J Vet Sci.
2018 Mar;19(2):251-259. 10.4142/jvs.2018.19.2.251.
Pathogenic and phylogenetic characteristics of non-O157 Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli isolates from retail meats in South Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1College of Veterinary Medicine & Institute of Veterinary Science, Kangwon National University, Chuncheon 24341, Korea. jwy706@kangwon.ac.kr
- 2Division of Enteric Diseases, Centers for Infectious Diseases, National Research Institute of Health, Cheongju 28159, Korea. micro487@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2407624
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2018.19.2.251
Abstract
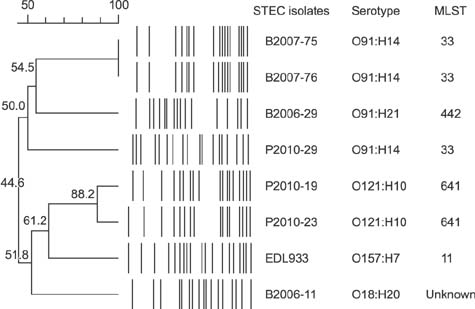
- Herein, we report the pathogenic and phylogenetic characteristics of seven Shiga toxin (Stx)-producing Escherichia coli (STEC) isolates from 434 retail meats collected in Korea during 2006 to 2012. The experimental analyses revealed that all isolates (i) were identified as non-O157 STEC, including O91:H14 (3 isolates), O121:H10 (2 isolates), O91:H21 (1 isolate), and O18:H20 (1 isolate), (ii) carried diverse Stx subtype genes (stxâ‚, stx(2c), stx(2e), or stxâ‚+ stx(2b)) whose expression levels varied strain by strain, and (iii) lacked the locus of enterocyte effacement (LEE) pathogenicity island, a major virulence factor of STEC, but they possessed one or more alternative virulence genes encoding cytotoxins (Cdt and SubAB) and/or adhesins (Saa, Iha, and EcpA). Notably, a significant heterogeneity in glutamate-induced acid resistance was observed among the STEC isolates (p < 0.05). In addition, phylogenetic analyses demonstrated that all three STEC O91:H14 isolates were categorized into sequence type (ST) 33, of which two beef isolates were identical in their pulsotypes. Similar results were observed with two O121:H10 pork isolates (ST641; 88.2% similarity). Interestingly, 96.0% of the 100 human STEC isolates collected in Korea during 2003 to 2014 were serotyped as O91:H14, and the ST33 lineage was confirmed in approximately 72.2% (13/18 isolates) of human STEC O91:H14 isolates from diarrheal patients.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Molecular epidemiology of sequence type 33 of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli O91:H14 isolates from human patients and retail meats in Korea
Jun Bong Lee, Se-Kye Kim, Seon Mi Wi, Young-Jae Cho, Tae-Wook Hahn, Jae-yon Yu, Sungsun Kim, Sahyun Hong, Jonghyun Kim, Jang Won Yoon
J Vet Sci. 2019;20(1):87-90. doi: 10.4142/jvs.2019.20.1.87.
Reference
-
1. Amigo N, Mercado E, Bentancor A, Singh P, Vilte D, Gerhardt E, Zotta E, Ibarra C, Manning SD, Larzábal M, Cataldi A. Clade 8 and clade 6 strains of Escherichia coli O157:H7 from cattle in argentina have hypervirulent-like phenotypes. PLoS One. 2015; 10:e0127710.2. Bandyopadhyay S, Lodh C, Rahaman H, Bhattacharya D, Bera AK, Ahmed FA, Mahanti A, Samanta I, Mondal DK, Bandyopadhyay S, Sarkar S, Dutta TK, Maity S, Paul V, Ghosh MK, Sarkar M, Baruah KK. Characterization of Shiga toxin producing (STEC) and enteropathogenic Escherichia coli (EPEC) in raw yak (Poephagus grunniens) milk and milk products. Res Vet Sci. 2012; 93:604–610.
Article3. Bettelheim KA. The non-O157 Shiga-toxigenic (verocytotoxigenic) Escherichia coli; under-rated pathogens. Crit Rev Microbiol. 2007; 33:67–87.
Article4. Bielaszewska M, Mellmann A, Zhang W, Köck R, Fruth A, Bauwens A, Peters G, Karch H. Characterisation of the Escherichia coli strain associated with an outbreak of haemolytic uraemic syndrome in Germany, 2011: a microbiological study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2011; 11:671–676.
Article5. Bosilevac JM, Koohmaraie M. Prevalence and characterization of non-O157 Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli isolates from commercial ground beef in the United States. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2011; 77:2103–2112.
Article6. Brunder W, Schmidt H, Karch H. EspP, a novel extracellular serine protease of enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7 cleaves human coagulation factor V. Mol Microbiol. 1997; 24:767–778.
Article7. Brusa V, Aliverti V, Aliverti F, Ortega EE, de la Torre JH, Linares LH, Sanz ME, Etcheverría AI, Padola NL, Galli L, Peral García P, Copes J, Leotta GA. Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli in beef retail markets from Argentina. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2013; 2:171.
