Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr.
2018 Apr;21(2):118-126. 10.5223/pghn.2018.21.2.118.
Accuracy of the 2008 Simplified Criteria for the Diagnosis of Autoimmune Hepatitis in Children
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition, Sant Joan de Déu Hospital (SJDH), Barcelona, Spain. jvicentearcos@gmail.com
- 2Department of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Vall d'Hebron Hospital (VHH), Barcelona, Spain.
- 3SJDH-VHH Comprehensive Unit of Complex Hepatology and Pediatric Liver Transplantation, Barcelona, Spain.
- 4Department of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Hepatology, University Hospital Complex of Santiago de Compostela, Santiago de Compostela, Spain.
- KMID: 2409363
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5223/pghn.2018.21.2.118
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Classical criteria for diagnosis of autoimmune hepatitis (AIH) are intended as research tool and are difficult to apply at patient's bedside. We aimed to study the accuracy of simplified criteria and the concordance with the expert diagnosis based on the original criteria.
METHODS
A cohort of children under study for liver disorder was selected through consecutive sampling to obtain the prevalence of AIH within the group of differential diagnoses. AIH was defined, based on classical criteria, through committee review of medical reports. Validity indicators of the simplified criteria were obtained in an intention to diagnose approach. Optimal cut-off and the area under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve were calculated.
RESULTS
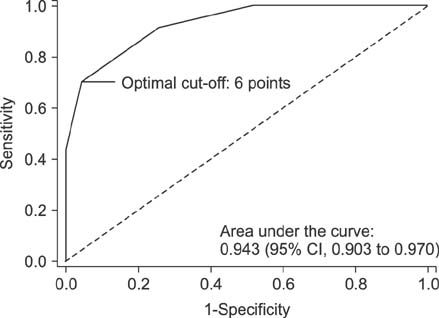
Out of 212 cases reviewed, 47.2% were AIH. For the optimal cut-off (6 points), the simplified criteria showed a sensitivity of 72.0% and a specificity of 96.4%, with a 94.7% positive and a 79.4% negative predictive value. The area under the ROC curve was 94.3%. There was a good agreement in the pre-treatment concordance between the classical and the simplified criteria (kappa index, 0.775).
CONCLUSION
Simplified criteria provide a moderate sensitivity for the diagnosis of AIH, but may help in indicating treatment in cases under suspicion with 6 or more points.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Krawitt EL. Clinical features and management of autoimmune hepatitis. World J Gastroenterol. 2008; 14:3301–3305.
Article2. Vergani D, Mieli-Vergani G. Cutting edge issues in autoimmune hepatitis. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2012; 42:309–321.
Article3. Mieli-Vergani G, Vergani D. Autoimmune hepatitis in children: what is different from adult AIH? Semin Liver Dis. 2009; 29:297–306.
Article4. Della Corte C, Sartorelli MR, Sindoni CD, Girolami E, Giovannelli L, Comparcola D, et al. Autoimmune hepatitis in children: an overview of the disease focusing on current therapies. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012; 24:739–746.5. Johnson PJ, McFarlane IG. Meeting report: International Autoimmune Hepatitis Group. Hepatology. 1993; 18:998–1005.
Article6. Alvarez F, Berg PA, Bianchi FB, Bianchi L, Burroughs AK, Cancado EL, et al. International Autoimmune Hepatitis Group Report: review of criteria for diagnosis of autoimmune hepatitis. J Hepatol. 1999; 31:929–938.
Article7. Ebbeson RL, Schreiber RA. Diagnosing autoimmune hepatitis in children: is the International Autoimmune Hepatitis Group scoring system useful? Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2004; 2:935–940.
Article8. Hennes EM, Zeniya M, Czaja AJ, Parés A, Dalekos GN, Krawitt EL, et al. Simplified criteria for the diagnosis of autoimmune hepatitis. Hepatology. 2008; 48:169–176.
Article9. Choi G, Peters MG. The challenge of diagnosing autoimmune hepatitis: less is more. Hepatology. 2008; 48:10–12.
Article10. Qiu D, Wang Q, Wang H, Xie Q, Zang G, Jiang H, et al. Validation of the simplified criteria for diagnosis of autoimmune hepatitis in Chinese patients. J Hepatol. 2011; 54:340–347.
Article11. Li Y, Peng M, Gong G. Evaluation of the revised versus the simplified scoring system in patients with autoimmune hepatitis. Exp Ther Med. 2014; 7:131–136.
Article12. Fujiwara K, Yasui S, Tawada A, Fukuda Y, Nakano M, Yokosuka O. Diagnostic value and utility of the simplified International Autoimmune Hepatitis Group criteria in acute-onset autoimmune hepatitis. Liver Int. 2011; 31:1013–1020.
Article13. Liu F, Pan ZG, Ye J, Xu D, Guo H, Li GP, et al. Primary biliary cirrhosis-autoimmune hepatitis overlap syndrome: simplified criteria may be effective in the diagnosis in Chinese patients. J Dig Dis. 2014; 15:660–668.
Article14. Gatselis NK, Zachou K, Papamichalis P, Koukoulis GK, Gabeta S, Dalekos GN, et al. Comparison of simplified score with the revised original score for the diagnosis of autoimmune hepatitis: a new or a complementary diagnostic score? Dig Liver Dis. 2010; 42:807–812.
