Kosin Med J.
2021 Dec;36(2):161-168. 10.7180/kmj.2021.36.2.161.
Efficacy of Hepatic Arterial Infusion Chemotherapy and Radiofrequency Ablation against Hepatocellular Carcinoma Refractory to Transarterial Chemoembolization and Vascular Variation: A Case Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, On hospital, Busan, Republic of Korea
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Dong-A University College of Medicine, Busan, Republic of Korea
- KMID: 2524660
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7180/kmj.2021.36.2.161
Abstract
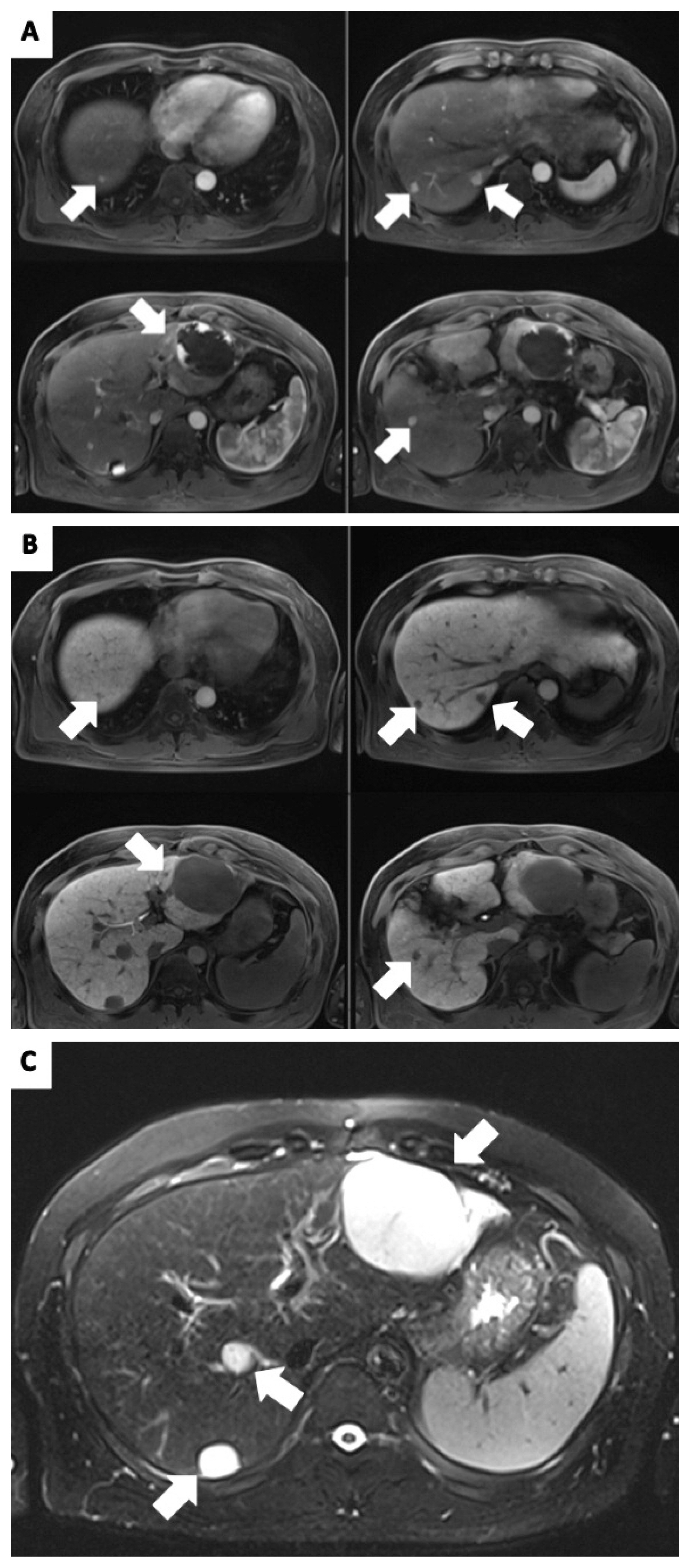
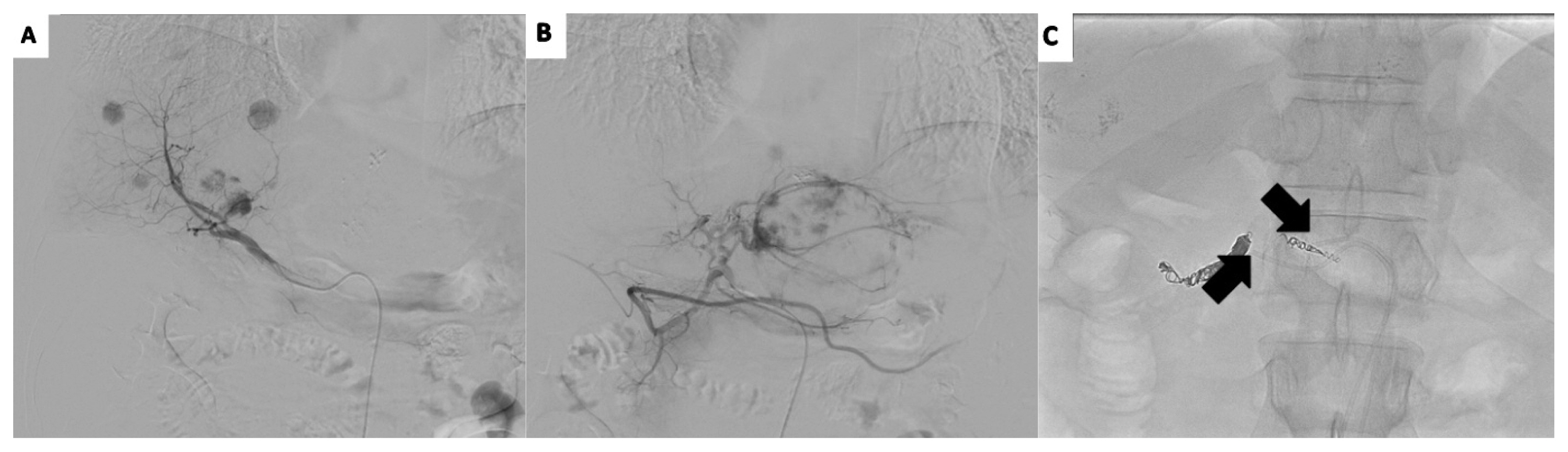
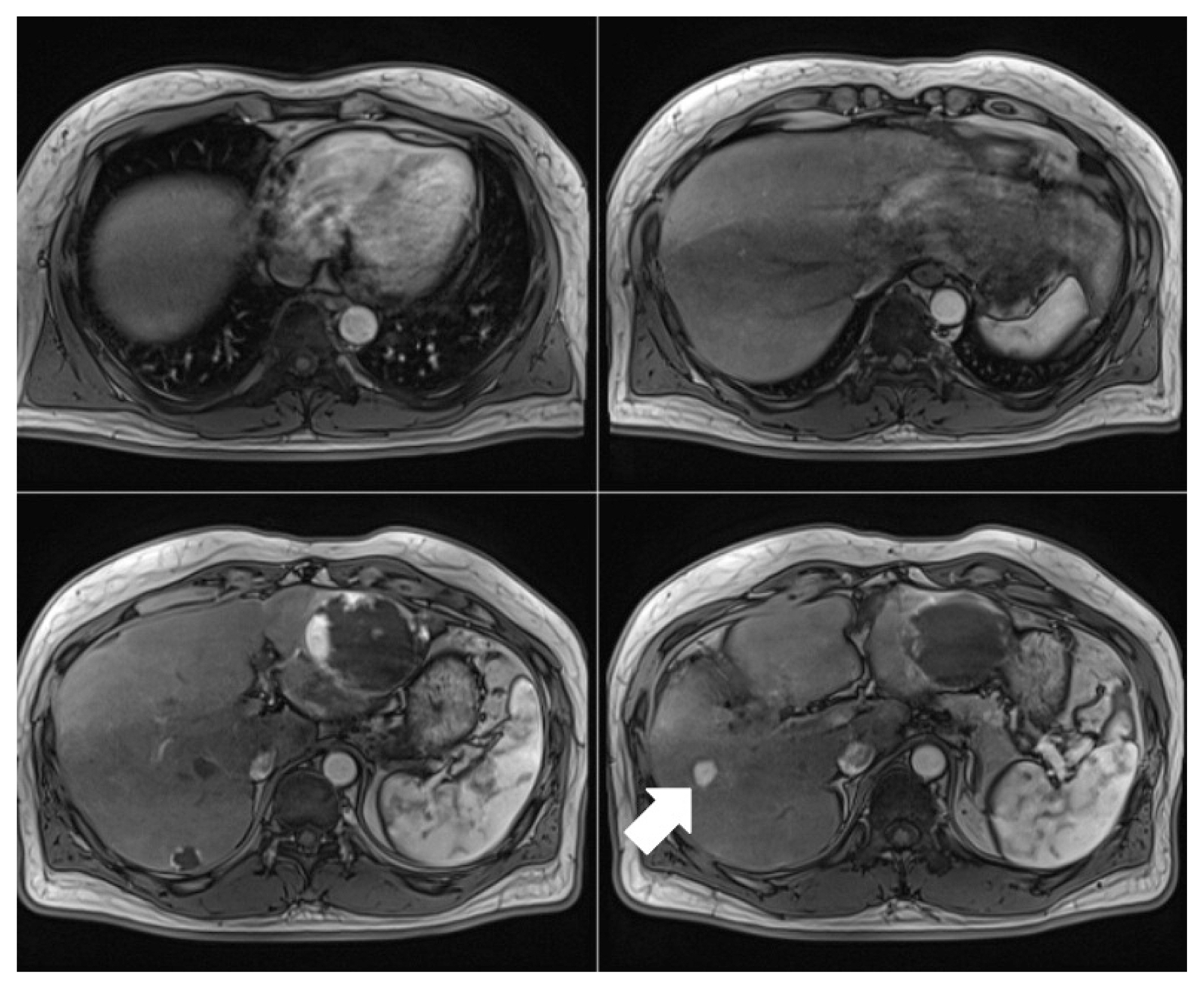
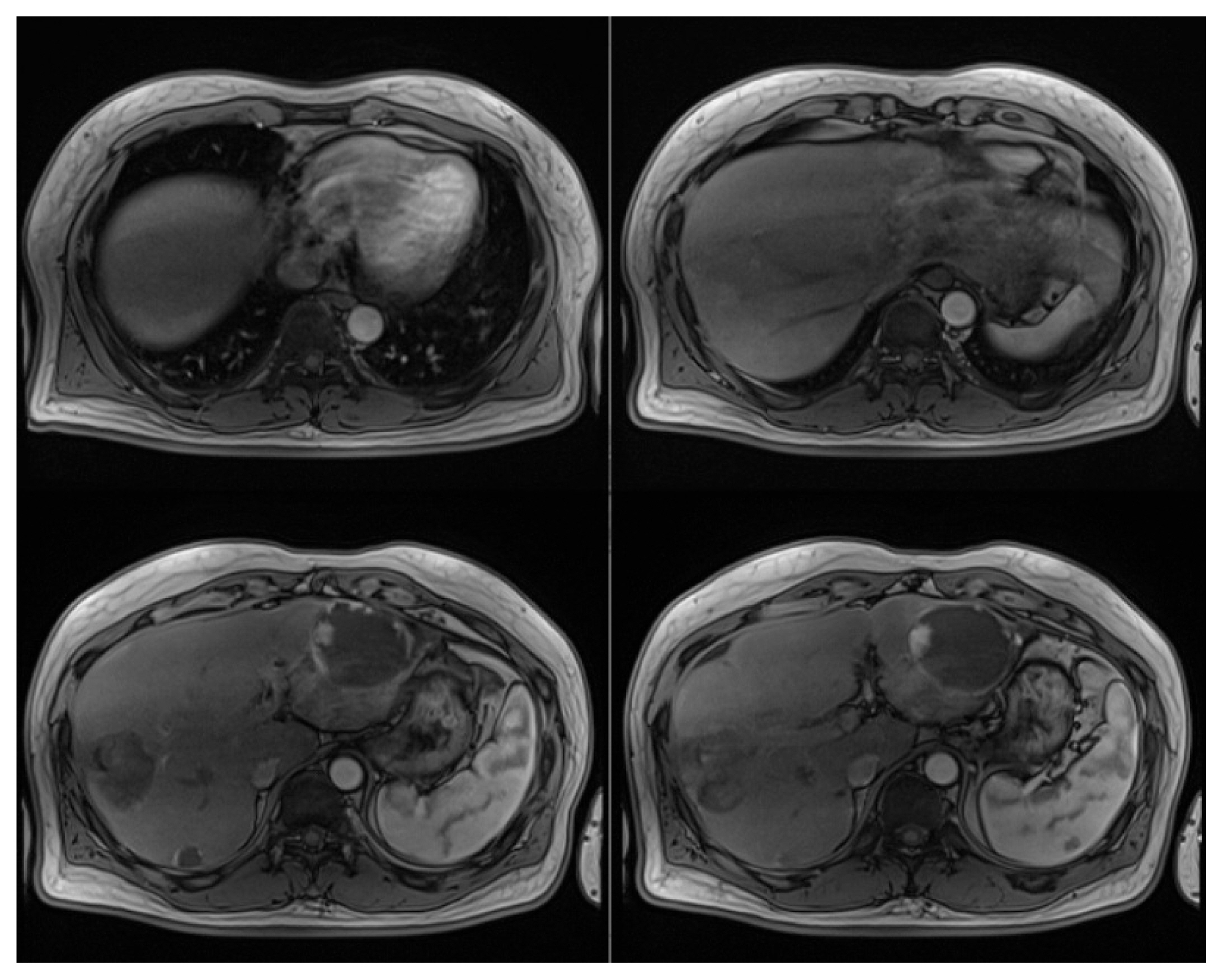
- Transarterial chemoembolization is often the first-line treatment for multiple hepatocellular carcinomas. However, hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy is a treatment option for hepatocellular carcinoma refractory to multiple sessions of transarterial chemoembolization. Hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy requires implantation of an appropriate port into the hepatic artery. However, it may be impossible to implant a port due to hepatic artery variation. We report a case of hepatocellular carcinoma refractory to