Pediatr Infect Vaccine.
2017 Aug;24(2):79-86. 10.14776/piv.2017.24.2.79.
Serotype Distribution of Invasive Group B Streptococcal Diseases in Infants at Two University Hospitals in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Gachon University College of Medicine, Incheon, the Republic of Korea.
- 2Division of Infection, Department of Internal Medicine, Gachon University College of Medicine, Incheon, the Republic of Korea.
- 3Department of Laboratory Medicine, Gachon University College of Medicine, Incheon, the Republic of Korea.
- 4Department of Pediatrics, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, the Republic of Korea.
- 5Department of Pediatrics, Nowon Eulji Medical Center, Eulji University School of Medicine, Seoul, the Republic of Korea. acet0125@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2401448
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14776/piv.2017.24.2.79
Abstract
- PURPOSE
This study was aimed at analyzing the serotypes of group B streptococcus (GBS) isolated from Korean infants with invasive disease and evaluating their association with disease manifestation.
METHODS
Data were retrospectively collected from invasive GBS infections at Gachon University Gil Medical Center from January 2006 to June 2012 and at Samsung Medical Center from April 2010 to November 2012. Serotypes were determined by slide agglutination test.
RESULTS
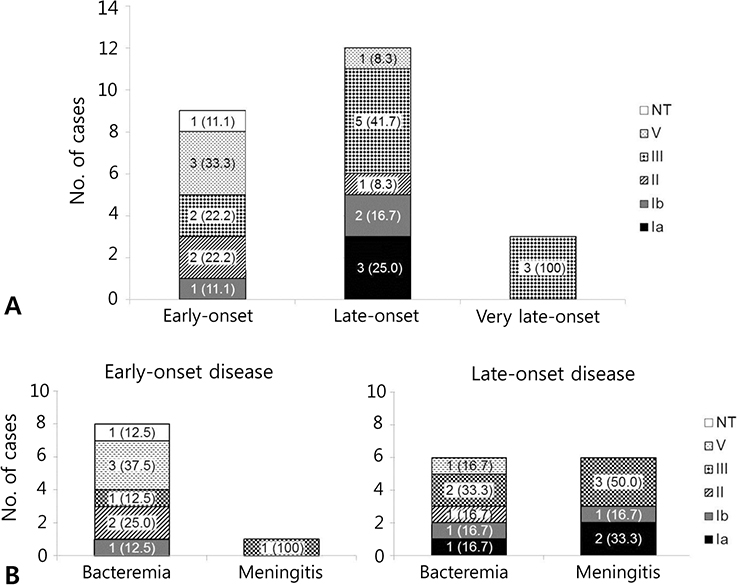
A total of 37 cases were identified, which included 22 full-term infants and 15 preterm infants. Fifteen cases (40.5%) were early-onset, 19 (51.4%) was late-onset, and three (8.1%) was very late-onset. Early-onset diseases among preterm infants were higher than those among full-term infants (60.0% [9/15] vs. 27.3% [6/22], P =0.17). The most common manifestation was bacteremia (70.3%), followed by meningitis and septic arthritis. Among 24 isolates retrievable for serotyping, serotype III (41.7%) was most common, followed by V (16.7%), Ia, Ib, and II (12.5%, respectively), and non-typeable (4.2%). Serotype III was more common in isolates from full-term infants (10/22) than from preterm infants (0/15), whereas serotype V was more common in isolates from preterm infants (4/15) than from full-term infants (0/22) (P =0.002). No penicillin-resistant strain was detected, and resistance to erythromycin and clindamycin were both 64.9%.
CONCLUSIONS
GBS is an important pathogen in both preterm and full-term infants, and serotype distribution of GBS causing invasive diseases can differ between preterm and full-term infants. It is necessary to monitor the nationwide epidemiology of GBS diseases, including in preterm infants, in order to prepare preventive measures without underestimating early-onset diseases.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Late-Onset Group B Streptococcal Meningitis Complicated with Extensive Cerebral Infarction
Min Su Cho, Yongmin Kim, Hye-Kyung Cho, Soo-Han Choi
Pediatr Infect Vaccine. 2018;25(1):45-49. doi: 10.14776/piv.2018.25.1.45.국내 3차 의료기관에서의 신생아 조기 발병 B군 사슬알균 감염증 역학: 2001-2022년, 22년간의 종단 연구
Hyeongyu Lee, Kwangjin Ahn, Jieun Kang, Seong Jin Choi, Yeong Myong Yoo, Young Uh
Lab Med Online. 2025;15(1):78-83. doi: 10.47429/lmo.2025.15.1.78.
