J Vet Sci.
2017 Sep;18(3):349-357. 10.4142/jvs.2017.18.3.349.
Are pulmonary hemostasis and fibrinolysis out of balance in equine chronic pneumopathies?
- Affiliations
-
- 1Equine Clinic, Freie Universitaet Berlin, 14163 Berlin, Germany. Ann-Kristin.Barton@fu-berlin.de
- 2Institute of Veterinary Biochemistry, Freie Universitaet Berlin, 14163 Berlin, Germany.
- KMID: 2412453
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2017.18.3.349
Abstract
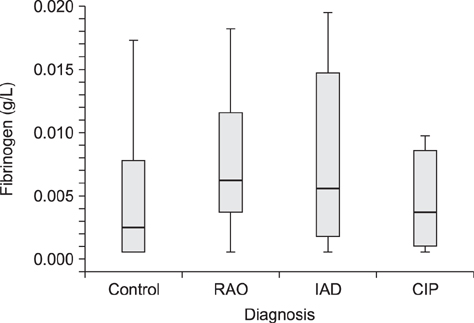
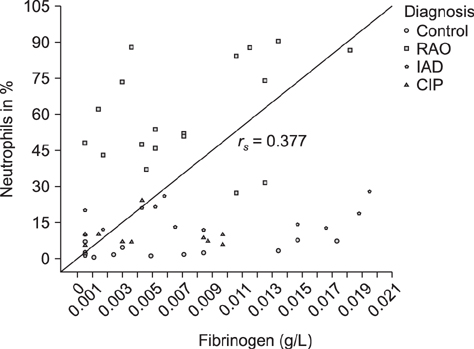
- Clinical examination, bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) cytology, acute-phase protein, and pulmonary hemostasis and fibrinolysis marker (fibrinogen, serum amyloid A [SAA], and D-dimer) results were compared between control and respiratory disease-affected horses. Using a clinical scoring system, horses (n = 58) were classified as respiratory disease-free (Controls, n = 15) or with recurrent airway obstruction (RAO; n = 18), inflammatory airway disease (n = 14) or chronic interstitial pneumopathy (n = 11). There were no significant differences in fibrinogen concentrations among groups, but there was a trend toward a lower value in controls (median 0.0024 g/L) than in horses with chronic pneumopathies (median 0.0052 g/L), in particular, those with RAO (median 0.0062 g/L). Fibrinogen concentration was positively correlated with percentage of neutrophils in BALF (r(s) = 0.377, p = 0.004). SAA concentrations were low; 65.5% of samples were below the detection limit. D-dimer concentrations were also low and quantifiable concentrations were only obtained after ultrafiltration and only in RAO (median 0.1 mg/L). In conclusion, there was limited evidence of increased coagulatory activity in chronic pneumopathies, apart from RAO. It is uncertain whether fibrinogen and D-dimer concentrations increased due to their role as acute-phase proteins or as a misbalance of coagulation and fibrinolysis.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Acute-Phase Proteins/analysis
Airway Obstruction/metabolism/physiopathology/veterinary
Animals
Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid/chemistry/cytology
Fibrin Fibrinogen Degradation Products/analysis
Fibrinogen/analysis
*Fibrinolysis/physiology
*Hemostasis/physiology
Horse Diseases/metabolism/*physiopathology
Horses
Lung Diseases/metabolism/physiopathology/*veterinary
Serum Amyloid A Protein/analysis
Acute-Phase Proteins
Fibrin Fibrinogen Degradation Products
Serum Amyloid A Protein
Fibrinogen
Figure
Reference
-
1. Anthony D, Seow HJ, Uddin M, Thompson M, Dousha L, Vlahos R, Irving LB, Levy BD, Anderson GP, Bozinovski S. Serum amyloid A promotes lung neutrophilia by increasing IL-17A levels in the mucosa and γδ T cells. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2013; 188:179–186.
Article2. Ather JL, Ckless K, Martin R, Foley KL, Suratt BT, Boyson JE, Fitzgerald KA, Flavell RA, Eisenbarth SC, Poynter ME. Serum amyloid A activates the NLRP3 inflammasome and promotes TH17 allergic asthma in mice. J Immunol. 2011; 187:64–73.
Article3. Barton MH, Morris DD, Norton N, Prasse KW. Hemostatic and fibrinolytic indices in neonatal foals with presumed septicemia. J Vet Intern Med. 1998; 12:26–35.
Article4. Brims FJ, Chauhan AJ, Higgins B, Shute JK. Up-regulation of the extrinsic coagulation pathway in acute asthma—a case study. J Asthma. 2010; 47:695–698.
Article5. Carretón E, González-Miguel J, Montoya-Alonso JA, Morchón R, Simón F, Passeri B, Cantoni AM, Kramer L. D-dimer deposits in lungs and kidneys suggest its use as a marker in the clinical workup of dogs with heartworm (Dirofilaria immitis) disease. Vet Parasitol. 2013; 191:182–186.
Article6. Cesarini C, Monreal L, Armengou L, Delgado MÁ, Ríos J, Jose-Cunilleras E. Association of admission plasma D-dimer concentration with diagnosis and outcome in horses with colic. J Vet Intern Med. 2010; 24:1490–1497.
