Korean J Radiol.
2018 Aug;19(4):613-622. 10.3348/kjr.2018.19.4.613.
Radiofrequency Ablation Combined with Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization Therapy Versus Surgical Resection for Hepatocellular Carcinoma within the Milan Criteria: A Meta-Analysis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Interventional Radiology, Sun Yat-sen Memorial Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510120, China. xu_linfeng0216@163.com
- 2Guangdong Women an Children Hospital, Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou 511400, China.
- KMID: 2413691
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2018.19.4.613
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To meta-analytically compare combined transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) plus radiofrequency ablation (RFA) and surgical resection (SR) for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) within the Milan criteria.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
PubMed, Medline, Embase, and Cochrane Library were searched for studies comparing these two therapies that were published between January 2006 and August 2017. Overall survival rate (OS), recurrence-free survival rate (RFS), major complications and the average length of hospital stay were compared between these two therapies. Meta-analytic pooled odds ratio (OR) was calculated using TACE plus RFA as the base category.
RESULTS
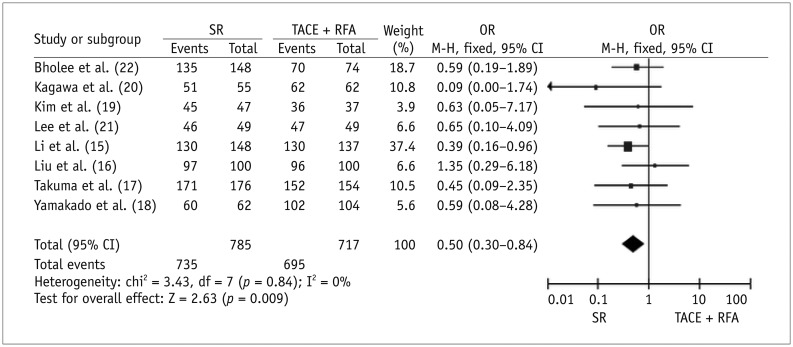
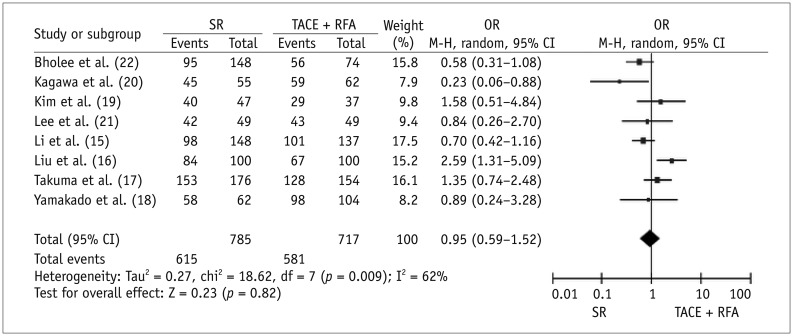
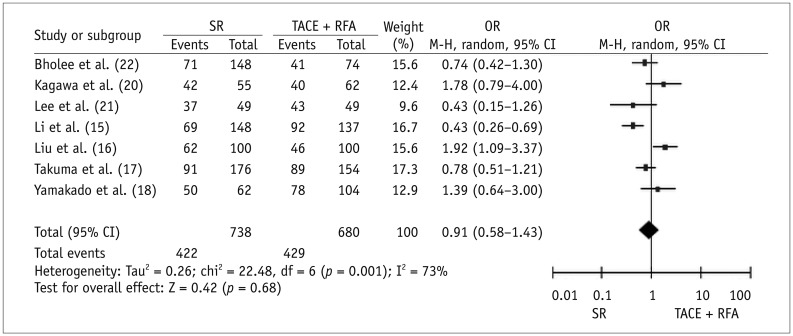
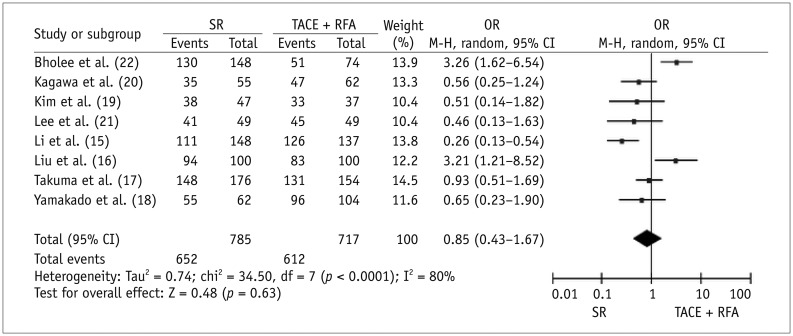
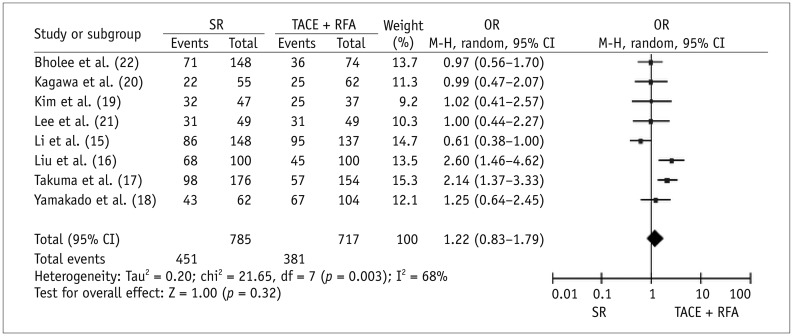
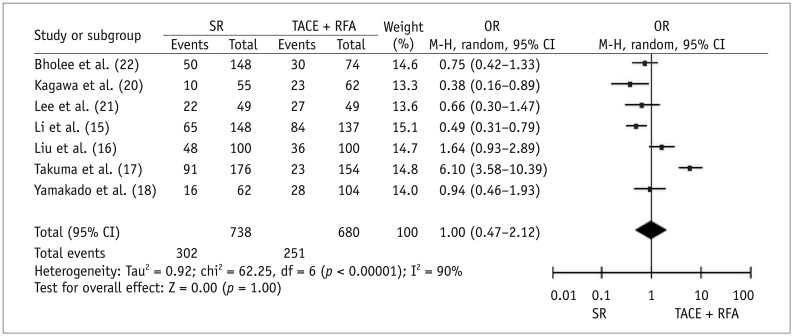
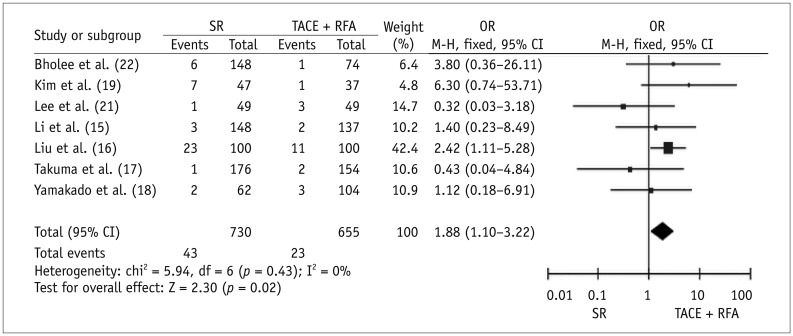