Article15. Yeoman AD, Westbrook RH, Al-Chalabi T, Carey I, Heaton ND, Portmann BC, et al. Diagnostic value and utility of the simplified International Autoimmune Hepatitis Group (IAIHG) criteria in acute and chronic liver disease. Hepatology. 2009; 50:538–545.
Article16. Muratori P, Granito A, Pappas G, Muratori L. Validation of simplified diagnostic criteria for autoimmune hepatitis in Italian patients. Hepatology. 2009; 49:1782–1783. author reply 1783.
Article17. Hiejima E, Komatsu H, Sogo T, Inui A, Fujisawa T. Utility of simplified criteria for the diagnosis of autoimmune hepatitis in children. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2011; 52:470–473.
Article18. Mileti E, Rosenthal P, Peters MG. Validation and modification of simplified diagnostic criteria for autoimmune hepatitis in children. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012; 10:417–421.
Article19. Squires RH Jr, Shneider BL, Bucuvalas J, Alonso E, Sokol RJ, Narkewicz MR, et al. Acute liver failure in children: the first 348 patients in the pediatric acute liver failure study group. J Pediatr. 2006; 148:652–658.
Article20. Kochar R, Fallon M. Diagnostic criteria for autoimmune hepatitis: what is the gold standard? Hepatology. 2010; 51:350–351. author reply 351.
Article21. Czaja AJ. Comparability of probable and definite autoimmune hepatitis by international diagnostic scoring criteria. Gastroenterology. 2011; 140:1472–1480.
Article22. Tiniakos DG, Brain JG, Bury YA. Role of histopathology in autoimmune hepatitis. Dig Dis. 2015; 33:Suppl 2. 53–64.
Article23. Schuetz GM, Schlattmann P, Dewey M. Use of 3x2 tables with an intention to diagnose approach to assess clinical performance of diagnostic tests: meta-analytical evaluation of coronary CT angiography studies. BMJ. 2012; 345:e6717.
Article24. Good IJ. Weight of evidence: A brief survey. Bayesian Stat. 1985; 2:249–270.25. Zweig MH, Campbell G. Receiver-operating characteristic (ROC) plots: a fundamental evaluation tool in clinical medicine. Clin Chem. 1993; 39:561–577.
Article26. Buderer NM. Statistical methodology: I. Incorporating the prevalence of disease into the sample size calculation for sensitivity and specificity. Acad Emerg Med. 1996; 3:895–900.
Article27. Stalpers LJ, Nelemans PJ, Geurts SM, Jansen E, de Boer P, Verbeek AL. The indication area of a diagnostic test. Part I--discounting gain and loss in diagnostic certainty. J Clin Epidemiol. 2015; 68:1120–1128.
Article28. Manns MP, Czaja AJ, Gorham JD, Krawitt EL, Mieli-Vergani G, Vergani D, et al. Diagnosis and management of autoimmune hepatitis. Hepatology. 2010; 51:2193–2213.
Article29. Björnsson E, Talwalkar J, Treeprasertsuk S, Neuhauser M, Lindor K. Patients with typical laboratory features of autoimmune hepatitis rarely need a liver biopsy for diagnosis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011; 9:57–63.
Article30. Czaja AJ. Performance parameters of the diagnostic scoring systems for autoimmune hepatitis. Hepatology. 2008; 48:1540–1548.
Article31. Mieli-Vergani G, Heller S, Jara P, Vergani D, Chang MH, Fujisawa T, et al. Autoimmune hepatitis. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2009; 49:158–164.
Article32. Gregorio GV, Portmann B, Karani J, Harrison P, Donaldson PT, Vergani D, et al. Autoimmune hepatitis/ sclerosing cholangitis overlap syndrome in childhood: a 16-year prospective study. Hepatology. 2001; 33:544–553.
Article33. Czaja AJ, Freese DK;. Diagnosis and treatment of autoimmune hepatitis. Hepatology. 2002; 36:479–497.
Article34. Kaya M, Angulo P, Lindor KD. Overlap of autoimmune hepatitis and primary sclerosing cholangitis: an evaluation of a modified scoring system. J Hepatol. 2000; 33:537–542.
Article35. Papamichalis PA, Zachou K, Koukoulis GK, Veloni A, Karacosta EG, Kypri L, et al. The revised international autoimmune hepatitis score in chronic liver diseases including autoimmune hepatitis/overlap syndromes and autoimmune hepatitis with concurrent other liver disorders. J Autoimmune Dis. 2007; 4:3.
Article36. Chandok N, Silveira MG, Lindor KD. Comparing the simplified and international autoimmune hepatitis group criteria in primary sclerosing cholangitis. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y). 2010; 6:108–112.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Diagnostic Value and Utility of the Simplified International Autoimmune Hepatitis Group (IAIHG) Criteria for Autoimmune Hepatitis in Korea
- The Clinical Significance of Simplified Scoring Criteria as a Diagnostic Tool for Overlap Syndrome in Korea
- A Case of Overlap Syndromebetween Autoimmune Hepatitis and Primary Biliary Cirrhosis
- Autoimmune Hepatitis: Recent Korean Trend
- A Case of Overlap Syndrome with Auoimmune Hepatitis and Cholangiopathy in a Child