality criteria.
RESULTS
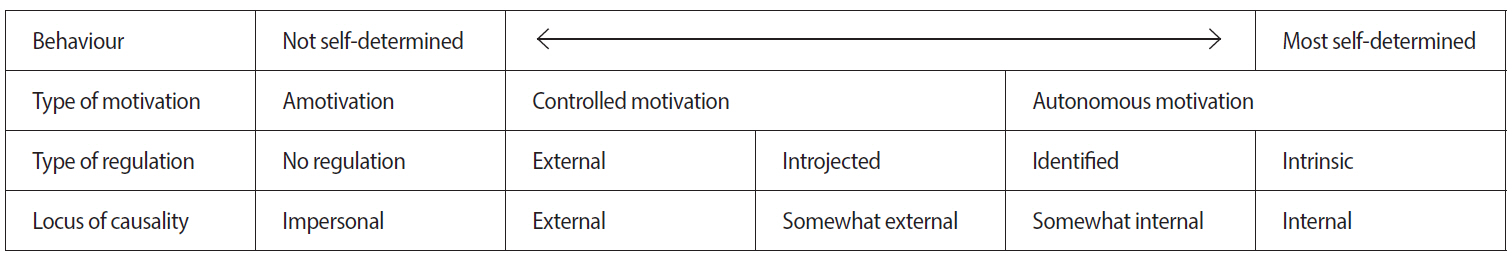
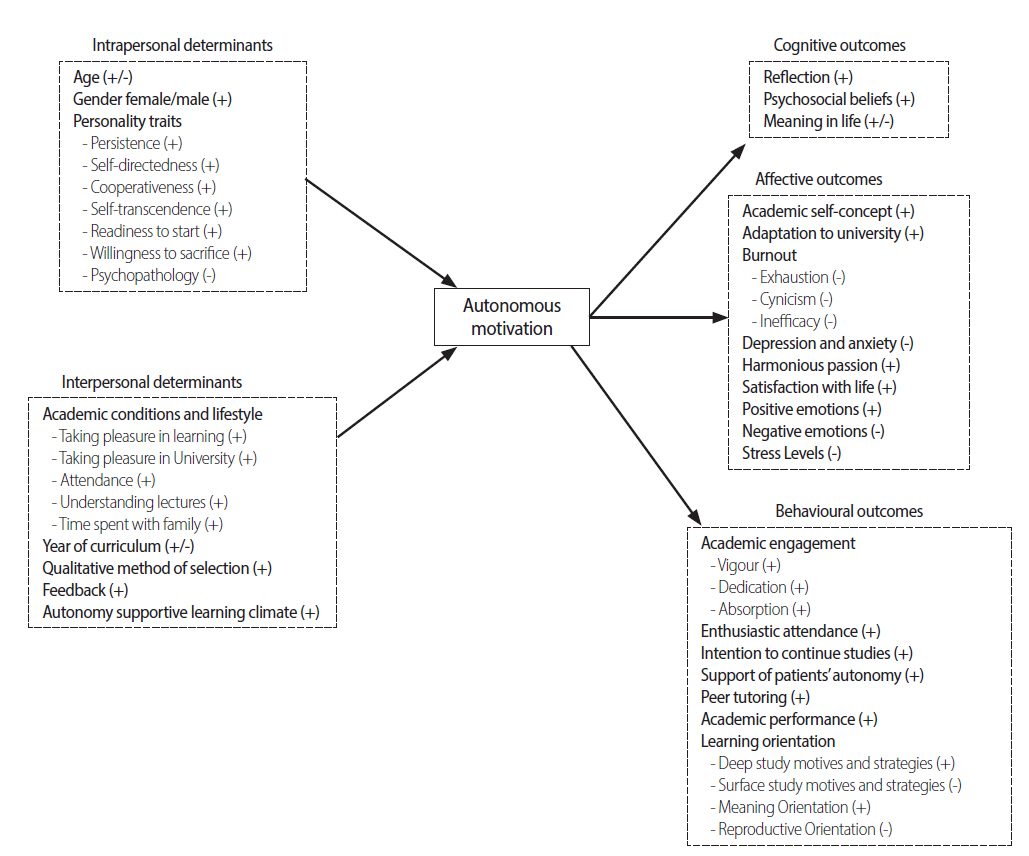
A total of 17 studies met the inclusion and quality criteria. Articles retrieved came from diverse locations and mainly from medical education and to a lesser extent from psychology and dental education. Intrapersonal (gender and personality traits) and interpersonal determinants (academic conditions and lifestyle, qualitative method of selection, feedback, and an autonomy supportive learning climate) have been reported to have a positive influence on students' motivation to engage in academic activities. No studies were found that tested mediation effects between determinants and students' motivation. In turn, students' self-determined motivation has been found to be positively associated with different cognitive, affective, and behavioural outcomes.
