Efficacy and Safety of Radiofrequency Ablation Combined with Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization for Hepatocellular Carcinomas Compared with Radiofrequency Ablation Alone: A Time-to-Event Meta-Analysis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Gastroenterology, First Affiliated Hospital of Xi'an Jiaotong University, Xi'an, Shaanxi Province 710061, China. hesx123@126.com
- KMID: 2351168
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2016.17.1.93
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To compare the efficacy and safety of combined radiofrequency ablation (RFA) and transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) with RFA alone for hepatocellular carcinomas (HCC).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Randomized controlled trial (RCT) studies that compared the clinical or oncologic outcomes of combination therapy of TACE and RFA versus RFA for the treatment of HCC were identified through literature searches of electronic databases (Pubmed, Embase, Cochrane Library, China Biology Medicine disc, China National Knowledge Infrastructure, and Google Scholar). Hazard ratios (HRs) or odds ratios (ORs) with their corresponding 95% confidence interval (CI) were combined as the effective value to assess the summary effects. The strength of evidence was rated by the Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development, and Evaluation system.
RESULTS
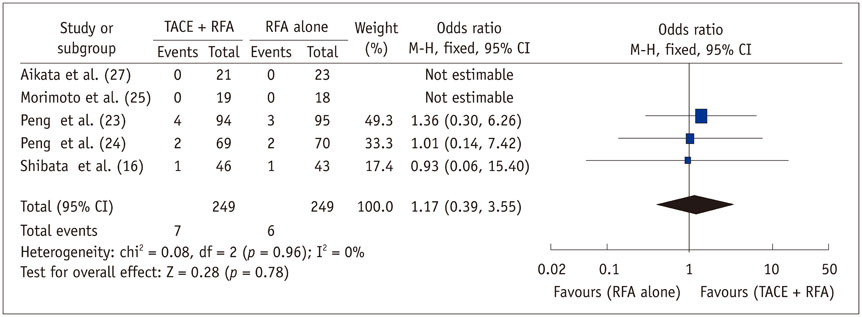
Six RCTs with 534 patients were eligible for inclusion in this meta-analysis. The meta-analysis showed that the combination of TACE and RFA is associated with a significantly longer overall survival (HR = 0.62, 95% CI: 0.49-0.78, p < 0.001) and recurrence-free survival (HR = 0.55, 95% CI: 0.40-0.76, p < 0.001) in contrast with RFA monotherapy. The seemingly higher incidence of major complications in the combination group compared with RFA group did not reach statistical significance (OR = 1.17, 95% CI: 0.39-3.55, p = 0.78).
CONCLUSION
In patients with HCC, the combination of TACE and RFA is associated with significantly higher overall survival and recurrence-free survival, as compared with RFA monotherapy, without significant difference in major complications.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 10 articles
-
Curative Loco-regional Therapies for Early Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Is Combination Effective?