Reference
-
1. Lachenauer CS, Wessels MR. Group B streptococcus. In : Kliegman RM, Stanton BF, St Geme JW, Schor NF, editors. Nelson textbook of pediatrics. 20th ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier;2015. p. 1337–1341.2. Kim KH, Sohn YM, Kang JH, Kim KN, Kim DS, Kim JH, et al. The causative organisms of bacterial meningitis in Korean children, 1986–1995. J Korean Med Sci. 1998; 13:60–64.
Article3. Cho HK, Lee H, Kang JH, Kim KN, Kim DS, Kim YK, et al. The causative organisms of bacterial meningitis in Korean children in 1996–2005. J Korean Med Sci. 2010; 25:895–899.
Article4. Edmond KM, Kortsalioudaki C, Scott S, Schrag SJ, Zaidi AK, Cousens S, et al. Group B streptococcal disease in infants aged younger than 3 months: systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet. 2012; 379:547–556.
Article5. Rivera L, Saez-Llorens X, Feris-Iglesias J, Ip M, Saha S, Adrian PV, et al. Incidence and serotype distribution of invasive group B streptococcal disease in young infants: a multicountry observational study. BMC Pediatr. 2015; 15:143.
Article6. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Perinatal group B streptococcal disease after universal screening recommendations: United States, 2003–2005. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2007; 56:701–705.7. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Trends in perinatal group B streptococcal disease: United States, 2000–2006. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2009; 58:109–112.8. Puopolo KM. Current status of vaccine development for group B streptococcus. NeoReviews. 2014; 15:e430–e438.
Article9. Melin P, Efstratiou A. Group B streptococcal epidemiology and vaccine needs in developed countries. Vaccine. 2013; 31:Suppl 4. D31–D42.
Article10. Park KH, Kim KH, Kang JH, Kim KN, Kim DS, Kim YK, et al. Current status and clinical presentations of invasive neonatal group B streptococcal infections in Korea. Pediatr Int. 2011; 53:236–239.
Article11. Lee JH, Cho HK, Kim KH, Kim CH, Kim DS, Kim KN, et al. Etiology of invasive bacterial infections in immunocompetent children in Korea (1996–2005): a retrospective multicenter study. J Korean Med Sci. 2011; 26:174–183.
Article12. Bekker V, Bijlsma MW, van de Beek D, Kuijpers TW, van der Ende A. Incidence of invasive group B streptococcal disease and pathogen genotype distribution in newborn babies in the Netherlands over 25 years: a nationwide surveillance study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2014; 14:1083–1089.
Article13. Manning SD, Springman AC, Lehotzky E, Lewis MA, Whittam TS, Davies HD. Multilocus sequence types associated with neonatal group B streptococcal sepsis and meningitis in Canada. J Clin Microbiol. 2009; 47:1143–1148.
Article14. Matsubara K, Hoshina K, Suzuki Y. Early-onset and lateonset group B streptococcal disease in Japan: a nationwide surveillance study, 2004–2010. Int J Infect Dis. 2013; 17:e379–e384.
Article15. Benitz WE, Gould JB, Druzin ML. Risk factors for early-onset group B streptococcal sepsis: estimation of odds ratios by critical literature review. Pediatrics. 1999; 103:e77.
Article16. Allen U, Nimrod C, Macdonald N, Toye B, Stephens D, Marchessault V. Relationship between antenatal group B streptococcal vaginal colonization and premature labour. Paediatr Child Health. 1999; 4:465–469.
Article17. Minakami H, Hiramatsu Y, Koresawa M, Fujii T, Hamada H, Iitsuka Y, et al. Guidelines for obstetrical practice in Japan: Japan Society of Obstetrics and Gynecology (JSOG) and Japan Association of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (JAOG) 2011 edition. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2011; 37:1174–1197.