Article8. Bustamante AV, Sanso AM, Lucchesi PM, Parma AE. Multiplex PCR assay for the detection of five putative virulence genes encoded in verotoxigenic Escherichia coli plasmids. Curr Microbiol. 2011; 62:1411–1415.
Article9. Castanie-Cornet MP, Penfound TA, Smith D, Elliott JF, Foster JW. Control of acid resistance in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1999; 181:3525–3535.10. Colello R, Cáceres ME, Ruiz MJ, Sanz M, Etcheverría AI, Padola NL. From farm to table: follow-up of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli throughout the pork production chain in Argentina. Front Microbiol. 2016; 7:93.
Article11. Erickson MC, Doyle MP. Food as a vehicle for transmission of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli. J Food Prot. 2007; 70:2426–2449.
Article12. Frank C, Werber D, Cramer JP, Askar M, Faber M, an der Heiden M, Bernard H, Fruth A, Prager R, Spode A, Wadl M, Zoufaly A, Jordan S, Kemper MJ, Follin P, Müller L, King LA, Rosner B, Buchholz U, Stark K, Krause G. HUS Investigation Team. Epidemic profile of Shiga-toxin-producing Escherichia coli O104:H4 outbreak in Germany. N Engl J Med. 2011; 365:1771–1780.
Article13. Funk J, Stoeber H, Hauser E, Schmidt H. Molecular analysis of subtilase cytotoxin genes of food-borne Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli reveals a new allelic subAB variant. BMC Microbiol. 2013; 13:230.14. Gill A, Gill CO. Non-O157 verotoxigenic Escherichia coli and beef: a Canadian perspective. Can J Vet Res. 2010; 74:161–169.15. Heiman KE, Mody RK, Johnson SD, Griffin PM, Gould LH. Escherichia coli O157 outbreaks in the United States, 2003–2012. Emerg Infect Dis. 2015; 21:1293–1301.16. Ito H, Terai A, Kurazono H, Takeda Y, Nishibuchi M. Cloning and nucleotide sequencing of Vero toxin 2 variant genes from Escherichia coli O91:H21 isolated from a patient with the hemolytic uremic syndrome. Microb Pathog. 1990; 8:47–60.
Article17. Janka A, Bielaszewska M, Dobrindt U, Greune L, Schmidt MA, Karch H. Cytolethal distending toxin gene cluster in enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H- and O157:H7: characterization and evolutionary considerations. Infect Immun. 2003; 71:3634–3638.
Article18. Kalchayanand N, Arthur TM, Bosilevac JM, Brichta-Harhay DM, Guerini MN, Shackelford SD, Wheeler TL, Koohmaraie M. Microbiological characterization of lamb carcasses at commercial processing plants in the United States. J Food Prot. 2007; 70:1811–1819.
Article19. Kobayashi H, Shimada J, Nakazawa M, Morozumi T, Pohjanvirta T, Pelkonen S, Yamamoto K. Prevalence and characteristics of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli from healthy cattle in Japan. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2001; 67:484–489.
Article20. Korth MJ, Lara JC, Moseley SL. Epithelial cell invasion by bovine septicemic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1994; 62:41–47.
Article21. Kudva IT, Krastins B, Torres AG, Griffin RW, Sheng H, Sarracino DA, Hovde CJ, Calderwood SB, John M. The Escherichia coli O157:H7 cattle immunoproteome includes outer membrane protein A (OmpA), a modulator of adherence to bovine rectoanal junction squamous epithelial (RSE) cells. Proteomics. 2015; 15:1829–1842.
Article22. Lee JC, Kim MJ. Epidemiological analysis of Shiga toxin-producing E. coli isolated in Gwangju, Korea, by pulse-field gel electrophoresis. J Bacteriol Virol. 2009; 39:195–203.
Article23. Luna-Gierke RE, Griffin PM, Gould LH, Herman K, Bopp CA, Strockbine N, Mody RK. Outbreaks of non-O157 Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli infection: USA. Epidemiol Infect. 2014; 142:2270–2280.24. Maeda E, Murakami K, Etoh Y, Onozuka D, Sera N, Asoshima N, Honda M, Narimatsu H, Iyoda S, Watahiki M, Fujimoto S. Does sequence type 33 of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli O91 cause only mild symptoms? J Clin Microbiol. 2015; 53:362–364.
Article25. Mellmann A, Fruth A, Friedrich AW, Wieler LH, Harmsen D, Werber D, Middendorf B, Bielaszewska M, Karch H. Phylogeny and disease association of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli O91. Emerg Infect Dis. 2009; 15:1474–1477.
