J Clin Neurol.
2018 Jan;14(1):48-57. 10.3988/jcn.2018.14.1.48.
Role of Language-Related Functional Connectivity in Patients with Benign Childhood Epilepsy with Centrotemporal Spikes
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Ewha Womans University School of Medicine and Ewha Medical Research Institute, Seoul, Korea. leeh@ewha.ac.kr
- 2Department of Medical Science, Ewha Womans University School of Medicine and Ewha Medical Research Institute, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Neurology, Samsung Changwon Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine and Samsung Biomedical Research Institute, Changwon, Korea.
- 4Department of Radiology, Ewha Womans University School of Medicine and Ewha Medical Research Institute, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2399599
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3988/jcn.2018.14.1.48
Abstract
- BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE
Benign childhood epilepsy with centrotemporal spikes (BECTS) does not always have a benign cognitive outcome. We investigated the relationship between cognitive performance and altered functional connectivity (FC) in the resting-state brain networks of BECTS patients.
METHODS
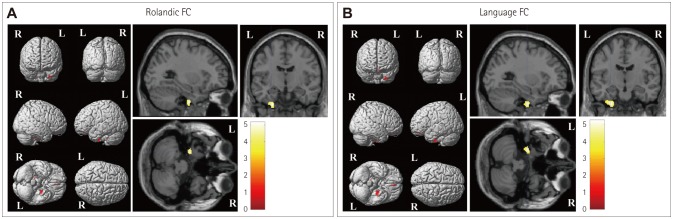
We studied 42 subjects, comprising 19 BECTS patients and 23 healthy controls. Cognitive performance was assessed using the Korean version of the Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children-III, in addition to verbal and visuospatial memory tests and executive function tests. Resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging was acquired in addition to high-resolution structural data. We selected Rolandic and language-related areas as regions of interest (ROIs) and analyzed the seed-based FC to voxels throughout the brain. We evaluated the correlations between the neuropsychological test scores and seed-based FC values using the same ROIs.
RESULTS
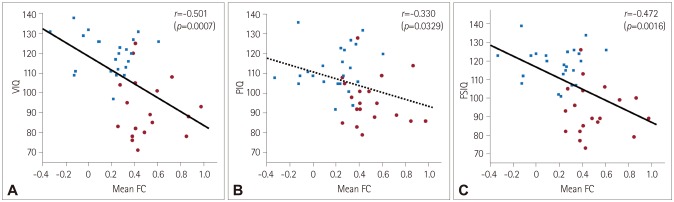
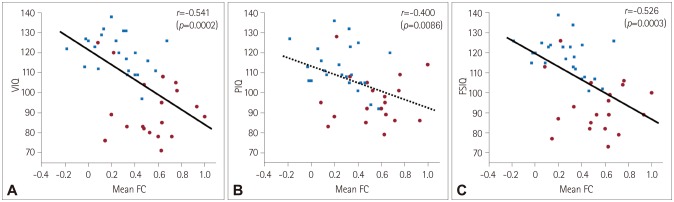
The verbal intelligence quotient (VIQ) and full-scale intelligence quotient (FSIQ) were lower in BECTS patients than in healthy controls (p < 0.001). The prevalence of subjects with a higher performance IQ than VIQ was significantly higher in BECTS patients than in healthy controls (73.7% vs. 26.1%, respectively; p=0.002). Both the Rolandic and language-related ROIs exhibited more enhanced FC to voxels in the left inferior temporal gyrus in BECTS patients than in healthy controls. A particularly interestingly finding was that the enhanced FC was correlated with lower cognitive performance as measured by the VIQ and the FSIQ in both patients and control subjects.
CONCLUSIONS
Our findings suggest that the FC alterations in resting-state brain networks related to the seizure onset zone and language processing areas could be related to adaptive plasticity for coping with cognitive dysfunction.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Berg AT, Zelko FA, Levy SR, Testa FM. Age at onset of epilepsy, pharmacoresistance, and cognitive outcomes: a prospective cohort study. Neurology. 2012; 79:1384–1391. PMID: 22972641.
Article2. Berg AT, Caplan R, Hesdorffer DC. Psychiatric and neurodevelopmental disorders in childhood-onset epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav. 2011; 20:550–555. PMID: 21315660.
Article3. Berg AT, Langfitt JT, Testa FM, Levy SR, DiMario F, Westerveld M, et al. Global cognitive function in children with epilepsy: a community-based study. Epilepsia. 2008; 49:608–614. PMID: 18070088.
