J Breast Cancer.
2015 Sep;18(3):264-270. 10.4048/jbc.2015.18.3.264.
Association between Metformin Therapy and Breast Cancer Incidence and Mortality: Evidence from a Meta-Analysis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing, China. liushengchun1968@126.com
- 2Department of Cardiovascular Medicine, The First Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing, China.
- KMID: 2407574
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4048/jbc.2015.18.3.264
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Metformin may be associated with a decreased risk of breast cancer. We performed a meta-analysis to assess the effect of metformin intake on breast cancer risk and mortality.
METHODS
We performed a PubMed and EMbase search for all available studies that described the risk of breast cancer and all-cause mortality in relation to the use of metformin among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Pooled relative risks (RRs) were determined using a random effects model to assess the strength of association between metformin and the risk of breast cancer.
RESULTS
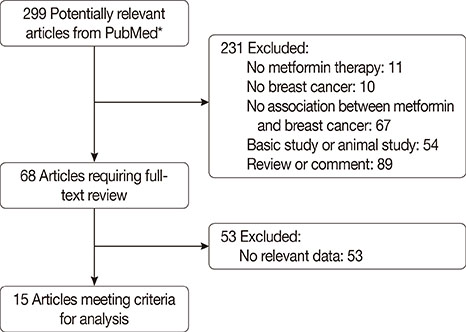
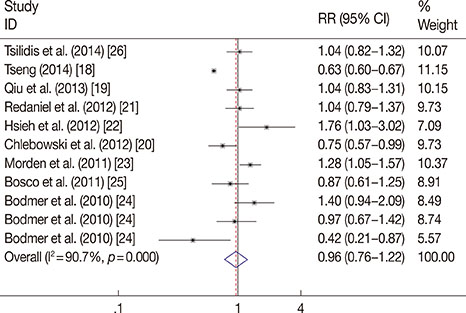
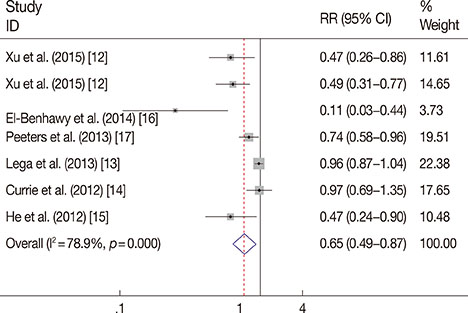
Fifteen articles from PubMed satisfied the inclusion criteria, including a total of 838,333 participants. Compared with the control group, metformin use was not related to a reduced incidence of breast cancer (RR, 0.964; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.761-1.221; p=0.761). However, metformin therapy was associated with decreased all-cause mortality (RR, 0.652; 95% CI, 0.488-0.873; p=0.004). No obvious publication bias was detected (incidence: p(Begg)=0.755, p(Egger)=0.008; mortality: p(Begg)=0.072, p(Egger)=0.185).
CONCLUSION
The present study suggested that metformin therapy may decrease the all-cause mortality of patients affected by breast cancer. However, this finding should be considered carefully and confirmed with further studies.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 2015; 136:E359–E386.
Article2. Garg SK, Maurer H, Reed K, Selagamsetty R. Diabetes and cancer: two diseases with obesity as a common risk factor. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2014; 16:97–110.
Article3. Ben Sahra I, Laurent K, Loubat A, Giorgetti-Peraldi S, Colosetti P, Auberger P, et al. The antidiabetic drug metformin exerts an antitumoral effect in vitro and in vivo through a decrease of cyclin D1 level. Oncogene. 2008; 27:3576–3586.
Article4. Kim J, Lim W, Kim EK, Kim MK, Paik NS, Jeong SS, et al. Phase II randomized trial of neoadjuvant metformin plus letrozole versus placebo plus letrozole for estrogen receptor positive postmenopausal breast cancer (METEOR). BMC Cancer. 2014; 14:170.
Article5. Oppong BA, Pharmer LA, Oskar S, Eaton A, Stempel M, Patil S, et al. The effect of metformin on breast cancer outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. Cancer Med. 2014; 3:1025–1034.
Article6. Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG. PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009; 6:e1000097.
Article7. Wells GA, Shea B, O'Connell D, Peterson J, Welch V, Losos M, et al. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Ottawa Hospital Research Institute;c2014. Accessed January 19th, 2014. http://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.htm.8. Wang T. The link between Parkinson's disease and breast and prostate cancers: a meta-analysis. Int J Neurosci. 2014; 12. 18. Epub. DOI: 10.3109/00207454.2014.986265.
Article9. Overton RC. A comparison of fixed-effects and mixed (random-effects) models for meta-analysis tests of moderator variable effects. Psychol Methods. 1998; 3:354–379.
Article10. Egger M, Davey Smith G, Schneider M, Minder C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ. 1997; 315:629–634.
Article11. Begg CB, Mazumdar M. Operating characteristics of a rank correlation test for publication bias. Biometrics. 1994; 50:1088–1101.
Article12. Xu H, Aldrich MC, Chen Q, Liu H, Peterson NB, Dai Q, et al. Validating drug repurposing signals using electronic health records: a case study of metformin associated with reduced cancer mortality. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2015; 22:179–191.
Article13. Lega IC, Austin PC, Gruneir A, Goodwin PJ, Rochon PA, Lipscombe LL. Association between metformin therapy and mortality after breast cancer: a population-based study. Diabetes Care. 2013; 36:3018–3026.
Article14. Currie CJ, Poole CD, Jenkins-Jones S, Gale EA, Johnson JA, Morgan CL. Mortality after incident cancer in people with and without type 2 diabetes: impact of metformin on survival. Diabetes Care. 2012; 35:299–304.
Article15. He X, Esteva FJ, Ensor J, Hortobagyi GN, Lee MH, Yeung SC. Metformin and thiazolidinediones are associated with improved breast cancer-specific survival of diabetic women with HER2+ breast cancer. Ann Oncol. 2012; 23:1771–1780.
Article16. El-Benhawy SA, El-Sheredy HG. Metformin and survival in diabetic patients with breast cancer. J Egypt Public Health Assoc. 2014; 89:148–153.
Article17. Peeters PJ, Bazelier MT, Vestergaard P, Leufkens HG, Schmidt MK, de Vries F, et al. Use of metformin and survival of diabetic women with breast cancer. Curr Drug Saf. 2013; 8:357–363.
Article18. Tseng CH. Metformin may reduce breast cancer risk in Taiwanese women with type 2 diabetes. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2014; 145:785–790.
Article19. Qiu H, Rhoads GG, Berlin JA, Marcella SW, Demissie K. Initial metformin or sulphonylurea exposure and cancer occurrence among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2013; 15:349–357.
Article20. Chlebowski RT, McTiernan A, Wactawski-Wende J, Manson JE, Aragaki AK, Rohan T, et al. Diabetes, metformin, and breast cancer in postmenopausal women. J Clin Oncol. 2012; 30:2844–2852.
Article21. Redaniel MT, Jeffreys M, May MT, Ben-Shlomo Y, Martin RM. Associations of type 2 diabetes and diabetes treatment with breast cancer risk and mortality: a population-based cohort study among British women. Cancer Causes Control. 2012; 23:1785–1795.22. Hsieh MC, Lee TC, Cheng SM, Tu ST, Yen MH, Tseng CH. The influence of type 2 diabetes and glucose-lowering therapies on cancer risk in the Taiwanese. Exp Diabetes Res. 2012; 2012:413782.
Article23. Morden NE, Liu SK, Smith J, Mackenzie TA, Skinner J, Korc M. Further exploration of the relationship between insulin glargine and incident cancer: a retrospective cohort study of older Medicare patients. Diabetes Care. 2011; 34:1965–1971.
Article24. Bodmer M, Meier C, Krähenbühl S, Jick SS, Meier CR. Long-term metformin use is associated with decreased risk of breast cancer. Diabetes Care. 2010; 33:1304–1308.25. Bosco JL, Antonsen S, Sørensen HT, Pedersen L, Lash TL. Metformin and incident breast cancer among diabetic women: a population-based case-control study in Denmark. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2011; 20:101–111.
Article26. Tsilidis KK, Capothanassi D, Allen NE, Rizos EC, Lopez DS, van Veldhoven K, et al. Metformin does not affect cancer risk: a cohort study in the U.K. Clinical Practice Research Datalink analyzed like an intention-to-treat trial. Diabetes Care. 2014; 37:2522–2532.
Article27. Xiao Y, Zhang S, Hou G, Zhang X, Hao X, Zhang J. Clinical pathological characteristics and prognostic analysis of diabetic women with luminal subtype breast cancer. Tumour Biol. 2014; 35:2035–2045.28. Hou G, Zhang S, Zhang X, Wang P, Hao X, Zhang J. Clinical pathological characteristics and prognostic analysis of 1,013 breast cancer patients with diabetes. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2013; 137:807–816.
Article29. Aguilar D, Chan W, Bozkurt B, Ramasubbu K, Deswal A. Metformin use and mortality in ambulatory patients with diabetes and heart failure. Circ Heart Fail. 2011; 4:53–58.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effects of Metformin on Breast Cancer Risk and Mortality in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
- Anticancer effects of metformin in experimental animal models of different types of cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- The Metformin Use and Gastric Cancer Risk
- Light Alcohol Drinking and Risk of Cancer: A Meta-Analysis of Cohort Studies
- National Guidelines for Breast Cancer Screening