Article7. Cho SH, Ryu CH, Oh CK. Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 in the pathogenesis of asthma. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2004; 229:138–146.
Article8. Collatos C, Barton MH, Moore JN. Fibrinolytic activity in plasma from horses with gastrointestinal diseases: changes associated with diagnosis, surgery, and outcome. J Vet Intern Med. 1995; 9:18–23.
Article9. Collatos C, Barton MH, Prasse KW, Moore JN. Intravascular and peritoneal coagulation and fibrinolysis in horses with acute gastrointestinal tract diseases. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1995; 207:465–470.10. Couëtil LL, Hoffman AM, Hodgson J, Buechner-Maxwell V, Viel L, Wood JLN, Lavoie JP. Inflammatory airway disease of horses. J Vet Intern Med. 2007; 21:356–361.
Article11. Delgado MA, Monreal L, Armengou L, Rios J, Segura D. Peritoneal D-dimer concentration for assessing peritoneal fibrinolytic activity in horses with colic. J Vet Intern Med. 2009; 23:882–889.
Article12. Dieckmann M, Klein HJ, Deegen E. [Chronic interstitial lung disease in the horse – findings in arterial bloodgas analysis, tracheobronchial mucus cytology and radiological examination of the thorax]. Pferdeheilkunde. 1990; 6:155–160. German.
Article13. Dunkel B, Chan DL, Boston R, Monreal L. Association between hypercoagulability and decreased survival in horses with ischemic or inflammatory gastrointestinal disease. J Vet Intern Med. 2010; 24:1467–1474.
Article14. Franchini M, Gilli U, Akens MK, Fellenberg RV, Bracher V. The role of neutrophil chemotactic cytokines in the pathogenesis of equine chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1998; 66:53–65.
Article15. Gehlen H, Oey L, Rohn K, Bilzer T, Stadler P. Pulmonary dysfunction and skeletal muscle changes in horses with RAO. J Vet Intern Med. 2008; 22:1014–1021.
Article16. Goldie RG, Pedersen KE. Mechanisms of increased airway microvascular permeability: role in airway inflammation and obstruction. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1995; 22:387–396.
Article17. Grünig G, Hermann M, Winder C, Von Fellenberg R. Procoagulant activity in respiratory tract secretions from horses with chronic pulmonary disease. Am J Vet Res. 1988; 49:705–709.18. Grünig G, Hulliger C, Hermann M, Winder C, von Fellenberg R. Separation of equine bronchopulmonary lavage cells by density gradient centrifugation and expression of procoagulant activity in unpurified cells and cell subpopulations. Res Vet Sci. 1990; 49:39–45.
Article19. Günther A, Mosavi P, Heinemann S, Ruppert C, Muth H, Markart P, Grimminger F, Walmrath D, Temmesfeld-Wollbrück B, Seeger W. Alveolar fibrin formation caused by enhanced procoagulant and depressed fibrinolytic capacities in severe pneumonia. Comparison with the acute respiratory distress syndrome. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000; 161:454–462.
Article20. Hoşgör I, Yarat A, Tüzüner N, Alkan F, Emekli N, Ahmad S. Biochemical and morphological alterations in lungs induced by experimental inhibition of fibrinolytic activity. Mol Cell Biochem. 2002; 241:9–19.21. Idell S. Coagulation, fibrinolysis, and fibrin deposition in acute lung injury. Crit Care Med. 2003; 31:4 Suppl. S213–S220.
Article22. Idell S, Gonzalez K, Bradford H, MacArthur CK, Fein AM, Maunder RJ, Garcia JG, Griffith DE, Weiland J, Martin TR, McLarty J, Fair DS, Walsh PN, Colman RW. Procoagulant activity in bronchoalveolar lavage in the adult respiratory distress syndrome. Contribution of tissue factor associated with factor VII. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987; 136:1466–1474.
Article23. Jacobsen S, Andersen PH. The acute phase protein serum amyloid A (SAA) as a marker of inflammation in horses. Equine Vet Educ. 2007; 19:38–46.
Article24. Lavoie JP. Recurrent airway obstruction (heaves) and summer-pasture-associated obstructive pulmonary disease. In : McGorum BC, Dixon PM, Robinson NE, Schumacher J, editors. Equine Respiratory Medicine and Surgery. Edinburgh: Elsevier;2007. p. 565–589.25. Lavoie-Lamoureux A, Leclere M, Lemos K, Wagner B, Lavoie JP. Markers of systemic inflammation in horses with heaves. J Vet Intern Med. 2012; 26:1419–1426.
Article26. Lu P, Takai K, Weaver VM, Werb Z. Extracellular matrix degradation and remodeling in development and disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2011; 3:a005058.
Article27. Lugo J, Harkema JR, deFeijter-Rupp H, Bartner L, Boruta D, Robinson NE. Airway inflammation is associated with mucous cell metaplasia and increased intraepithelial stored mucosubstances in horses. Vet J. 2006; 172:293–301.
