J Clin Neurol.
2018 Apr;14(2):234-241. 10.3988/jcn.2018.14.2.234.
Prevalence of Multiple Sclerosis in a Turkish City Bordering an Iron and Steel Factory
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, University of Health Sciences Dr. Lütfi Kırdar Kartal Training and Research Hospital, Istanbul, Turkey. cem_boluk@hotmail.com
- 2Department of Public Health, Istanbul Medeniyet University, Istanbul, Turkey.
- 3Department of Neurology, Koç University, Istanbul, Turkey.
- 4Department of Neurology, Maltepe State Hospital, Istanbul, Turkey.
- KMID: 2407952
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3988/jcn.2018.14.2.234
Abstract
- BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an autoimmune disease characterized by inflammatory demyelination. Recent studies have shown that long-term exposure to air pollutants (including PM10 particulates) is potentially an environmental risk factor for MS. We aimed to determine the prevalence rates of MS in two cities with different levels of air pollution.
METHODS
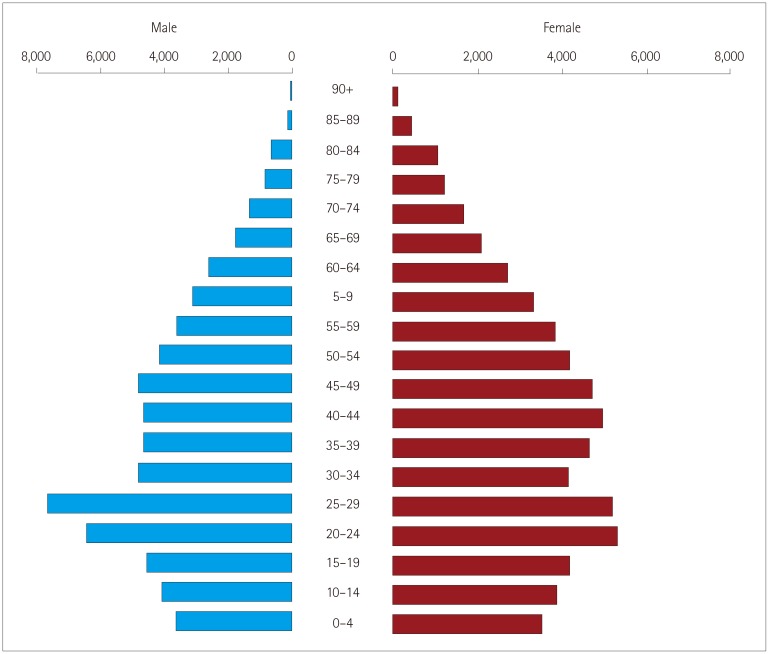
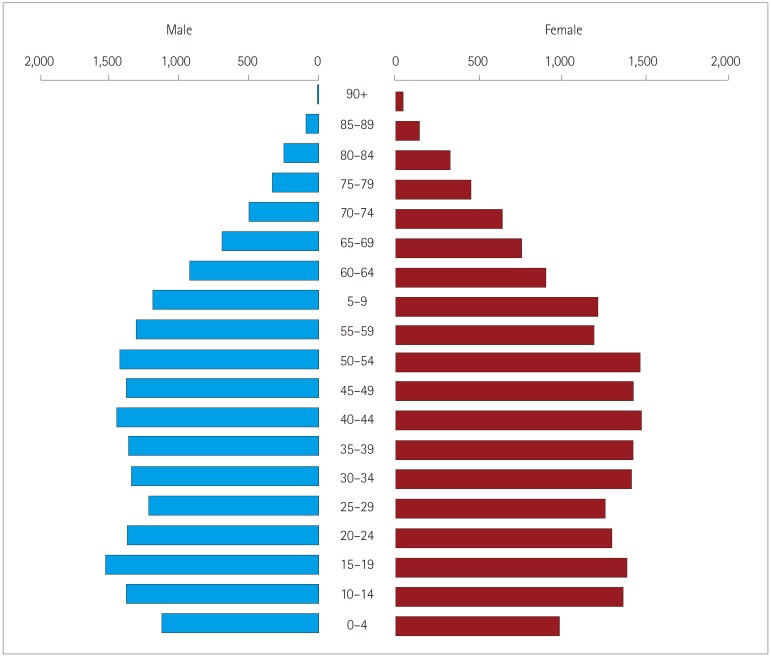
This door-to-door population-based study was conducted between April 2014 and June 2015. Two cities were screened for the prevalence rates of MS: 1) Karabük, which borders an iron-and-steel factory, and 2) Akçakoca, which is a coastal city located in the same region. A validated survey form was used for screening MS. The 2010 McDonald Criteria were used for diagnosing MS. The patients were examined twice, first by a neurology assistant in the field and then by a senior neurologist in public health centers in the cities.
