Immune Netw.
2017 Dec;17(6):437-450. 10.4110/in.2017.17.6.437.
Heterogeneous Nuclear Ribonucleoprotein A2B1 Exerts a Regulatory Role in Lipopolysaccharide-stimulated 38B9 B Cell Activation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Bioactive Material Sciences and Institute of Bioactive Materials, Chonbuk National University, Jeonju 54896, Korea. yongsuk@jbnu.ac.kr omfs1109@korea.ac.kr
- 2NBM Inc., Wanju 55322, Korea.
- 3Department of Molecular Biology and Institute for Molecular Biology and Genetics, Chonbuk National University, Jeonju 54896, Korea.
- 4Department of Dentistry, Graduate School of Medicine, Korea University, Seoul 02841, Korea. yongsuk@jbnu.ac.kr omfs1109@korea.ac.kr
- 5Department of Oral Maxillofacial Surgery, Korea University Ansan Hospital, Ansan 15355, Korea.
- KMID: 2400629
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4110/in.2017.17.6.437
Abstract
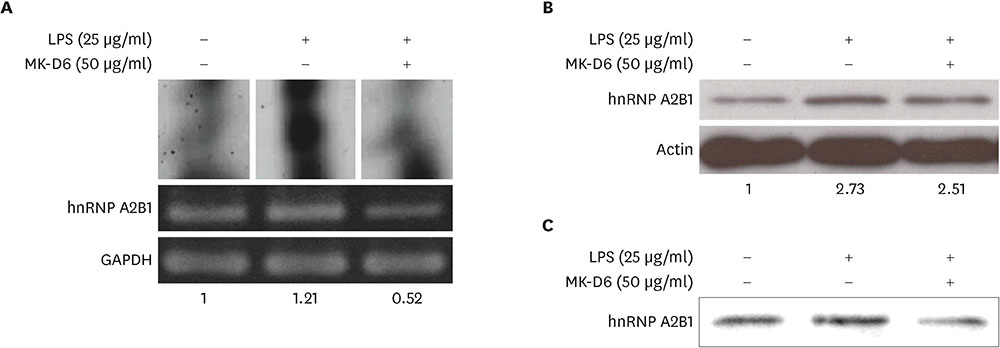
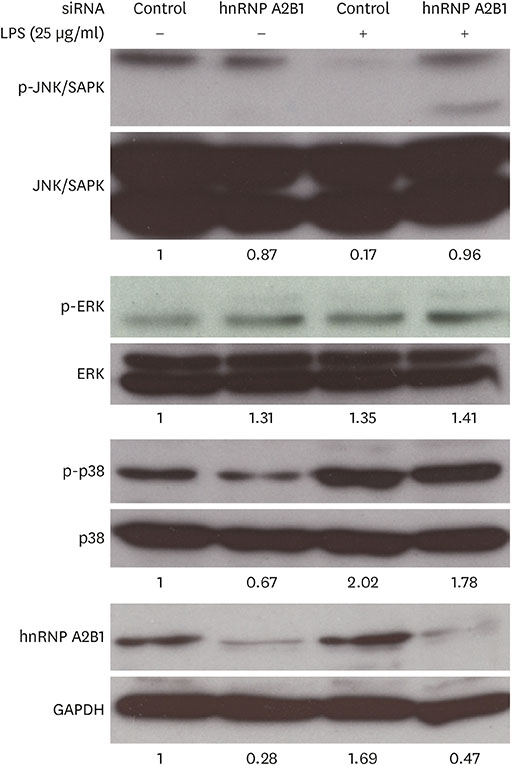
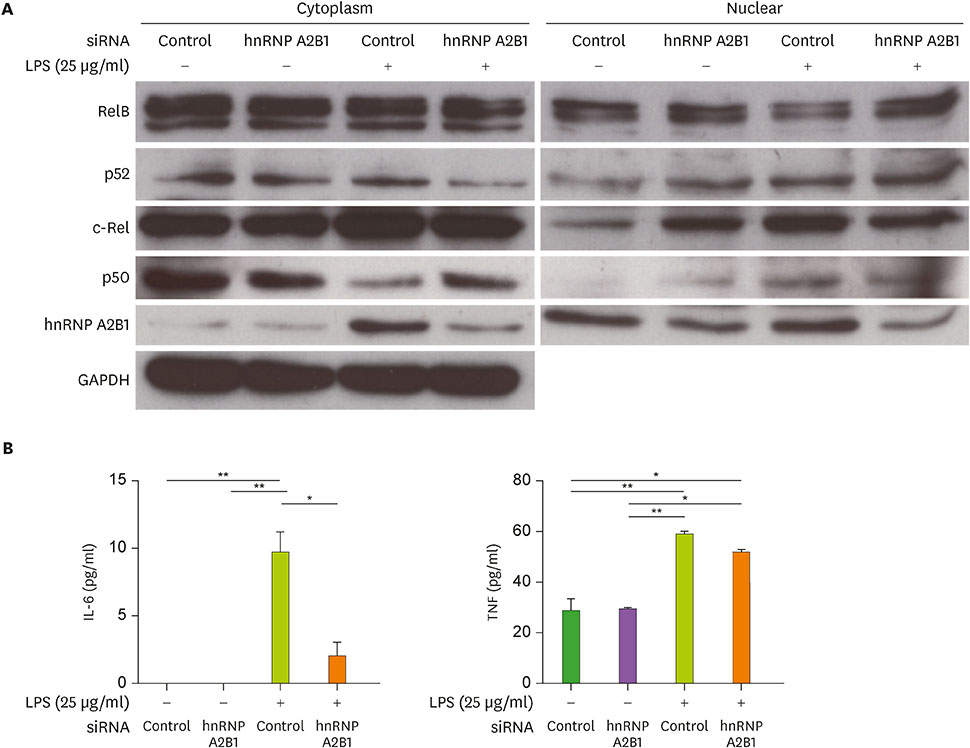
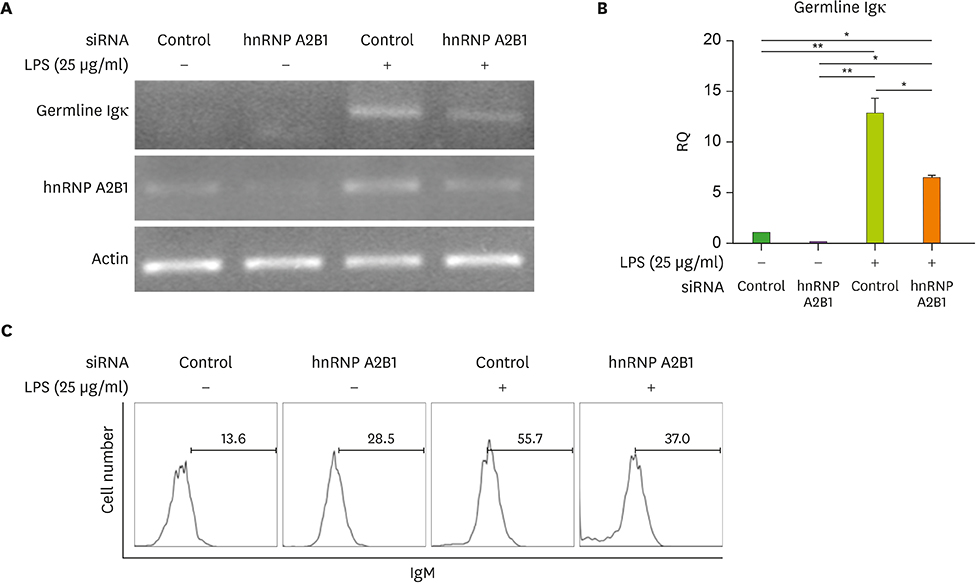
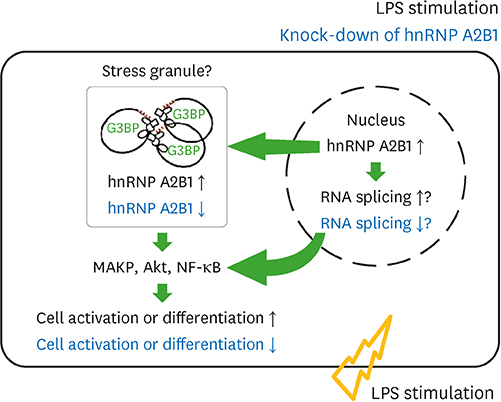
- Major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II molecules, which are recognized for their primary function of presenting an antigen to the T cell receptor, are involved in various signaling pathways in B cell activation. We identified heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein (hnRNP) A2B1 as an MHC class II molecule-associated protein involved in MHC class II-mediated signal transduction in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated 38B9 B cells. Although the function of hnRNP A2B1 in the nucleus is primarily known, the level of hnRNP A2B1 in the cytoplasm was increased in LPS-stimulated 38B9 cells, while it was not detected in the cytoplasm of non-treated 38B9 cells. The silencing of hnRNP A2B1 expression using siRNA disturbed B cell maturation by regulation of mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling, NF-κB activation, and protein kinase B activation. These results suggest that hnRNP A2B1 is associated with MHC class II molecules and is involved in B cell activation signaling pathways in LPS-stimulated 38B9 cells.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
B-Lymphocytes
Cytoplasm
Heterogeneous-Nuclear Ribonucleoproteins*
Major Histocompatibility Complex
Protein Kinases
Proto-Oncogene Proteins c-akt
Receptors, Antigen, T-Cell
RNA, Small Interfering
Signal Transduction
Heterogeneous-Nuclear Ribonucleoproteins
Protein Kinases
Proto-Oncogene Proteins c-akt
RNA, Small Interfering
Receptors, Antigen, T-Cell
Figure
Reference
-
1. Zhang W, Liu HT. MAPK signal pathways in the regulation of cell proliferation in mammalian cells. Cell Res. 2002; 12:9–18.
Article2. Huang G, Shi LZ, Chi H. Regulation of JNK and p38 MAPK in the immune system: signal integration, propagation and termination. Cytokine. 2009; 48:161–169.
Article3. Khiem D, Cyster JG, Schwarz JJ, Black BL. p38 MAPK-MEF2C pathway regulates B-cell proliferation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008; 105:17067–17072.4. Limon JJ, Fruman DA. Akt and mTOR in B cell activation and differentiation. Front Immunol. 2012; 3:228.
Article5. Huang H, Tindall DJ. Dynamic FoxO transcription factors. J Cell Sci. 2007; 120:2479–2487.
Article6. Robinson JH, Delvig AA. Diversity in MHC class II antigen presentation. Immunology. 2002; 105:252–262.
Article7. Al-Daccak R, Mooney N, Charron D. MHC class II signaling in antigen-presenting cells. Curr Opin Immunol. 2004; 16:108–113.
Article8. Liu X, Zhan Z, Li D, Xu L, Ma F, Zhang P, Yao H, Cao X. Intracellular MHC class II molecules promote TLR-triggered innate immune responses by maintaining activation of the kinase Btk. Nat Immunol. 2011; 12:416–424.
Article9. Schneppenheim J, Loock AC, Hüttl S, Schweizer M, Lüllmann-Rauch R, Oberg HH, Arnold P, Lehmann CH, Dudziak D, Kabelitz D, et al. The influence of MHC class II on B cell defects induced by invariant chain/CD74 N-terminal fragments. J Immunol. 2017; 199:172–185.
Article10. Schneppenheim J, Hüttl S, Kruchen A, Fluhrer R, Müller I, Saftig P, Schneppenheim R, Martin CL, Schröder B. Signal-peptide-peptidase-like 2a is required for CD74 intramembrane proteolysis in human B cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014; 451:48–53.
Article11. Yang HY, Kim J, Lee KY, Jang YS. Rac/ROS-related protein kinase C and phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase signaling are involved in a negative regulating cascade in B cell activation by antibody-mediated cross-linking of MHC class II molecules. Mol Immunol. 2010; 47:706–712.
Article12. Yang HY, Kim J, Kim SH, Choe CH, Jang YS. Pro-IL-16 is associated with MHC class II-mediated negative regulation of mouse resting B cell activation through MAP kinases, NF-κB and Skp2-dependent p27kip regulation. Scand J Immunol. 2013; 77:177–186.