Sae Hwan Lee
Korean J Gastroenterol. 2019;73(3):121-123. doi: 10.4166/kjg.2019.73.3.121.Recent Advances in the Image-Guided Tumor Ablation of Liver Malignancies: Radiofrequency Ablation with Multiple Electrodes, Real-Time Multimodality Fusion Imaging, and New Energy Sources
Dong Ho Lee, Jeong Min Lee
Korean J Radiol. 2018;19(4):545-559. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2018.19.4.545.Percutaneous Dual-Switching Monopolar Radiofrequency Ablation Using a Separable Clustered Electrode: A Preliminary Study
Tae Won Choi, Jeong Min Lee, Dong Ho Lee, Jeong-Hoon Lee, Su Jong Yu, Yoon Jun Kim, Jung-Hwan Yoon, Joon Koo Han
Korean J Radiol. 2017;18(5):799-808. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2017.18.5.799.Comparison of Combined Therapy Using Conventional Chemoembolization and Radiofrequency Ablation Versus Conventional Chemoembolization for Ultrasound-Invisible Early-Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma (Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer Stage 0 or A)
Hyukjoon Lee, Chang Jin Yoon, Nak Jong Seong, Sook-Hyang Jeong, Jin-Wook Kim
Korean J Radiol. 2018;19(6):1130-1139. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2018.19.6.1130.Comparison of the Efficacy and Prognostic Factors of Transarterial Chemoembolization Plus Microwave Ablation versus Transarterial Chemoembolization Alone in Patients with a Large Solitary or Multinodular Hepatocellular Carcinomas
Lin Zheng, Hai-Liang Li, Chen-Yang Guo, Su-Xia Luo
Korean J Radiol. 2018;19(2):237-246. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2018.19.2.237.Ultrasound-Guided Intraoperative Radiofrequency Ablation and Surgical Resection for Liver Metastasis from Malignant Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors
In Sun Yoon, Ji Hoon Shin, Kichang Han, Pyo Nyun Kim, Ki Hun Kim, Yoon-Koo Kang, Heung Kyu Ko
Korean J Radiol. 2018;19(1):54-62. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2018.19.1.54.Radiofrequency Ablation Combined with Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization Therapy Versus Surgical Resection for Hepatocellular Carcinoma within the Milan Criteria: A Meta-Analysis
Wei-dong Wang, Li-hua Zhang, Jia-Yan Ni, Xiong-ying Jiang, Dong Chen, Yao-ting Chen, Hong-liang Sun, Jiang-hong Luo, Lin-feng Xu
Korean J Radiol. 2018;19(4):613-622. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2018.19.4.613.2018 Korean Liver Cancer Association–National Cancer Center Korea Practice Guidelines for the Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
,
Korean J Radiol. 2019;20(7):1042-1113. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2019.0140.2022 KLCA-NCC Korea practice guidelines for the management of hepatocellular carcinoma
J Liver Cancer. 2023;23(1):1-120. doi: 10.17998/jlc.2022.11.07.Local ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma: 2024 expert consensus-based practical recommendation of the Korean Liver Cancer Association
Seungchul Han, Pil Soo Sung, Soo Young Park, Jin Woong Kim, Hyun Pyo Hong, Jung-Hee Yoon, Dong Jin Chung, Joon Ho Kwon, Sanghyeok Lim, Jae Hyun Kim, Seung Kak Shin, Tae Hyung Kim, Dong Ho Lee, Jong Young Choi
J Liver Cancer. 2024;24(2):131-144. doi: 10.17998/jlc.2024.08.04.
Reference
-
1. Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015; 65:87–108.2. Sangiovanni A, Del Ninno E, Fasani P, De Fazio C, Ronchi G, Romeo R, et al. Increased survival of cirrhotic patients with a hepatocellular carcinoma detected during surveillance. Gastroenterology. 2004; 126:1005–1014.3. Shiina S, Teratani T, Obi S, Sato S, Tateishi R, Fujishima T, et al. A randomized controlled trial of radiofrequency ablation with ethanol injection for small hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 2005; 129:122–130.4. Lencioni R. Loco-regional treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2010; 52:762–773.5. N'Kontchou G, Mahamoudi A, Aout M, Ganne-Carrié N, Grando V, Coderc E, et al. Radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma: long-term results and prognostic factors in 235 Western patients with cirrhosis. Hepatology. 2009; 50:1475–1483.6. Livraghi T, Goldberg SN, Lazzaroni S, Meloni F, Ierace T, Solbiati L, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma: radio-frequency ablation of medium and large lesions. Radiology. 2000; 214:761–768.7. McGhana JP, Dodd GD 3rd. Radiofrequency ablation of the liver: current status. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2001; 176:3–16.8. Idée JM, Guiu B. Use of Lipiodol as a drug-delivery system for transcatheter arterial chemoembolization of hepatocellular carcinoma: a review. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2013; 88:530–549.9. Maluccio MA, Covey AM, Porat LB, Schubert J, Brody LA, Sofocleous CT, et al. Transcatheter arterial embolization with only particles for the treatment of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2008; 19:862–869.10. Min JH, Lee MW, Cha DI, Jeon YH, Shin SW, Cho SK, et al. Radiofrequency ablation combined with chemoembolization for intermediate-sized (3-5 cm) hepatocellular carcinomas under dual guidance of biplane fluoroscopy and ultrasonography. Korean J Radiol. 2013; 14:248–258.11. Takaki H, Yamakado K, Uraki J, Nakatsuka A, Fuke H, Yamamoto N, et al. Radiofrequency ablation combined with chemoembolization for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinomas larger than 5 cm. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2009; 20:217–224.12. Chang NK, Shin SS, Kim JW, Kim HJ, Jeong YY, Heo SH, et al. Effect of ultrasound-guided radiofrequency ablation in incompletely treated hepatocellular carcinoma after transcatheter arterial chemoembolization. Korean J Radiol. 2012; 13:Suppl 1. S104–S111.13. Kim JW, Shin SS, Kim JK, Choi SK, Heo SH, Lim HS, et al. Radiofrequency ablation combined with transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for the treatment of single hepatocellular carcinoma of 2 to 5 cm in diameter: comparison with surgical resection. Korean J Radiol. 2013; 14:626–635.14. Hu YQ. Radiofrequency ablation and transcatheter arterial chemoembolization in primary hepatic carcinoma. Contemp Med. 2011; 17:39–40.15. Tiong L, Maddern GJ. Systematic review and meta-analysis of survival and disease recurrence after radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma. Br J Surg. 2011; 98:1210–1224.16. Shibata T, Isoda H, Hirokawa Y, Arizono S, Shimada K, Togashi K. Small hepatocellular carcinoma: is radiofrequency ablation combined with transcatheter arterial chemoembolization more effective than radiofrequency ablation alone for treatment? Radiology. 2009; 252:905–913.17. Kang CB, Xu HB, Wang SL, Rui JA. Treatment of large hepatoma by TACE in combination with RFA. Zhonghua Gandan Waike Zazhi. 2007; 13:828–830.18. Higgins JP, Altman DG, Gøtzsche PC, Jüni P, Moher D, Oxman AD, et al. The Cochrane Collaboration's tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ. 2011; 343:d5928.19. Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Vist GE, Kunz R, Falck-Ytter Y, Alonso-Coello P, et al. GRADE: an emerging consensus on rating quality of evidence and strength of recommendations. BMJ. 2008; 336:924–926.20. Parmar MK, Torri V, Stewart L. Extracting summary statistics to perform meta-analyses of the published literature for survival endpoints. Stat Med. 1998; 17:2815–2834.21. Tierney JF, Stewart LA, Ghersi D, Burdett S, Sydes MR. Practical methods for incorporating summary time-to-event data into meta-analysis. Trials. 2007; 8:16.22. Higgins JPT, Green S. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.0.2. The Cochrane Collaboration Web site;Published September 2009. http://www.cochrane-handbook.org.23. Peng ZW, Zhang YJ, Chen MS, Xu L, Liang HH, Lin XJ, et al. Radiofrequency ablation with or without transcatheter arterial chemoembolization in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: a prospective randomized trial. J Clin Oncol. 2013; 31:426–432.24. Peng ZW, Zhang YJ, Liang HH, Lin XJ, Guo RP, Chen MS. Recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma treated with sequential transcatheter arterial chemoembolization and RF ablation versus RF ablation alone: a prospective randomized trial. Radiology. 2012; 262:689–700.25. Morimoto M, Numata K, Kondou M, Nozaki A, Morita S, Tanaka K. Midterm outcomes in patients with intermediate-sized hepatocellular carcinoma: a randomized controlled trial for determining the efficacy of radiofrequency ablation combined with transcatheter arterial chemoembolization. Cancer. 