transarterial chemoembolization and hepatic artery variation treated successfully with hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy and radiofrequency ablation with complete response after implantation of ports in both liver lobes.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Yang JD, Hainaut P, Gores GJ, Amadou A, Plymoth A, Roberts LR. A global view of hepatocellular carcinoma: trends, risk, prevention and management. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019; 16:589–604.
Article2. Llovet JM, Zucman-Rossi J, Pikarsky E, Sangro B, Schwartz M, Sherman M, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2016; 2:16018.
Article3. Marrero JA, Kulik LM, Sirlin CB, Zhu AX, Finn RS, Abecassis MM, et al. Diagnosis, Staging, and Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: 2018 Practice Guidance by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology. 2018; 68:723–50.
Article4. Kudo M, Matsui O, Izumi N, Kadoya M, Okusaka T, Miyayama S, et al. Transarterial chemoembolization failure/refractoriness: JSH-LCSGJ criteria 2014 update. Oncology. 2014; 87:Suppl 1. 22–31.
Article5. Kodama K, Kawaoka T, Aikata H, Uchikawa S, Inagaki Y, Hatooka M, et al. Comparison of clinical outcome of hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy and sorafenib for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma according to macrovascular invasion and transcatheter arterial chemoembolization refractory status. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018; 33:1780–6.
Article6. Chon YE, Lee HA, Yoon JS, Park JY, Kim BH, Lee IJ, et al. Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Korea between 2012 and 2014: an Analysis of Data from the Korean Nationwide Cancer Registry. J Liver Cancer. 2020; 20:135–47.
Article7. Ueshima K, Ogasawara S, Ikeda M, Yasui Y, Terashima T, Yamashita T, et al. Hepatic Arterial Infusion Chemotherapy versus Sorafenib in Patients with Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Liver Cancer. 2020; 9:583–95.
Article8. Ikeda M, Morizane C, Ueno M, Okusaka T, Ishii H, Furuse J. Chemotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: current status and future perspectives. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2018; 48:103–14.
Article9. Ensminger WD, Rosowsky A, Raso V, Levin DC, Glode M, Come S, et al. A clinical-pharmacological evaluation of hepatic arterial infusions of 5-fluoro-2′-deoxyuridine and 5-fluorouracil. Cancer Res. 1978; 38:3784–92.10. Song DS, Bae SH, Song MJ, Lee SW, Kim HY, Lee YJ, et al. Hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy in hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis. World J Gastroenterol. 2013; 19:4679–88.
Article11. Ricke J, Hildebrandt B, Miersch A, Nicolaou A, Warschewske G, Teichgräer U, et al. Hepatic arterial port systems for treatment of liver metastases: factors affecting patency and adverse events. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2004; 15:825–33.
Article12. Qi X, Tang Y, An D, Bai M, Shi X, Wang J, et al. Radiofrequency Ablation Versus Hepatic Resection for Small Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J of Clin Gastroenterol. 2014; 48:450–7.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Role of Combination of Transarterial Chemoebolization and Radiofrequency Ablation for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treatment
- Chemoembolization combined with radiofrequency ablation is the best option for the local treatment of early hepatocellular carcinoma?
- A Case of Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Portal Vein Tumor Thrombosis Treated by Hepatic Artery Injection Chemotherapy and Radiotherapy
- Which treatment modality should we choose for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma?
- Current status and future of radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma