Endocrinol Metab.
2015 Sep;30(3):297-304. 10.3803/EnM.2015.30.3.297.
Limited Diagnostic Utility of Plasma Adrenocorticotropic Hormone for Differentiation between Adrenal Cushing Syndrome and Cushing Disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. seongyk@plaza.snu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2407080
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2015.30.3.297
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Measurement of the plasma adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) level has been recommended as the first diagnostic test for differentiating between ACTH-independent Cushing syndrome (CS) and ACTH-dependent CS. When plasma ACTH values are inconclusive, a differential diagnosis of CS can be made based upon measurement of the serum dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate (DHEA-S) level and results of the high-dose dexamethasone suppression test (HDST). The aim of this study was to assess the utility of plasma ACTH to differentiate adrenal CS from Cushing' disease (CD) and compare it with that of the HDST results and serum DHEA-S level.
METHODS
We performed a retrospective, multicenter study from January 2000 to May 2012 involving 92 patients with endogenous CS. The levels of plasma ACTH, serum cortisol, 24-hour urine free cortisol (UFC) after the HDST, and serum DHEA-S were measured.
RESULTS
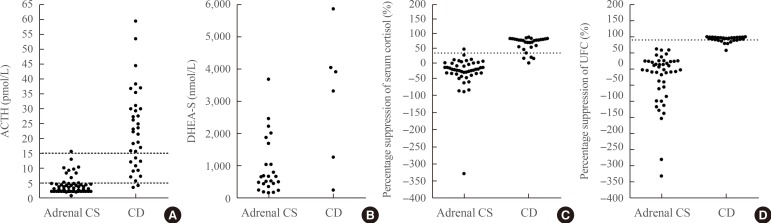
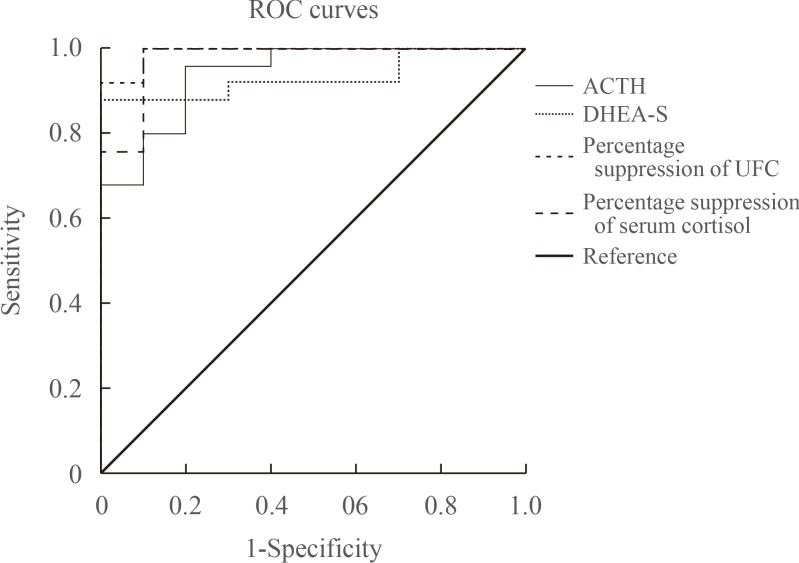
Fifty-seven patients had adrenal CS and 35 patients had CD. The area under the curve of plasma ACTH, serum DHEA-S, percentage suppression of serum cortisol, and UFC after HDST were 0.954, 0.841, 0.950, and 0.997, respectively (all P<0.001). The cut-off values for plasma ACTH, percentage suppression of serum cortisol, and UFC after HDST were 5.3 pmol/L, 33.3%, and 61.6%, respectively. The sensitivity and specificity of plasma ACTH measurement were 84.2% and 94.3%, those of serum cortisol were 95.8% and 90.6%, and those of UFC after the HDST were 97.9% and 96.7%, respectively.
CONCLUSION
Significant overlap in plasma ACTH levels was seen between patients with adrenal CS and those with CD. The HDST may be useful in differentiating between these forms of the disease, especially when the plasma ACTH level alone is not conclusive.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adrenocorticotropic Hormone*
Cushing Syndrome*
Dehydroepiandrosterone Sulfate
Dexamethasone
Diagnosis, Differential
Diagnostic Tests, Routine
Humans
Hydrocortisone
Pituitary ACTH Hypersecretion*
Plasma*
Retrospective Studies
Sensitivity and Specificity
Adrenocorticotropic Hormone
Dehydroepiandrosterone Sulfate
Dexamethasone
Hydrocortisone
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Clinical and Molecular Characteristics of
PRKACA L206R Mutant Cortisol-Producing Adenomas in Korean Patients
Insoon Jang, Su-jin Kim, Ra-Young Song, Kwangsoo Kim, Seongmin Choi, Jang-Seok Lee, Min-Kyeong Gwon, Moon Woo Seong, Kyu Eun Lee, Jung Hee Kim
Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(6):1287-1297. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2021.1217.
Reference
-
1. Pecori Giraldi F. Recent challenges in the diagnosis of Cushing's syndrome. Horm Res. 2009; 71(Suppl 1):123–127. PMID: 19153521.
Article2. Kuhn JM, Proeschel MF, Seurin DJ, Bertagna XY, Luton JP, Girard FL. Comparative assessment of ACTH and lipotropin plasma levels in the diagnosis and follow-up of patients with Cushing's syndrome: a study of 210 cases. Am J Med. 1989; 86(6 Pt 1):678–684. PMID: 2543219.
Article3. Nieman LK, Chrousos GP, Oldfield EH, Avgerinos PC, Cutler GB Jr, Loriaux DL. The ovine corticotropin-releasing hormone stimulation test and the dexamethasone suppression test in the differential diagnosis of Cushing's syndrome. Ann Intern Med. 1986; 105:862–867. PMID: 3022629.
Article4. Vogeser M, Engelhardt D, Jacob K. Comparison of two automated adrenocorticotropic hormone assays. Clin Chem. 2000; 46:1998–2000. PMID: 11106336.
Article5. Howe LA, Smeaton T. Anomalous results with the CIS-Sorin adrenocorticotrophic hormone radioimmunoassay kit. Clin Chem. 1979; 25:816–817. PMID: 219967.
Article6. Pecori Giraldi F, Saccani A, Cavagnini F. Study Group on the Hypothalamo-Pituitary-Adrenal Axis of the Italian Society of Endocrinology. Assessment of ACTH assay variability: a multicenter study. Eur J Endocrinol. 2011; 164:505–512. PMID: 21252174.
Article7. Newell-Price J, Perry L, Medbak S, Monson J, Savage M, Besser M, et al. A combined test using desmopressin and corticotropin-releasing hormone in the differential diagnosis of Cushing's syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1997; 82:176–181. PMID: 8989255.
Article8. al-Saadi N, Diederich S, Oelkers W. A very high dose dexamethasone suppression test for differential diagnosis of Cushing's syndrome. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 1998; 48:45–51. PMID: 9509067.
Article9. Kaye TB, Crapo L. The Cushing syndrome: an update on diagnostic tests. Ann Intern Med. 1990; 112:434–444. PMID: 2178536.
Article10. Aron DC, Raff H, Findling JW. Effectiveness versus efficacy: the limited value in clinical practice of high dose dexamethasone suppression testing in the differential diagnosis of adrenocorticotropin-dependent Cushing's syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1997; 82:1780–1785. PMID: 9177382.
Article11. Arnaldi G, Angeli A, Atkinson AB, Bertagna X, Cavagnini F, Chrousos GP, et al. Diagnosis and complications of Cushing's syndrome: a consensus statement. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2003; 88:5593–5602. PMID: 14671138.
Article12. Barbetta L, Dall'Asta C, Re T, Colombo P, Travaglini P, Ambrosi B. Androgen secretion in ectopic ACTH syndrome and in Cushing's disease: modifications before and after surgery. Horm Metab Res. 2001; 33:596–601. PMID: 11607879.
Article13. Yamaji T, Ishibashi M, Sekihara H, Itabashi A, Yanaihara T. Serum dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate in Cushing's syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1984; 59:1164–1168. PMID: 6238041.
Article14. Kleiber H, Rey F, Temler E, Gomez F. Dissociated recovery of cortisol and dehydroepiandrosterone sulphate after treatment for Cushing's syndrome. J Endocrinol Invest. 1991; 14:489–492. PMID: 1663528.
Article15. Gilbert R, Lim EM. The diagnosis of Cushing's syndrome: an endocrine society clinical practice guideline. Clin Biochem Rev. 2008; 29:103–106. PMID: 19107223.16. Schisterman EF, Perkins NJ, Liu A, Bondell H. Optimal cut-point and its corresponding Youden Index to discriminate individuals using pooled blood samples. Epidemiology. 2005; 16:73–81. PMID: 15613948.
Article17. Klose M, Kofoed-Enevoldsen A, Ostergaard Kristensen L. Single determination of plasma ACTH using an immunoradiometric assay with high detectability differentiates between ACTH-dependent and -independent Cushing's syndrome. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 2002; 62:33–37. PMID: 12002411.
Article18. Invitti C, Pecori Giraldi F, de Martin M, Cavagnini F. Diagnosis and management of Cushing's syndrome: results of an Italian multicentre study. Study Group of the Italian Society of Endocrinology on the Pathophysiology of the Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal Axis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1999; 84:440–448. PMID: 10022398.19. Oldfield EH, Doppman JL, Nieman LK, Chrousos GP, Miller DL, Katz DA, et al. Petrosal sinus sampling with and without corticotropin-releasing hormone for the differential diagnosis of Cushing's syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1991; 325:897–905. PMID: 1652686.
Article20. The Korean Society of Endocrinology. The Survey Committee for Endocrine Disease in Korea. The incidence and clinical characteristics of Cushing's syndrome in Korea. J Korean Soc Endocrinol. 2000; 15:31–45.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A case of pseudo-Cushing's syndrome with unilateral nonfunctioning adrenal adenoma
- A Case of Persistent Cushing's Syndrome
- A Case of Carney Complex with Multiple Spinal Fractures
- Clinical Usefulness of Corticotropin Releasing Hormone Testing in Subclinical Cushing's Syndrome for Predicting Cortisol Replacement after Adrenalectomy
- Adrenocorticotropic Hormone-Independent Cushing Syndrome with Bilateral Cortisol-Secreting Adenomas