Seven case-control studies and one randomized trial were identified. Meta-analytic results revealed that, compared with SR, TACE plus RFA had significantly higher 1-year OS (OR for survival = 0.50, p = 0.009) and lower major complications (OR = 1.88, p = 0.02) after therapy. Three studies reported on the length of hospital stay. The average length ± standard deviation reported in individual studies for SR and TACE plus RFA groups was 19.8 ± 8.4 days and 7.4 ± 2.2 days, respectively; 18.7 ± 4.9 days and 11.5 ± 6.9 days, respectively; and 16.6 ± 6.7 days and 8.5 ± 4.1 days, respectively (p < 0.0001 for all studies). Three or 5-year OS and 1-, 3-, or 5-year RFS did not significantly differ between the two therapies.
CONCLUSION
Combined TACE plus RFA may be an alternative to SR for the treatment of patients with HCC within Milan the criteria. Non-randomized design in most of the original studies was a limitation.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Curative Loco-regional Therapies for Early Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Is Combination Effective?
Sae Hwan Lee
Korean J Gastroenterol. 2019;73(3):121-123. doi: 10.4166/kjg.2019.73.3.121.
Reference
-
1. Forner A, Llovet JM, Bruix J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 2012; 379:1245–1255. PMID: 22353262.
Article2. Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D, Mathers C, Parkin DM. Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 2010; 127:2893–2917. PMID: 21351269.
Article3. Han KH, Kudo M, Ye SL, Choi JY, Poon RT, Seong J, et al. Asian consensus workshop report: expert consensus guideline for the management of intermediate and advanced hepatocellular carcinoma in Asia. Oncology. 2011; 81(Suppl 1):158–164.
Article4. Hsu CY, Hsia CY, Huang YH, Su CW, Lin HC, Lee PC, et al. Selecting an optimal staging system for hepatocellular carcinoma: comparison of 5 currently used prognostic models. Cancer. 2010; 116:3006–3014. PMID: 20564406.5. Bruix J, Sherman M. American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Management of hepatocellular carcinoma: an update. Hepatology. 2011; 53:1020–1022. PMID: 21374666.