Article13. Schlissel MS, Baltimore D. Activation of immunoglobulin kappa gene rearrangement correlates with induction of germline kappa gene transcription. Cell. 1989; 58:1001–1007.
Article14. Kim J, Kim HR, Lee JC, Jang YS. Involvement of ERK, p38 MAP kinase, and PKC in MHC class II-mediated signal transduction in a resting B cell line. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2002; 291:139–145.
Article15. Choi HS, Lee HM, Jang YJ, Kim CH, Ryu CJ. Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A2/B1 regulates the self-renewal and pluripotency of human embryonic stem cells via the control of the G1/S transition. Stem Cells. 2013; 31:2647–2658.
Article16. Gerondakis S, Siebenlist U. Roles of the NF-κB pathway in lymphocyte development and function. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2010; 2:a000182.
Article17. Alt FW, Yancopoulos GD, Blackwell TK, Wood C, Thomas E, Boss M, Coffman R, Rosenberg N, Tonegawa S, Baltimore D. Ordered rearrangement of immunoglobulin heavy chain variable region segments. EMBO J. 1984; 3:1209–1219.
Article18. Krecic AM, Swanson MS. hnRNP complexes: composition, structure, and function. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1999; 11:363–371.
Article19. Piñol-Roma S, Dreyfuss G. hnRNP proteins: localization and transport between the nucleus and the cytoplasm. Trends Cell Biol. 1993; 3:151–155.
Article20. Hernández-Díaz I, Giraldez T, Morales S, Hernandez G, Salido E, Canessa CM, Alvarez de la Rosa D. Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A2/B1 is a tissue-specific aldosterone target gene with prominent induction in the rat distal colon. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2013; 304:G122–G131.
Article21. Hayashi EA, Akira S, Nobrega A. Role of TLR in B cell development: signaling through TLR4 promotes B cell maturation and is inhibited by TLR2. J Immunol. 2005; 174:6639–6647.
Article22. Feng B, Cheng S, Pear WS, Liou HC. NF-κB inhibitor blocks B cell development at two checkpoints. Med Immunol. 2004; 3:1.23. Faes S, Dormond O. PI3K and AKT: unfaithful partners in cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 2015; 16:21138–21152.
Article24. Vikström IB, Slomp A, Carrington EM, Moesbergen LM, Chang C, Kelly GL, Glaser SP, Jansen JH, Leusen JH, Strasser A, et al. MCL-1 is required throughout B-cell development and its loss sensitizes specific B-cell subsets to inhibition of BCL-2 or BCL-XL. Cell Death Dis. 2016; 7:e2345.
Article25. Shilo A, Ben Hur V, Denichenko P, Stein I, Pikarsky E, Rauch J, Kolch W, Zender L, Karni R. Splicing factor hnRNP A2 activates the Ras-MAPK-ERK pathway by controlling A-Raf splicing in hepatocellular carcinoma development. RNA. 2014; 20:505–515.
Article26. Kim HJ, Kim NC, Wang YD, Scarborough EA, Moore J, Diaz Z, MacLea KS, Freibaum B, Li S, Molliex A, et al. Mutations in prion-like domains in hnRNPA2B1 and hnRNPA1 cause multisystem proteinopathy and ALS. Nature. 2013; 495:467–473.
Article27. Lemieux B, Blanchette M, Monette A, Mouland AJ, Wellinger RJ, Chabot B. A function for the hnRNP A1/A2 proteins in transcription elongation. PLoS One. 2015; 10:e0126654.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Antineuroinflammatory Effects of 7,3’,4’-Trihydroxyisoflavone in Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated BV2 Microglial Cells through MAPK and NF-κB Signaling Suppression
- The Regulatory Mechanism of Src Familly Kinase in Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) induced HF-kappaB Activation Pathway
- Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase Inhibitor Enhances Nitric Oxide Synthesis and Apoptosis in LPS-Stimulated Macrophages
- Shikonin Isolated from Lithospermum erythrorhizon Downregulates Proinflammatory Mediators in Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated BV2 Microglial Cells by Suppressing Crosstalk between Reactive Oxygen Species and NF-kappaB
- Effect of Modulation of hnRNP L Levels on the Decay of bcl-2 mRNA in MCF-7 Cells