Article18. Di Renzo GC, Melin P, Berardi A, Blennow M, Carbonell-Estrany X, Donzelli GP, et al. Intrapartum GBS screening and antibiotic prophylaxis: a European consensus conference. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2015; 28:766–782.
Article19. Money DM, Dobson S. Canadian Paediatric Society. Infectious Diseases Commitee. The prevention of early-onset neonatal group B streptococcal disease. J Obstet Gynaecol Can. 2004; 26:826–840.
Article20. Darlow B, Campbell N, Austin N, Chin A, Grigg C, Skidmore C, et al. The prevention of early-onset neonatal group B streptococcus infection: New Zealand Consensus Guidelines 2014. N Z Med J. 2015; 128:69–76.21. South Australian Maternal and Neonatal Clinical Network. South Australian Perinatal Practice Guidelines: neonatal sepsis (including maternal group B streptococcal colonisation) [Internet]. Adelaide: South Australian Health;c2012. cited Jun 29. Available from: http://www.sahealth.sa.gov.au/wps/wcm/connect/35cac4804ee510ca997f9dd150ce4f37/Neonatal+sepsis_June2014.pdf?MOD=AJPERES&CACHEID=35cac4804ee510ca997f9dd150ce4f37.22. Barcaite E, Bartusevicius A, Tameliene R, Kliucinskas M, Maleckiene L, Nadisauskiene R. Prevalence of maternal group B streptococcal colonisation in European countries. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2008; 87:260–271.
Article23. Lee BK, Song YR, Kim MY, Yang JH, Shin JH, Seo YS, et al. Epidemiology of group B streptococcus in Korean pregnant women. Epidemiol Infect. 2010; 138:292–298.
Article24. Hickman ME, Rench MA, Ferrieri P, Baker CJ. Changing epidemiology of group B streptococcal colonization. Pediatrics. 1999; 104(2 Pt 1):203–209.
Article25. Hong JS, Choi CW, Park KU, Kim SN, Lee HJ, Lee HR, et al. Genital group B streptococcus carrier rate and serotype distribution in Korean pregnant women: implications for group B streptococcal disease in Korean neonates. J Perinat Med. 2010; 38:373–377.
Article26. Uh Y, Jang IH, Yoon KJ, Lee CH, Kwon JY, Kim MC. Colonization rates and serotypes of group B streptococci isolated from pregnant women in a Korean tertiary hospital. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1997; 16:753–756.
Article27. Park JS, Cho DH, Yang JH, Kim MY, Shin SM, Kim EC, et al. Usefulness of a rapid real-time PCR assay in prenatal screening for group B streptococcus colonization. Ann Lab Med. 2013; 33:39–44.
Article28. Kim EJ, Oh KY, Kim MY, Seo YS, Shin JH, Song YR, et al. Risk factors for group B streptococcus colonization among pregnant women in Korea. Epidemiol Health. 2011; 33:e2011010.
Article29. Yoon IA, Jo DS, Cho EY, Choi EH, Lee HJ, Lee H. Clinical significance of serotype V among infants with invasive group B streptococcal infections in South Korea. Int J Infect Dis. 2015; 38:136–140.
Article30. Johri AK, Lata H, Yadav P, Dua M, Yang Y, Xu X, et al. Epidemiology of group B streptococcus in developing countries. Vaccine. 2013; 31:Suppl 4. D43–D45.
Article31. Ferrieri P, Lynfield R, Creti R, Flores AE. Serotype IV and invasive group B Streptococcus disease in neonates, Minnesota, USA, 2000–2010. Emerg Infect Dis. 2013; 19:551–558.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Analysis for Group B Streptococci Isolated from Bacteremic Patients
- Group B Streptococcal Disease in Korean Neonates
- Clinical study of group B streptococcal infection in infants less than two months of age
- Seroprevalence of Opsonophagocytic Antibodies against Serotype Ia, Ib, II, III, and V Group B Streptococcus among Korean Population
- Direct and Indirect Effects of Pneumococcal Protein Conjugate Vaccine