Article6. European Association For The Study Of The Liver. European Organisation For Research And Treatment Of Cancer. EASL-EORTC clinical practice guidelines: management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2012; 56:908–943. PMID: 22424438.7. Lam VW, Ng KK, Chok KS, Cheung TT, Yuen J, Tung H, et al. Risk factors and prognostic factors of local recurrence after radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Am Coll Surg. 2008; 207:20–29. PMID: 18589357.
Article8. Minami Y, Kudo M. Radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma: a literature review. Int J Hepatol. 2011; 2011:104685. PMID: 21994847.
Article9. Pompili M, Saviano A, de Matthaeis N, Cucchetti A, Ardito F, Federico B, et al. Long-term effectiveness of resection and radiofrequency ablation for single hepatocellular carcinoma ≤3 cm. Results of a multicenter Italian survey. J Hepatol. 2013; 59:89–97. PMID: 23523578.10. Fang Y, Chen W, Liang X, Li D, Lou H, Chen R, et al. Comparison of long-term effectiveness and complications of radiofrequency ablation with hepatectomy for small hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014; 29:193–200. PMID: 24224779.
Article11. Peng ZW, Zhang YJ, Chen MS, Xu L, Liang HH, Lin XJ, et al. Radiofrequency ablation with or without transcatheter arterial chemoembolization in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: a prospective randomized trial. J Clin Oncol. 2013; 31:426–432. PMID: 23269991.
Article12. Morimoto M, Numata K, Kondo M, Moriya S, Morita S, Maeda S, et al. Radiofrequency ablation combined with transarterial chemoembolization for subcapsular hepatocellular carcinoma: a prospective cohort study. Eur J Radiol. 2013; 82:497–503. PMID: 23068563.
Article13. Ni JY, Liu SS, Xu LF, Sun HL, Chen YT. Transarterial chemoembolization combined with percutaneous radiofrequency ablation versus TACE and PRFA monotherapy in the treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2013; 139:653–659. PMID: 23292073.
Article14. Wang X, Hu Y, Ren M, Lu X, Lu G, He S. Efficacy and safety of radiofrequency ablation combined with transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinomas compared with radiofrequency ablation alone: a time-to-event meta-analysis. Korean J Radiol. 2016; 17:93–102. PMID: 26798221.
Article15. Li S, Zhang L, Huang ZM, Wu PH. Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization combined with CT-guided percutaneous thermal ablation versus hepatectomy in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Chin J Cancer. 2015; 34:254–263. PMID: 26063407.
Article16. Liu H, Wang ZG, Fu SY, Li AJ, Pan ZY, Zhou WP, et al. Randomized clinical trial of chemoembolization plus radiofrequency ablation versus partial hepatectomy for hepatocellular carcinoma within the Milan criteria. Br J Surg. 2016; 103:348–356. PMID: 26780107.
Article17. Takuma Y, Takabatake H, Morimoto Y, Toshikuni N, Kayahara T, Makino Y, et al. Comparison of combined transcatheter arterial chemoembolization and radiofrequency ablation with surgical resection by using propensity score matching in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma within Milan criteria. Radiology. 2013; 269:927–937. PMID: 24086071.
Article18. Yamakado K, Nakatsuka A, Takaki H, Yokoi H, Usui M, Sakurai H, et al. Early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma: radiofrequency ablation combined with chemoembolization versus hepatectomy. Radiology. 2008; 247:260–266. PMID: 18305190.
Article19. Kim JW, Shin SS, Kim JK, Choi SK, Heo SH, Lim HS, et al. Radiofrequency ablation combined with transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for the treatment of single hepatocellular carcinoma of 2 to 5 cm in diameter: comparison with surgical resection. Korean J Radiol. 2013; 14:626–635. PMID: 23901320.
Article20. Kagawa T, Koizumi J, Kojima S, Nagata N, Numata M, Watanabe N, et al. Tokai RFA Study Group. Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization plus radiofrequency ablation therapy for early stage hepatocellular carcinoma: comparison with surgical resection. Cancer. 2010; 116:3638–3644. PMID: 20564097.21. Lee HJ, Kim JW, Hur YH, Shin SS, Heo SH, Cho SB, et al. Combined therapy of transcatheter arterial chemoembolization and radiofrequency ablation versus surgical resection for single 2–3 cm hepatocellular carcinoma: a propensity-score matching analysis. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2017; 28:1240–1247.e3. PMID: 28688816.22. Bholee AK, Peng K, Zhou Z, Chen J, Xu L, Zhang Y, et al. Radiofrequency ablation combined with transarterial chemoembolization versus hepatectomy for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma within Milan criteria: a retrospective case-control study. Clin Transl Oncol. 2017; 19:844–852. PMID: 28070766.
Article23. Stang A. Critical evaluation of the Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Eur J Epidemiol. 2010; 25:603–605. PMID: 20652370.