2010; 116:5452–5460.26. Yang P, Liang M, Zhang Y, Shen B. Clinical application of a combination therapy of lentinan, multi-electrode RFA and TACE in HCC. Adv Ther. 2008; 25:787–794.27. Aikata H, Shirakawa H, Takaki S, Uka K, Miki D, Yamashina K, et al. Radiofrequency ablation combined with transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for small hepatocellular carcinomas. Hepatology. 2006; 44:494A.28. Lin JJ, Wu W, Jiang XF, Jin XJ, Lu LJ, Bao LW. [Clinical outcomes of radiofrequency ablation combined with transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: a single-center experience]. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2013; 35:144–147.29. Cheng BQ, Jia CQ, Liu CT, Fan W, Wang QL, Zhang ZL, et al. Chemoembolization combined with radiofrequency ablation for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma larger than 3 cm: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2008; 299:1669–1677.30. Shen SQ, Xiang JJ, Xiong CL, Wu SM, Zhu SS. Intraoperative radiofrequency thermal ablation combined with portal vein infusion chemotherapy and transarterial chemoembolization for unresectable HCC. Hepatogastroenterology. 2005; 52:1403–1407.31. Wang YB, Chen MH, Yan K, Yang W, Dai Y, Yin SS. [Quality of life of primary hepatocellular carcinoma patients after radiofrequency ablation]. Ai Zheng. 2005; 24:827–833.32. Shibata T, Shibata T, Maetani Y, Isoda H, Hiraoka M. Radiofrequency ablation for small hepatocellular carcinoma: prospective comparison of internally cooled electrode and expandable electrode. Radiology. 2006; 238:346–353.33. Jiang G, Xu X, Ren S, Wang L. Combining transarterial chemoembolization with radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma. Tumour Biol. 2014; 35:3405–3408.34. Goldberg SN, Girnan GD, Lukyanov AN, Ahmed M, Monsky WL, Gazelle GS, et al. Percutaneous tumor ablation: increased necrosis with combined radio-frequency ablation and intravenous liposomal doxorubicin in a rat breast tumor model. Radiology. 2002; 222:797–804.35. Seki T, Tamai T, Nakagawa T, Imamura M, Nishimura A, Yamashiki N, et al. Combination therapy with transcatheter arterial chemoembolization and percutaneous microwave coagulation therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer. 2000; 89:1245–1251.36. Ni JY, Liu SS, Xu LF, Sun HL, Chen YT. Meta-analysis of radiofrequency ablation in combination with transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 2013; 19:3872–3882.37. Lu Z, Wen F, Guo Q, Liang H, Mao X, Sun H. Radiofrequency ablation plus chemoembolization versus radiofrequency ablation alone for hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis of randomized-controlled trials. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013; 25:187–194.38. Kong QF, Jiao JB, Chen QQ, Li L, Wang DG, Lv B. Comparative effectiveness of radiofrequency ablation with or without transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma. Tumour Biol. 2014; 35:2655–2659.39. Yan S, Xu D, Sun B. Combination of radiofrequency ablation with transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis. Dig Dis Sci. 2012; 57:3026–3031.40. Yan S, Xu D, Sun B. Combination of radiofrequency ablation with transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis. Dig Dis Sci. 2013; 58:2107–2113.41. Wang W, Shi J, Xie WF. Transarterial chemoembolization in combination with percutaneous ablation therapy in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis. Liver Int. 2010; 30:741–749.42. Liu Z, Gao F, Yang G, Singh S, Lu M, Zhang T, et al. Combination of radiofrequency ablation with transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma: an up-to-date meta-analysis. Tumour Biol. 2014; 35:7407–7413.43. Spruance SL, Reid JE, Grace M, Samore M. Hazard ratio in clinical trials. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004; 48:2787–2792.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Chemoembolization combined with radiofrequency ablation is the best option for the local treatment of early hepatocellular carcinoma?
- The Role of Combination of Transarterial Chemoebolization and Radiofrequency Ablation for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treatment
- Current status and future of radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma
- Efficacy of Hepatic Arterial Infusion Chemotherapy and Radiofrequency Ablation against Hepatocellular Carcinoma Refractory to Transarterial Chemoembolization and Vascular Variation: A Case Study
- Radiofrequency Thermal Ablation of Hepatocellular Carcinomas