CONCLUSION
This study has found that generally, motivation could be enhanced by changes in the educational environment and by an early detection of students' characteristics. Doing so may support future health practitioners' self-determined motivation and positively influence how they process information and their emotions and how they approach their learning activities.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 4 articles
-
Effect of practical training on the learning motivation profile of Japanese pharmacy students using structural equation modeling
Shigeo Yamamura, Rieko Takehira, Sun Huh
J Educ Eval Health Prof. 2017;14:2. doi: 10.3352/jeehp.2017.14.2.Motivational profiles and their relationships with basic psychological needs, academic performance, study strategies, self-esteem, and vitality in dental students in Chile
Cesar A. Orsini, Vivian I. Binnie, Jorge A. Tricio, Sun Huh
J Educ Eval Health Prof. 2018;15:11. doi: 10.3352/jeehp.2018.15.11.How dental students’ course experiences and satisfaction of their basic psychological needs influence passion for studying in Chile
Cesar Orsini, Jorge Tricio, Doris Tapia, Cristina Segura, Sun Huh
J Educ Eval Health Prof. 2019;16:37. doi: 10.3352/jeehp.2019.16.37.Impact of a change from A–F grading to honors/pass/fail grading on academic performance at Yonsei University College of Medicine in Korea: a cross-sectional serial mediation analysis
Min-Kyeong Kim, Hae Won Kim, Sun Huh
J Educ Eval Health Prof. 2024;21:20. doi: 10.3352/jeehp.2024.21.20.
Reference
-
References
1. Ten Cate TJ, Kusurkar RA, Williams GC. How self-determination theory can assist our understanding of the teaching and learning processes in medical education. AMEE guide No. 59. Med Teach. 2011; 33:961–973. http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/0142159X.2011.595435.2. Deci EL, Ryan RM. Self-determination theory: a macrotheory of human motivation, development, and health. Can Psychol. 2008; 49:182–185. http://dx.doi.org/10.1037/a0012801.
Article3. Orsini C, Evans P, Jerez O. How to encourage intrinsic motivation in the clinical teaching environment?: a systematic review from the self-determination theory. J Educ Eval Health Prof. 2015; 12:8. http://dx.doi.org/10.3352/jeehp.2015.12.8.
Article4. Ryan RM, Deci EL. Intrinsic and extrinsic motivations: classic definitions and new directions. Contemp Educ Psychol. 2000; 25:54–67. http://dx.doi.org/10.1006/ceps.1999.1020.
Article5. Deci EL, Ryan RM. Facilitating optimal motivation and psychological well-being across life’s domains. Can Psychol. 2008; 49:14–23. http://dx.doi.org/10.1037/0708-5591.49.1.14.
Article6. Hulsman RL, Oort FJ, Michels RP, Casteelen G, Griffioen FM. Effectiveness of selection in medical school admissions: evaluation of the outcomes among freshmen. Med Educ. 2007; 41:369–377. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2929.2007.02708.x.
Article7. Williams GC, Deci EL. Internalization of biopsychosocial values by medical students: a test of self-determination theory. J Pers Soc Psychol. 1996; 70:767–779. http://dx.doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.70.4.767.
Article8. Kusurkar RA, Ten Cate TJ, van Asperen M, Croiset G. Motivation as an independent and a dependent variable in medical education: a review of the literature. Med Teach. 2011; 33:e242–e262. http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/0142159X.2011.558539.
Article9. Gordon M, Gibbs T. STORIES statement: publication standards for healthcare education evidence synthesis. BMC Med. 2014; 12:143. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s12916-014-0143-0.
Article10. Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009; 6:e1000097. http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1000097.
Article11. Harden RM, Grant J, Buckley G, Hart IR. BEME guide no. 1: best evidence medical education. Med Teach. 1999; 21:553–562. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/01421599978960.12. Thomas J, Harden A. Methods for the thematic synthesis of qualitative research in systematic reviews. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2008; 8:45. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1471-2288-8-45.
Article13. Tanaka M, Mizuno K, Fukuda S, Tajima S, Watanabe Y. Personality traits associated with intrinsic academic motivation in medical students. Med Educ. 2009; 43:384–387. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2923.2008.03279.x.
Article14. Kusurkar R, Croiset G, ten Cate O. Implications of gender differences in motivation among medical students. Med Teach. 2013; 35:173–174. http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/0142159X.2012.737056.
Article15. Sobral DT. What kind of motivation drives medical students’ learning quests? Med Educ. 2004; 38:950–957. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2929.2004.01913.x.
Article16. Kusurkar RA, Croiset G, Galindo-Garre F, Ten Cate O. Motivational profiles of medical students: association with study effort, academic performance and exhaustion. BMC Med Educ. 2013; 13:87. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1472-6920-13-87.
Article17. Kusurkar RA, Ten Cate TJ, Vos CM, Westers P, Croiset G. How motivation affects academic performance: a structural equation modelling analysis. Adv Health Sci Educ Theory Pract. 2013; 18:57–69. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10459-012-9354-3.
Article18. Orsini C, Binnie V, Evans P, Ledezma P, Fuentes F, Villegas MJ. Psychometric validation of the academic motivation scale in a dental student sample. J Dent Educ. 2015; 79:971–981.