Article26. Mora A, Herrrera A, López C, Dahbi G, Mamani R, Pita JM, Alonso MP, Llovo J, Bernárdez MI, Blanco JE, Blanco M, Blanco J. Characteristics of the Shiga-toxin-producing enteroaggregative Escherichia coli O104:H4 German outbreak strain and of STEC strains isolated in Spain. Int Microbiol. 2011; 14:121–141.27. Park HJ, Yoon JW, Heo EJ, Ko EK, Kim KY, Kim YJ, Yoon HJ, Wee SH, Park YH, Moon JS. Antibiotic resistance and virulence potentials of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli isolates from raw meats of slaughterhouses and retail markets in Korea. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2015; 25:1460–1466.
Article28. Paton AW, Paton JC. Detection and characterization of Shiga toxigenic Escherichia coli by using multiplex PCR assays for stx1, stx2, eaeA, enterohemorrhagic E. coli hlyA, rfbO111, and rfbO157. J Clin Microbiol. 1998; 36:598–602.29. Paton AW, Paton JC. Direct detection and characterization of Shiga toxigenic Escherichia coli by multiplex PCR for stx1, stx2, eae, ehxA, and saa. J Clin Microbiol. 2002; 40:271–274.30. Paton AW, Srimanote P, Woodrow MC, Paton JC. Characterization of Saa, a novel autoagglutinating adhesin produced by locus of enterocyte effacement-negative Shiga-toxigenic Escherichia coli strains that are virulent for humans. Infect Immun. 2001; 69:6999–7009.
Article31. Rendón MA, Saldaña Z, Erdem AL, Monteiro-Neto V, Vázquez A, Kaper JB, Puente JL, Girón JA. Commensal and pathogenic Escherichia coli use a common pilus adherence factor for epithelial cell colonization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007; 104:10637–10642.
Article32. Rhoades JR, Duffy G, Koutsoumanis K. Prevalence and concentration of verocytotoxigenic Escherichia coli, Salmonella enterica and Listeria monocytogenes in the beef production chain: a review. Food Microbiol. 2009; 26:357–376.
Article33. Riley LW, Remis RS, Helgerson SD, McGee HB, Wells JG, Davis BR, Hebert RJ, Olcott ES, Johnson LM, Hargrett NT, Blake PA, Cohen ML. Hemorrhagic colitis associated with a rare Escherichia coli serotype. N Engl J Med. 1983; 308:681–685.
Article34. Scheutz F, Teel LD, Beutin L, Piérard D, Buvens G, Karch H, Mellmann A, Caprioli A, Tozzoli R, Morabito S, Strockbine NA, Melton-Celsa AR, Sanchez M, Persson S, O'Brien AD. Multicenter evaluation of a sequence-based protocol for subtyping Shiga toxins and standardizing Stx nomenclature. J Clin Microbiol. 2012; 50:2951–2963.
Article35. Schmidt H, Zhang WL, Hemmrich U, Jelacic S, Brunder W, Tarr PI, Dobrindt U, Hacker J, Karch H. Identification and characterization of a novel genomic island integrated at selC in locus of enterocyte effacement-negative, Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 2001; 69:6863–6873.
Article36. Tarr PI, Bilge SS, Vary JC Jr, Jelacic S, Habeeb RL, Ward TR, Baylor MR, Besser TE. Iha: a novel Escherichia coli O157:H7 adherence-conferring molecule encoded on a recently acquired chromosomal island of conserved structure. Infect Immun. 2000; 68:1400–1407.
Article37. Terajima J, Iyoda S, Ohnishi M, Watanabe H. Shiga toxin (verotoxin)-producing Escherichia coli in Japan. Microbiol Spectr. 2014; 2.
Article38. Tzipori S, Karch H, Wachsmuth KI, Robins-Browne RM, O'Brien AD, Lior H, Cohen ML, Smithers J, Levine MM. Role of a 60-megadalton plasmid and Shiga-like toxins in the pathogenesis of infection caused by enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7 in gnotobiotic piglets. Infect Immun. 1987; 55:3117–3125.
Article39. Werber D, Beutin L, Pichner R, Stark K, Fruth A. Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli serogroups in food and patients, Germany. Emerg Infect Dis. 2008; 14:1803–1806.
Article40. Wirth T, Falush D, Lan R, Colles F, Mensa P, Wieler LH, Karch H, Reeves PR, Maiden MC, Ochman H, Achtman M. Sex and virulence in Escherichia coli: an evolutionary perspective. Mol Microbiol. 2006; 60:1136–1151.
Article41. Yoon JW, Hovde CJ. All blood, no stool: enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7 infection. J Vet Sci. 2008; 9:219–231.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Molecular epidemiology of sequence type 33 of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli O91:H14 isolates from human patients and retail meats in Korea
- Detection of Escherichia coli O157 and Escherichia coli O157:H7 by the immunomagnetic separation technique and stx1 and stx2 genes by multiplex PCR in slaughtered cattle in Samsun Province, Turkey
- A Case of Escherichia coli O157 Hemorrhagic Colitis
- Isolation of Escherichia coli O157 in Children with Diarrhea
- A Case of Escherichia coli O157 and Campylobacter species Gastroenteritis