Korean J Pain.
2018 Jan;31(1):10-15. 10.3344/kjp.2018.31.1.10.
Allopregnanolone suppresses mechanical allodynia and internalization of neurokinin-1 receptors at the spinal dorsal horn in a rat postoperative pain model
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology, Tsukuba University Hospital, Tsukubba, Japan.
- 2Department of Anesthesiology, Tsuchiura Center for Medical Education and Training, Faculty of Medicine, University of Tsukuba (National Hospital Organization, Kasumigaura Medical Center), Tsuchiura, Japan. taekof@md.tsukuba.ac.jp
- 3Social Welfare Organization, Mito-Saiseikai Hospital, Mito, Japan.
- 4Department of Anesthesiology, School of Medicine, Dokkyo Medical University, Mibu, Japan.
- 5Department of Anesthesiology, University of Tsukuba, Faculty of Medicine, Tsukuba, Japan.
- KMID: 2400903
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2018.31.1.10
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
To identify a new strategy for postoperative pain management, we investigated the analgesic effects of allopregnanolone (Allo) in an incisional pain model, and also assessed its effects on the activities of the primary afferent fibers at the dorsal horn.
METHODS
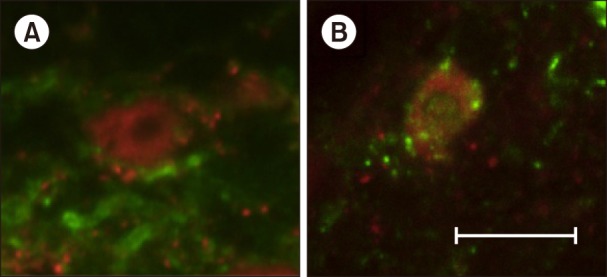
In experiment 1, 45 rats were assigned to Control, Allo small-dose (0.16 mg/kg), and Allo large-dose (1.6 mg/kg) groups (n = 15 in each). The weight bearing and mechanical withdrawal thresholds of the hind limb were measured before and at 2, 24, 48, and 168 h after Brennan's surgery. In experiment 2, 16 rats were assigned to Control and Allo (0.16 mg/kg) groups (n = 8 in each). The degree of spontaneous pain was measured using the grimace scale after the surgery. Activities of the primary afferent fibers in the spinal cord (L6) were evaluated using immunohistochemical staining.
RESULTS
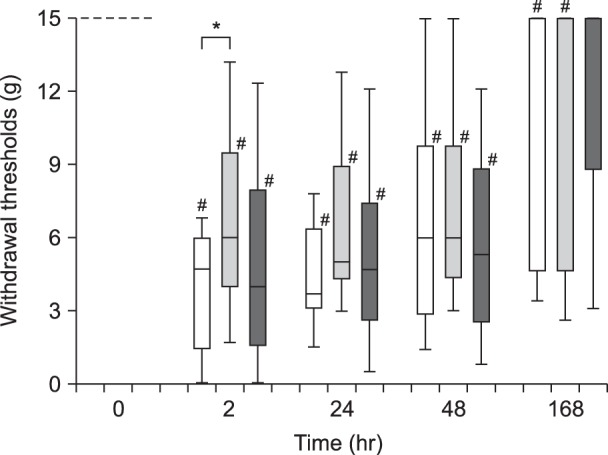
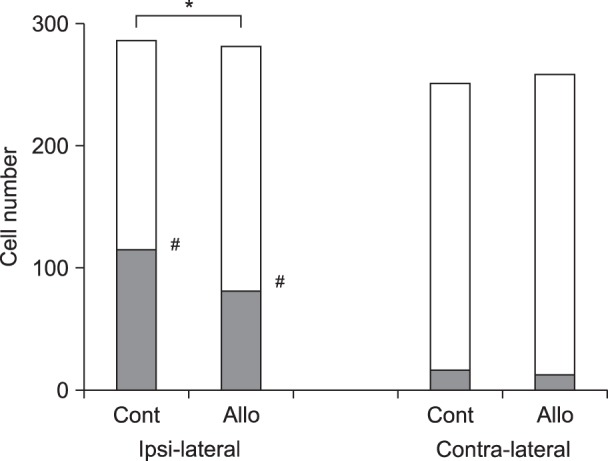
In experiment 1, the withdrawal threshold of the Allo small-dose group was significantly higher than that of the Control group at 2 h after surgery. Intergroup differences in weight bearing were not significant. In experiment 2, intergroup differences in the grimace scale scores were not significant. Substance P release in the Allo (0.16 mg/kg) group was significantly lower than that in the Control group.
CONCLUSIONS
Systemic administration of Allo inhibited mechanical allodynia and activities of the primary afferent fibers at the dorsal horn in a rat postoperative pain model. Allo was proposed as a candidate for postoperative pain management.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Diverse characters of Brennan’s paw incision model regarding certain parameters in the rat
Rahul Kumar, Shivani Gupta, Mayank Gautam, Saroj Kaler Jhajhria, Subrata Basu Ray
Korean J Pain. 2019;32(3):168-177. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2019.32.3.168.
Reference
-
1. Tan M, Law LS, Gan TJ. Optimizing pain management to facilitate enhanced recovery after surgery pathways. Can J Anaesth. 2015; 62:203–218. PMID: 25501696.
Article2. Apfelbaum JL, Chen C, Mehta SS, Gan TJ. Postoperative pain experience: results from a national survey suggest postoperative pain continues to be undermanaged. Anesth Analg. 2003; 97:534–540. PMID: 12873949.
Article3. Kim SH, Yoon KB, Yoon DM, Kim CM, Shin YS. Patient-controlled epidural analgesia with ropivacaine and fentanyl: experience with 2,276 surgical patients. Korean J Pain. 2013; 26:39–45. PMID: 23342206.
Article4. Frye CA, Duncan JE. Progesterone metabolites, effective at the GABAA receptor complex, attenuate pain sensitivity in rats. Brain Res. 1994; 643:194–203. PMID: 8032914.
Article5. Pathirathna S, Todorovic SM, Covey DF, Jevtovic-Todorovic V. 5alpha-reduced neuroactive steroids alleviate thermal and mechanical hyperalgesia in rats with neuropathic pain. Pain. 2005; 117:326–339. PMID: 16150542.
Article6. Meyer L, Venard C, Schaeffer V, Patte-Mensah C, Mensah-Nyagan AG. The biological activity of 3alpha-hydroxysteroid oxido-reductase in the spinal cord regulates thermal and mechanical pain thresholds after sciatic nerve injury. Neurobiol Dis. 2008; 30:30–41. PMID: 18291663.
Article7. Ocvirk R, Pearson Murphy BE, Franklin KB, Abbott FV. Antinociceptive profile of ring A-reduced progesterone metabolites in the formalin test. Pain. 2008; 138:402–409. PMID: 18343034.
Article8. Charlet A, Lasbennes F, Darbon P, Poisbeau P. Fast non-genomic effects of progesterone-derived neurosteroids on nociceptive thresholds and pain symptoms. Pain. 2008; 139:603–609. PMID: 18614289.
Article9. Patte-Mensah C, Meyer L, Schaeffer V, Mensah-Nyagan AG. Selective regulation of 3 alpha-hydroxysteroid oxidoreductase expression in dorsal root ganglion neurons: a possible mechanism to cope with peripheral nerve injury-induced chronic pain. Pain. 2010; 150:522–534. PMID: 20605070.
Article10. Meyer L, Patte-Mensah C, Taleb O, Mensah-Nyagan AG. Allopregnanolone prevents and suppresses oxaliplatin-evoked painful neuropathy: multi-parametric assessment and direct evidence. Pain. 2011; 152:170–181. PMID: 21071147.
Article11. Kawano T, Soga T, Chi H, Eguchi S, Yamazaki F, Kumagai N, et al. Role of the neurosteroid allopregnanolone in the hyperalgesic behavior induced by painful nerve injury in rats. J Anesth. 2011; 25:942–945. PMID: 21879341.
Article12. Afrazi S, Esmaeili-Mahani S. Allopregnanolone suppresses diabetes-induced neuropathic pain and motor deficit through inhibition of GABAA receptor down-regulation in the spinal cord of diabetic rats. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2014; 17:312–317. PMID: 24967058.13. Marvizón JC, Wang X, Matsuka Y, Neubert JK, Spigelman I. Relationship between capsaicin-evoked substance P release and neurokinin 1 receptor internalization in the rat spinal cord. Neuroscience. 2003; 118:535–545. PMID: 12699788.
Article14. Mantyh PW. Neurobiology of substance P and the NK1 receptor. J Clin Psychiatry. 2002; 63(Suppl 11):6–10. PMID: 12562137.15. Kondo I, Marvizon JC, Song B, Salgado F, Codeluppi S, Hua XY, et al. Inhibition by spinal mu- and delta-opioid agonists of afferent-evoked substance P release. J Neurosci. 2005; 25:3651–3660. PMID: 15814796.
Article16. Brennan TJ, Vandermeulen EP, Gebhart GF. Characterization of a rat model of incisional pain. Pain. 1996; 64:493–501. PMID: 8783314.
Article17. Chaplan SR, Bach FW, Pogrel JW, Chung JM, Yaksh TL. Quantitative assessment of tactile allodynia in the rat paw. J Neurosci Methods. 1994; 53:55–63. PMID: 7990513.
Article18. Sotocinal SG, Sorge RE, Zaloum A, Tuttle AH, Martin LJ, Wieskopf JS, et al. The Rat Grimace Scale: a partially automated method for quantifying pain in the laboratory rat via facial expressions. Mol Pain. 2011; 7:55. PMID: 21801409.
Article19. Takasusuki T, Yaksh TL. Regulation of spinal substance P release by intrathecal calcium channel blockade. Anesthesiology. 2011; 115:153–164. PMID: 21577088.
Article20. Belelli D, Lambert JJ. Neurosteroids: endogenous regulators of the GABA(A) receptor. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2005; 6:565–575. PMID: 15959466.
Article21. Maksay G, Laube B, Betz H. Subunit-specific modulation of glycine receptors by neurosteroids. Neuropharmacology. 2001; 41:369–376. PMID: 11522328.
Article22. Pathirathna S, Brimelow BC, Jagodic MM, Krishnan K, Jiang X, Zorumski CF, et al. New evidence that both T-type calcium channels and GABAA channels are responsible for the potent peripheral analgesic effects of 5alpha-reduced neuroactive steroids. Pain. 2005; 114:429–443. PMID: 15777868.
Article23. Kawashiri T, Egashira N, Kurobe K, Tsutsumi K, Yamashita Y, Ushio S, et al. L type Ca2± channel blockers prevent oxaliplatin-induced cold hyperalgesia and TRPM8 overexpression in rats. Mol Pain. 2012; 8:7. PMID: 22292988.24. Dogrul A, Bilsky EJ, Ossipov MH, Lai J, Porreca F. Spinal L-type calcium channel blockade abolishes opioid-induced sensory hypersensitivity and antinociceptive tolerance. Anesth Analg. 2005; 101:1730–1735. PMID: 16301251.
Article25. Jasmin L, Wu MV, Ohara PT. GABA puts a stop to pain. Curr Drug Targets CNS Neurol Disord. 2004; 3:487–505. PMID: 15578966.
Article26. Roychowdhury SM, Fields HL. Endogenous opioids acting at a medullary mu-opioid receptor contribute to the behavioral antinociception produced by GABA antagonism in the midbrain periaqueductal gray. Neuroscience. 1996; 74:863–872. PMID: 8884782.
Article27. Gilbert AK, Franklin KB. GABAergic modulation of descending inhibitory systems from the rostral ventromedial medulla (RVM). Dose-response analysis of nociception and neurological deficits. Pain. 2001; 90:25–36. PMID: 11166967.
Article28. Wang JM, Singh C, Liu L, Irwin RW, Chen S, Chung EJ, et al. Allopregnanolone reverses neurogenic and cognitive deficits in mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010; 107:6498–6503. PMID: 20231471.
Article29. Wang JM, Johnston PB, Ball BG, Brinton RD. The neurosteroid allopregnanolone promotes proliferation of rodent and human neural progenitor cells and regulates cell-cycle gene and protein expression. J Neurosci. 2005; 25:4706–4718. PMID: 15888646.
Article30. Kehlet H, Jensen TS, Woolf CJ. Persistent postsurgical pain: risk factors and prevention. Lancet. 2006; 367:1618–1625. PMID: 16698416.
Article31. Macrae WA. Chronic post-surgical pain: 10 years on. Br J Anaesth. 2008; 101:77–86. PMID: 18434337.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Sequential Activation of AMPA Receptors and Glial Cells in a Pain Model of Lumbar Spine Disc Herniation
- Effects of NO Synthase Inhibitor on Responsiveness of Dorsal Horn Neurons in Neuropathic Pain Animal Model
- Involvement of Ionotropic, rather than Metabotropic, Glutamate Receptors in Hyperexcitability of Spinal orsal Neurons Induced after Spinal Cord Injury
- Imbalance in the spinal serotonergic pathway induces aggravation of mechanical allodynia and microglial activation in carrageenan inflammation
- The Effect of Nitric Oxide on Mechanical and Theraml Allodynia in Neuropathic Pain Model of Rat