Article24. Oremus M, Oremus C, Hall GB, McKinnon MC. ECT & Cognition Systematic Review Team. Inter-rater and test-retest reliability of quality assessments by novice student raters using the Jadad and Newcastle-Ottawa Scales. BMJ Open. 2012; 2:e001368.
Article25. Feng K, Yan J, Li X, Xia F, Ma K, Wang S, et al. A randomized controlled trial of radiofrequency ablation and surgical resection in the treatment of small hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2012; 57:794–802. PMID: 22634125.
Article26. Wang JH, Wang CC, Hung CH, Chen CL, Lu SN. Survival comparison between surgical resection and radiofrequency ablation for patients in BCLC very early/early stage hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2012; 56:412–418. PMID: 21756858.
Article27. Feng Q, Chi Y, Liu Y, Zhang L, Liu Q. Efficacy and safety of percutaneous radiofrequency ablation versus surgical resection for small hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis of 23 studies. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2015; 141:1–9. PMID: 24889505.
Article28. Kim JM, Kang TW, Kwon CH, Joh JW, Ko JS, Park JB, et al. Single hepatocellular carcinoma ≤ 3 cm in left lateral segment: liver resection or radiofrequency ablation? World J Gastroenterol. 2014; 20:4059–4065. PMID: 24744596.
Article29. Ke S, Ding XM, Kong J, Gao J, Wang SH, Cheng Y, et al. Low temperature of radiofrequency ablation at the target sites can facilitate rapid progression of residual hepatic VX2 carcinoma. J Transl Med. 2010; 8:73. PMID: 20667141.
Article30. Roayaie S, Obeidat K, Sposito C, Mariani L, Bhoori S, Pellegrinelli A, et al. Resection of hepatocellular cancer ≤2 cm: results from two Western centers. Hepatology. 2013; 57:1426–1435. PMID: 22576353.
Article31. Shibata T, Isoda H, Hirokawa Y, Arizono S, Shimada K, Togashi K. Small hepatocellular carcinoma: is radiofrequency ablation combined with transcatheter arterial chemoembolization more effective than radiofrequency ablation alone for treatment? Radiology. 2009; 252:905–913. PMID: 19567647.
Article32. Kim JH, Won HJ, Shin YM, Kim SH, Yoon HK, Sung KB, et al. Medium-sized (3.1–5.0 cm) hepatocellular carcinoma: transarterial chemoembolization plus radiofrequency ablation versus radiofrequency ablation alone. Ann Surg Oncol. 2011; 18:1624–1629. PMID: 21445671.33. Morimoto M, Numata K, Kondou M, Nozaki A, Morita S, Tanaka K. Midterm outcomes in patients with intermediate-sized hepatocellular carcinoma: a randomized controlled trial for determining the efficacy of radiofrequency ablation combined with transcatheter arterial chemoembolization. Cancer. 2010; 116:5452–5460. PMID: 20672352.34. Veltri A, Moretto P, Doriguzzi A, Pagano E, Carrara G, Gandini G. Radiofrequency thermal ablation (RFA) after transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) as a combined therapy for unresectable non-early hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Eur Radiol. 2006; 16:661–669. PMID: 16228211.
Article35. Yang W, Chen MH, Wang MQ, Cui M, Gao W, Wu W, et al. Combination therapy of radiofrequency ablation and transarterial chemoembolization in recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatectomy compared with single treatment. Hepatol Res. 2009; 39:231–240. PMID: 19054154.
Article36. Siriapisith T, Siwasattayanon P, Tongdee T. Radiofrequency ablation alone versus radiofrequency ablation combined with chemoembolization in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. J Med Assoc Thai. 2012; 95:430–436. PMID: 22550844.37. Li JX, Wu H, Huang JW, Zeng Y. The influence on liver function after transcatheter arterial chemoembolization combined with percutaneous radiofrequency ablation in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. J Formos Med Assoc. 2012; 111:510–515. PMID: 23021508.
Article38. Guo W, He X, Li Z, Li Y. Combination of transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) and radiofrequency ablation (RFA) vs. surgical resection (SR) on survival outcome of early hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis. Hepatogastroenterology. 2015; 62:710–714. PMID: 26897959.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Chemoembolization combined with radiofrequency ablation is the best option for the local treatment of early hepatocellular carcinoma?
- Efficacy and Safety of Radiofrequency Ablation Combined with Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization for Hepatocellular Carcinomas Compared with Radiofrequency Ablation Alone: A Time-to-Event Meta-Analysis
- Radiofrequency Ablation Combined with Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization for the Treatment of Single Hepatocellular Carcinoma of 2 to 5 cm in Diameter: Comparison with Surgical Resection
- Current status and future of radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma
- The Role of Combination of Transarterial Chemoebolization and Radiofrequency Ablation for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treatment