RESULTS
The prevalence of MS was 95.9/100,000 in Karabük and 46.1/100,000 in Akçakoca. In total, 33 patients were diagnosed with clinically definite MS. The female/male ratio was 1.5, and 21 patients were diagnosed with relapsing-remitting MS, 9 with secondary progressive MS, and 3 with primary progressive MS.
CONCLUSIONS
We found that the prevalence of MS was more than two fold higher in Karabük than in Akçakoca, which supports a link between air pollution and the pathogenesis of MS. However, larger etiological and epidemiological studies are needed to confirm this hypothesis.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Noseworthy JH, Lucchinetti C, Rodriguez M, Weinshenker BG. Multiple sclerosis. N Engl J Med. 2000; 343:938–952. PMID: 11006371.
Article2. Koch-Henriksen N, Sørensen PS. The changing demographic pattern of multiple sclerosis epidemiology. Lancet Neurol. 2010; 9:520–532. PMID: 20398859.
Article3. Heydarpour P, Khoshkish S, Abtahi S, Moradi-Lakeh M, Sahraian MA. Multiple sclerosis epidemiology in Middle East and North Africa: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Neuroepidemiology. 2015; 44:232–244. PMID: 26088327.
Article4. Cocco E, Sardu C, Massa R, Mamusa E, Musu L, Ferrigno P, et al. Epidemiology of multiple sclerosis in south-western Sardinia. Mult Scler. 2011; 17:1282–1289. PMID: 21652610.
Article5. Türk Börü U, Alp R, Sur H, Gül L. Prevalence of multiple sclerosis door-to-door survey in Maltepe, Istanbul, Turkey. Neuroepidemiology. 2006; 27:17–21. PMID: 16770082.
Article6. Börü UT, Taşdemir M, Güler N, Ayık ED, Kumaş A, Yıldırım S, et al. Prevalence of multiple sclerosis: door-to-door survey in three rural areas of coastal Black Sea regions of Turkey. Neuroepidemiology. 2011; 37:231–235. PMID: 22133733.
Article7. Axelson O. Neurobehavioural effects. In : Mcdonald C, editor. Epidemiology of Work Related Diseases. London: BMJ Publishing Group;1995. p. 166–170.8. Reis J, Dietemann JL, Warter JM, Poser CM. A case of multiple sclerosis triggered by organic solvents. Neurol Sci. 2001; 22:155–158. PMID: 11603618.
Article9. Nelson NA, Robins TG, White RF, Garrison RP. A case-control study of chronic neuropsychiatric disease and organic solvent exposure in automobile assembly plant workers. Occup Environ Med. 1994; 51:302–307. PMID: 8199679.
Article10. Stein EC, Schiffer RB, Hall WJ, Young N. Multiple sclerosis and the workplace: report of an industry-based cluster. Neurology. 1987; 37:1672–1677. PMID: 3658175.
Article11. Schiffer RB, McDermott MP, Copley C. A multiple sclerosis cluster associated with a small, north-central Illinois community. Arch Environ Health. 2001; 56:389–395. PMID: 11777019.
Article12. Ingalls TH. Clustering of multiple sclerosis in Galion, Ohio, 1982–1985. Am J Forensic Med Pathol. 1989; 10:213–215. PMID: 2782299.