Article19. Park J, Chung S, An H, Park S, Lee C, Kim SY, Lee JD, Kim KS. A structural model of stress, motivation, and academic performance in medical students. Psychiatry Investig. 2012; 9:143–149. http://dx.doi.org/10.4306/pi.2012.9.2.143.
Article20. Kusurkar R, Croiset G, Kruitwagen C, ten Cate O. Validity evidence for the measurement of the strength of motivation for medical school. Adv Health Sci Educ Theory Pract. 2011; 16:183–195. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10459-010-9253-4.
Article21. Tanaka M, Watanabea Y. Academic and family conditions associated with intrinsic academic motivation in Japanese medical students: a pilot study. Health Educ J. 2011; 71:358–364. http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/0017896911401004.
Article22. Wouters A, Bakker AH, van Wijk IJ, Croiset G, Kusurkar RA. A qualitative analysis of statements on motivation of applicants for medical school. BMC Med Educ. 2014; 14:200. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1472-6920-14-200.
Article23. Orsini C, Evans P, Binnie V, Ledezma P, Fuentes F. Encouraging intrinsic motivation in the clinical setting: teachers’ perspectives from the self-determination theory. Eur J Dent Educ. 2016; 20:102–111. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/eje.12147.
Article24. Williams GC, Saizow R, Ross L, Deci EL. Motivation underlying career choice for internal medicine and surgery. Soc Sci Med. 1997; 45:1705–1713. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0277-9536(97)00103-2.
Article25. Williams GC, Wiener MW, Markakis KM, Reeve J, Deci EL. Medical students’ motivation for internal medicine. J Gen Intern Med. 1994; 9:327–333. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/BF02599180.
Article26. Bailey TH, Phillips LJ. The influence of motivation and adaptation on students’ subjective well-being, meaning in life and academic performance. High Educ Res Dev. 2016; 35:201–216. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/07294360.2015.1087474.
Article27. Baker SR. Intrinsic, extrinsic, and amotivational orientations: their role in university adjustment, stress, well-being, and subsequent academic performance. Curr Psychol. 2004; 23:189–202. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s12144-004-1019-9.
Article28. Stoeber J, Childs JH, Hayward JA, Feast AR. Passion and motivation for studying: predicting academic engagement and burnout in university students. Educ Psychol. 2011; 31:513–528. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/01443410.2011.570251.
Article29. Vansteenkiste M, Sierens E, Soenens B, Luyckx K, Lens W. Motivational profiles from a self-determination perspective: the quality of motivation matters. J Educ Psychol. 2009; 101:671–688. http://dx.doi.org/10.1037/a0015083.
Article30. Kusurkar RA, Croiset G, Ten Cate TJ. Twelve tips to stimulate intrinsic motivation in students through autonomy-supportive classroom teaching derived from self-determination theory. Med Teach. 2011; 33:978–982. http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/0142159X.2011.599896.
Article31. Ten Cate O, Chen HC, Hoff RG, Peters H, Bok H. Curriculum development for the workplace using entrustable professional activities (EPAs): AMEE guide no. 99. Med Teach. 2015; 37:983–1002. http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/0142159X.2015.1060308.
Article32. Chen B, Vansteenkiste M, Beyers W, Boone L, Deci EL, Duriez B, Lens W, Matos L, Mouratidis A. Basic psychological need satisfaction, need frustration, and need strength across four cultures. Motiv Emot. 2014; 39:216–236. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11031-014-9450-1.
Article33. Kaufman DM, Mann KV. Teaching and learning in medical education: how theory can inform practice. In : Swanwick T, editor. Understanding medical education: evidence, theory and practice. Oxford: John Wiley & Sons;2010. p. 16–36. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/9781118472361.ch2.34. Deci EL, Ryan RM, Williams GC. Need satisfaction and the self-regulation of learning. Learn Individ Differ. 1996; 8:165–183. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S1041-6080(96)90013-8.
Article35. James R, Krause KD, Jennings C; Centre for the Study of Higher Education, University of Melbourne. The first-year experience in Australian universities: findings from 1994 to 2009. Melbourne: Centre for the Study of Higher Education, University of Melbourne;2010.36. Vansteenkiste M, Zhou M, Lens W, Soenens B. Experiences of autonomy and control among chinese learners: vitalizing or immobilizing? J Educ Psychol. 2005; 97:468–483. http://dx.doi.org/10.1037/0022-0663.97.3.468.
Article37. Davy JA, Kincaid JF, Smith KJ, Trawick MA. An examination of the role of attitudinal characteristics and motivation on the cheating behavior of business students. Ethics Behav. 2007; 17:281–302. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/10508420701519304.
Article38. Angell LR. The relationship of impulsiveness, personal efficacy, and academic motivation to college cheating. Coll Stud J. 2006; 40:118–131.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- How to encourage intrinsic motivation in the clinical teaching environment?: a systematic review from the self-determination theory
- Osteoporosis knowledge assessment and osteoporosis education recommendations in the health professions
- Impact of interprofessional education on students of the health professions: a systematic review
- Factors influencing the self-management of kidney transplant patients based on self-determination theory: a cross-sectional study
- E-learning in health professions education during the COVID-19 pandemic: a systematic review