Article28. Mazan MR, Vin R, Hoffman AM. Radiographic scoring lacks predictive value in inflammatory airway disease. Equine Vet J. 2005; 37:541–545.
Article29. Monreal L, Anglés A, Espada Y, Monasterio J, Monreal M. Hypercoagulation and hypofibrinolysis in horses with colic and DIC. Equine Vet J Suppl. 2000; 19–25.
Article30. Moran G, Carcamo C, Concha M, Folch H. [Expression of the protein serum amyloid A (SAA) in response to Aspergillus fumigatus in murine models of allergic airway inflammation]. Rev Iberoam Micol. 2015; 32:25–29.
Article31. Ohnesorge B, Trötschel Ch, Deegen E. [Diagnostic value of capnography in horses with COPD]. Pferdeheilkunde. 1998; 14:450–455.
Article32. Ozseker F, Buyukozturk S, Depboylu B, Yilmazbayhan D, Karayigit E, Gelincik A, Genc S, Colakoglu B, Dal M, Issever H. Serum amyloid A (SAA) in induced sputum of asthmatics: a new look to an old marker. Int Immunopharmacol. 2006; 6:1569–1576.
Article33. Pizzichini E, Pizzichini MM, Efthimiadis A, Evans S, Morris MM, Squillace D, Gleich GJ, Dolovich J, Hargreave FE. Indices of airway inflammation in induced sputum: reproducibility and validity of cell and fluid-phase measurements. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1996; 154:308–317.
Article34. Pollock PJ, Prendergast M, Schumacher J, Bellenger CR. Effects of surgery on the acute phase response in clinically normal and diseased horses. Vet Rec. 2005; 156:538–542.
Article35. Ribera T, Monreal L, Armengou L, Rios J, Prades M. Synovial fluid D-dimer concentration in foals with septic joint disease. J Vet Intern Med. 2011; 25:1113–1117.
Article36. Ribera T, Monreal L, Delgado MA, Rios J, Prades M. Synovial fluid D-dimer concentration in horses with osteochondritis dissecans and osteoarthritis. Vet Comp Orthop Traumatol. 2013; 26:54–60.
Article37. Robinson NE. International workshop on equine chronic airway disease, Michigan State University, 16-18 June 2000. Equine Vet J. 2001; 33:5–19.
Article38. Shetty S, Padijnayayveetil J, Tucker T, Stankowska D, Idell S. The fibrinolytic system and the regulation of lung epithelial cell proteolysis, signaling, and cellular viability. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2008; 295:L967–L975.
Article39. Shinagawa K, Martin JA, Ploplis VA, Castellino FJ. Coagulation factor Xa modulates airway remodeling in a murine model of asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2007; 175:136–143.
Article40. Shinagawa K, Ploplis VA, Castellino FJ. A severe deficiency of coagulation factor VIIa results in attenuation of the asthmatic response in mice. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2009; 296:L763–L770.
Article41. Stokol T, Erb HN, De Wilde L, Tornquist SJ, Brooks M. Evaluation of latex agglutination kits for detection of fibrin(ogen) degradation products and D-dimer in healthy horses and horses with severe colic. Vet Clin Pathol. 2005; 34:375–382.
Article42. Tilley P, Sales Luis JP, Branco Ferreira M. Correlation and discriminant analysis between clinical, endoscopic, thoracic X-ray and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid cytology scores, for staging horses with recurrent airway obstruction (RAO). Res Vet Sci. 2012; 93:1006–1014.
Article43. Van den Ingh TSGAM. Morphological aspects of bronchitis and bronchiolitis in the horse. Pferdeheilkunde. 1985; 1:13–15.44. Wagers SS, Norton RJ, Rinaldi LM, Bates JHT, Sobel BE, Irvin CG. Extravascular fibrin, plasminogen activator, plasminogen activator inhibitors, and airway hyperresponsiveness. J Clin Invest. 2004; 114:104–111.
Article45. Winder NC, Grünig G, Hermann M, von Fellenberg R. Fibrin/fibrinogen in lungs and respiratory secretions of horses with chronic pulmonary disease. Am J Vet Res. 1990; 51:945–949.46. Yuda H, Adachi Y, Taguchi O, Gabazza EC, Hataji O, Fujimoto H, Tamaki S, Nishikubo K, Fukudome K, D’Alessandro-Gabazza CN, Maruyama J, Izumizaki M, Iwase M, Homma I, Inoue R, Kamada H, Hayashi T, Kasper M, Lambrecht BN, Barnes PJ, Suzuki K. Activated protein C inhibits bronchial hyperresponsiveness and Th2 cytokine expression in mice. Blood. 2004; 103:2196–2204.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A study on changes of coagulation inhibitors and fibrinolysis inhibitors in patients with liver cirrhosis and hepatoma
- A Case of Protein S Deficiency with Cerebral Infarction
- Clot Waveform Analysis for Hemostatic Abnormalities
- A Case of Spontaneous Remission of Acute Pulmonary Embolism
- Effect of Rivaroxaban on Fibrinolytic Therapy in Massive Pulmonary Embolism: Two Cases