Article13. Cansaran-Duman D, Aras S. Heavy metal accumulation of five biomonitor lichen species in the vicinity of the karabük iron and steel factory in Karabük, Turkey and their comparative analysis. Turk Hij Deney Biyol Derg. 2012; 69:179–192.14. Karabük Belediyesi (TR). Online city information [Internet]. Karabük: Karabük Municipality;2014. cited 2016 Feb 15. Available from: http://www.karabuk.bel.tr/icerik.asp?i_id=40.15. Türkiye İstatistik Kurumu (TR). Statistical indications [Internet]. Ankara: Turkish Statistical Institute;2014. cited 2016 Feb 15. Available fromhttps://biruni.tuik.gov.tr/gosterge/?locale=tr.16. Akçakoka Belediyesi (TR). Online city information [Internet]. Düzce: Akçakoca Municipality;2014. cited 2016 Feb 15. Available from: http://www.akcakoca.bel.tr/akcakoca/cografi-yapi/.17. Polman CH, Reingold SC, Banwell B, Clanet M, Cohen JA, Filippi M, et al. Diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: 2010 revisions to the McDonald criteria. Ann Neurol. 2011; 69:292–302. PMID: 21387374.
Article18. Kurtzke JF. Disability rating scales in multiple sclerosis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1984; 436:347–360. PMID: 6598017.
Article19. Börü U, Duman A, Kulualp A, Taşdemir M. [Karadeniz Bögesi Ordu İlinde Multiple Skleroz Prevalans Çalışması: Kapı Kapı Dolaşılarak Yapılan Çalışma]. In : The 49th Turkish National Neurology Congress 2013; Antalya. 2013. p. 96–97.20. T.C. Cevre ve Sehircilik Bakanligi. Ulusal Hava Kalitesi İzleme İstasyonları official web site [Internet]. Ankara: National Air Pollution Monitoring Network System;2014. cited 2014 Feb 15. Available from: www.havaizleme.gov.tr.21. Cansaran-Duman D, Atakol O, Aras S. Assessment of air pollution genotoxicity by RAPD in Evernia prunastri L. Ach. from around ironsteel factory in Karabük, Turkey. J Environ Sci (China). 2011; 23:1171–1178. PMID: 22125911.
Article22. Heydarpour P, Amini H, Khoshkish S, Seidkhani H, Sahraian MA, Yunesian M. Potential impact of air pollution on multiple sclerosis in Tehran, Iran. Neuroepidemiology. 2014; 43:233–238. PMID: 25501708.
Article23. Oikonen M, Laaksonen M, Laippala P, Oksaranta O, Lilius EM, Lindgren S, et al. Ambient air quality and occurrence of multiple sclerosis relapse. Neuroepidemiology. 2003; 22:95–99. PMID: 12566960.
Article24. Angelici L, Piola M, Cavalleri T, Randi G, Cortini F, Bergamaschi R, et al. Effects of particulate matter exposure on multiple sclerosis hospital admission in Lombardy region, Italy. Environ Res. 2016; 145:68–73. PMID: 26624240.
Article25. Roux J, Bard D, Le Pabic E, Segala C, Reis J, Ongagna JC, et al. Air pollution by particulate matter PM10 may trigger multiple sclerosis relapses. Environ Res. 2017; 156:404–410. PMID: 28407574.
Article26. Calderón-Garcidueñas L, Solt AC, Henríquez-Roldán C, Torres-Jardón R, Nuse B, Herritt L, et al. Long-term air pollution exposure is associated with neuroinflammation, an altered innate immune response, disruption of the blood-brain barrier, ultrafine particulate deposition, and accumulation of amyloid beta-42 and alpha-synuclein in children and young adults. Toxicol Pathol. 2008; 36:289–310. PMID: 18349428.27. Chen L, Yokel RA, Hennig B, Toborek M. Manufactured aluminum oxide nanoparticles decrease expression of tight junction proteins in brain vasculature. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2008; 3:286–295. PMID: 18830698.
Article28. Hartz AM, Bauer B, Block ML, Hong JS, Miller DS. Diesel exhaust particles induce oxidative stress, proinflammatory signaling, and P-glycoprotein up-regulation at the blood-brain barrier. FASEB J. 2008; 22:2723–2733. PMID: 18474546.
Article29. Block ML, Calderón-Garcidueñas L. Air pollution: mechanisms of neuroinflammation and CNS disease. Trends Neurosci. 2009; 32:506–516. PMID: 19716187.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Pulmonary Siderosis
- A Study on Sickness Absence
- Application of Iron Related Magnetic Resonance Imaging in the Neurological Disorders
- A survey of traumatic reticular diseases in Korea and the effects on beef quality grade
- Recognized cases of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in automobile workers by the Korean Epidemiologic Investigation Evaluation Committee