Korean J Pain.
2018 Jan;31(1):50-53. 10.3344/kjp.2018.31.1.50.
Transient paraplegia after neurolytic splanchnic block in a patient with metastatic colon carcinoma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology, Pain and Palliative Care Clinic, Dr AY Ankara Oncology Education and Research Hospital, Ankara, Turkey. goncatuncel@hotmail.com
- KMID: 2400908
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2018.31.1.50
Abstract
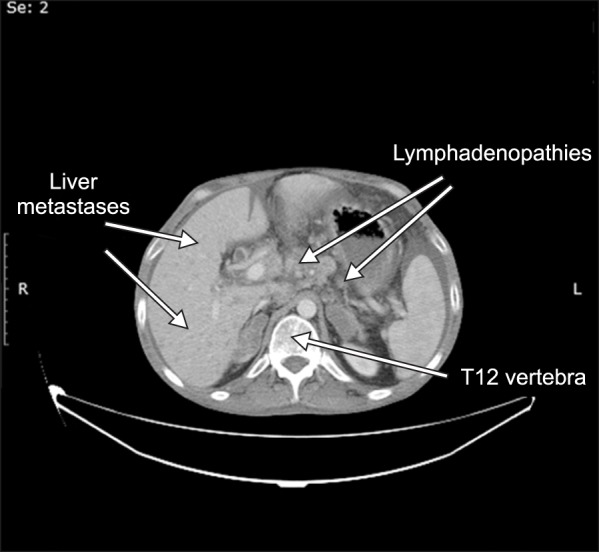
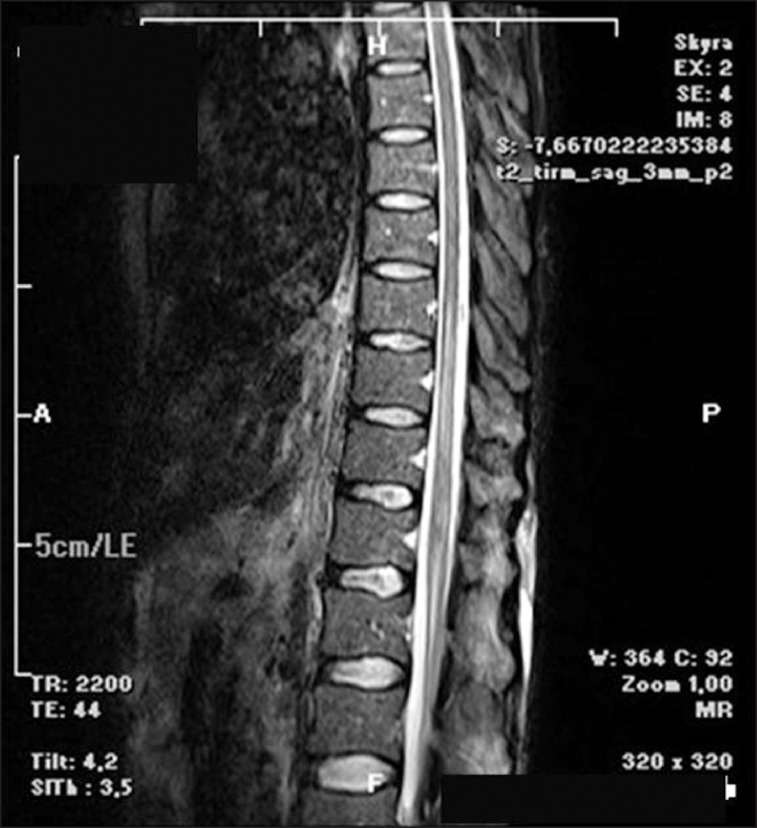
- We present a patient with metastatic colon carcinoma who developed paraplegia following a neurolytic splanchnic block. A 41-year old man with metastatic adenocarcinoma of the colon received a splanchnic neurolytic block using alcohol because of severe abdominal pain. Bilateral motor weakness and a sensorial deficit in both legs developed after the procedure. Diffusion magnetic resonance imaging revealed spinal cord ischemia between T8 and L1. The motor and sensorial deficits were almost completely resolved at the end of the third month. We think that anterior spinal artery syndrome due to reversible spasms of the lumbar radicular arteries using alcohol have resulted in transient paraplegia. The retrograde spread of alcohol to neural structures may have also contributed.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Splanchnic nerve neurolysis via the transdiscal approach under fluoroscopic guidance: a retrospective study
Zhenhua Cai, Xiaolin Zhou, Mengli Wang, Jiyu Kang, Mingshuo Zhang, Huacheng Zhou
Korean J Pain. 2022;35(2):202-208. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2022.35.2.202.
Reference
-
1. Vargas-Schaffer G. Is the WHO analgesic ladder still valid? Twenty-four years of experience. Can Fam Physician. 2010; 56:514–517. PMID: 20547511.2. Mercadante S, Catala E, Arcuri E, Casuccio A. Celiac plexus block for pancreatic cancer pain: factors influencing pain, symptoms and quality of life. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2003; 26:1140–1147. PMID: 14654266.
Article3. Süleyman Ozyalçin N, Talu GK, Camlica H, Erdine S. Efficacy of coeliac plexus and splanchnic nerve blockades in body and tail located pancreatic cancer pain. Eur J Pain. 2004; 8:539–545. PMID: 15531222.
Article4. Papadopoulos D, Kostopanagiotou G, Batistaki C. Bilateral thoracic splanchnic nerve radiofrequency thermocoagulation for the management of end-stage pancreatic abdominal cancer pain. Pain Physician. 2013; 16:125–133. PMID: 23511679.5. Shwita AH, Amr YM, Okab MI. Comparative study of the effects of the retrocrural celiac plexus block versus splanchnic nerve block, C-arm guided, for upper gastrointestinal tract tumors on pain relief and the quality of life at a six-month follow up. Korean J Pain. 2015; 28:22–31. PMID: 25589943.
Article6. Sehgal S, Ghaleb A. Neurolytic celiac plexus block for pancreatic cancer pain: a review of literature. Indian J Pain. 2013; 27:121–131.
Article7. World Health Organization. WHO's cancer pain ladder for adults [Internet]. Geneva: World Health Organization;cited 2017 Jun 22. Available at http://www.who.int/cancer/palliative/painladder/en/.8. Stefaniak T, Basinski A, Vingerhoets A, Makarewicz W, Connor S, Kaska L, et al. A comparison of two invasive techniques in the management of intractable pain due to inoperable pancreatic cancer: neurolytic celiac plexus block and videothoracoscopic splanchnicectomy. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2005; 31:768–773. PMID: 15923103.
Article9. De Conno F, Caraceni A, Aldrighetti L, Magnani G, Ferla G, Comi G, et al. Paraplegia following coeliac plexus block. Pain. 1993; 55:383–385. PMID: 8121700.
Article10. Dommisse GF. The arteries, arterioles, and capillaries of the spinal cord. Surgical guidelines in the prevention of postoperative paraplegia. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 1980; 62:369–376. PMID: 7436294.11. Bowen Wright RM. Precautions against injection into the spinal artery during coeliac plexus block. Anaesthesia. 1990; 45:247–248. PMID: 2334038.
Article12. Eisenberg E, Carr DB, Chalmers TC. Neurolytic celiac plexus block for treatment of cancer pain: a meta-analysis. Anesth Analg. 1995; 80:290–295. PMID: 7818115.13. Davies DD. Incidence of major complications of neurolytic coeliac plexus block. J R Soc Med. 1993; 86:264–266. PMID: 8505748.
Article14. Jabbal SS, Hunton J. Reversible paraplegia following coeliac plexus block. Anaesthesia. 1992; 47:857–858. PMID: 1280001.
Article15. van Dongen RT, Crul BJ. Paraplegia following coeliac plexus block. Anaesthesia. 1991; 46:862–863. PMID: 1952003.
Article16. Wong GY, Brown DL. Transient paraplegia following alcohol celiac plexus block. Reg Anesth. 1995; 20:352–355. PMID: 7577786.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Transient Unilateral Paraplegia after Splanchnic Nerve Block
- Splanchnic Nerve Block with Transdiscal Approach
- Dysaesthesia of Inguinal Area Following Splanchnic Nerve Block with Alcohol
- Acute Respiratory Failure during Splanchnic Nerve Block in COPD a Patient
- Neurolytic Splanchnic Nerve Block for Treatment of Upper Abdominal Pain