Article4. Filippini M, Ardu E, Stefanelli S, Boni A, Gobbi G, Benso F. Neuropsychological profile in new-onset benign epilepsy with centrotemporal spikes (BECTS): focusing on executive functions. Epilepsy Behav. 2016; 54:71–79. PMID: 26667848.
Article5. Lee JH, Kim SE, Park CH, Yoo JH, Lee HW. Gray and white matter volumes and cognitive dysfunction in drug-naïve newly diagnosed pediatric epilepsy. Biomed Res Int. 2015; 2015:923861. PMID: 26417604.
Article6. Bhise VV, Burack GD, Mandelbaum DE. Baseline cognition, behavior, and motor skills in children with new-onset, idiopathic epilepsy. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2010; 52:22–26. PMID: 19702836.
Article7. Fastenau PS, Johnson CS, Perkins SM, Byars AW, deGrauw TJ, Austin JK, et al. Neuropsychological status at seizure onset in children: risk factors for early cognitive deficits. Neurology. 2009; 73:526–534. PMID: 19675309.
Article8. Kim SE, Lee JH, Chung HK, Lim SM, Lee HW. Alterations in white matter microstructures and cognitive dysfunctions in benign childhood epilepsy with centrotemporal spikes. Eur J Neurol. 2014; 21:708–717. PMID: 24330132.
Article9. Englot DJ, Konrad PE, Morgan VL. Regional and global connectivity disturbances in focal epilepsy, related neurocognitive sequelae, and potential mechanistic underpinnings. Epilepsia. 2016; 57:1546–1557. PMID: 27554793.
Article10. Tracy JI, Doucet GE. Resting-state functional connectivity in epilepsy: growing relevance for clinical decision making. Curr Opin Neurol. 2015; 28:158–165. PMID: 25734954.11. Damoiseaux JS, Greicius MD. Greater than the sum of its parts: a review of studies combining structural connectivity and resting-state functional connectivity. Brain Struct Funct. 2009; 213:525–533. PMID: 19565262.
Article12. Guerrini R, Pellacani S. Benign childhood focal epilepsies. Epilepsia. 2012; 53(Suppl 4):9–18.
Article13. Panayiotopoulos CP, Michael M, Sanders S, Valeta T, Koutroumanidis M. Benign childhood focal epilepsies: assessment of established and newly recognized syndromes. Brain. 2008; 131:2264–2286. PMID: 18718967.
Article14. Kavros PM, Clarke T, Strug LJ, Halperin JM, Dorta NJ, Pal DK. Attention impairment in rolandic epilepsy: systematic review. Epilepsia. 2008; 49:1570–1580. PMID: 18410358.
Article15. Datta AN, Oser N, Bauder F, Maier O, Martin F, Ramelli GP, et al. Cognitive impairment and cortical reorganization in children with benign epilepsy with centrotemporal spikes. Epilepsia. 2013; 54:487–494. PMID: 23297860.
Article16. Lillywhite LM, Saling MM, Harvey AS, Abbott DF, Archer JS, Vears DF, et al. Neuropsychological and functional MRI studies provide converging evidence of anterior language dysfunction in BECTS. Epilepsia. 2009; 50:2276–2284. PMID: 19292755.
Article17. Besseling RM, Overvliet GM, Jansen JF, van der Kruijs SJ, Vles JS, Ebus SC, et al. Aberrant functional connectivity between motor and language networks in rolandic epilepsy. Epilepsy Res. 2013; 107:253–262. PMID: 24210960.
Article18. Zeng H, Ramos CG, Nair VA, Hu Y, Liao J, La C, et al. Regional homogeneity (ReHo) changes in new onset versus chronic benign epilepsy of childhood with centrotemporal spikes (BECTS): a resting state fMRI study. Epilepsy Res. 2015; 116:79–85. PMID: 26354170.
Article19. Xiao F, Li L, An D, Lei D, Tang Y, Yang T, et al. Altered attention networks in benign childhood epilepsy with centrotemporal spikes (BECTS): a resting-state fMRI study. Epilepsy Behav. 2015; 45:234–241. PMID: 25825370.
Article20. Tang YL, Ji GJ, Yu Y, Wang J, Wang ZJ, Zang YF, et al. Altered regional homogeneity in rolandic epilepsy: a resting-state FMRI study. Biomed Res Int. 2014; 2014:960395. PMID: 25247197.
Article21. Smith AB, Bajomo O, Pal DK. A meta-analysis of literacy and language in children with rolandic epilepsy. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2015; 57:1019–1026. PMID: 26219529.
Article22. Oser N, Hubacher M, Specht K, Datta AN, Weber P, Penner IK. Default mode network alterations during language task performance in children with benign epilepsy with centrotemporal spikes (BECTS). Epilepsy Behav. 2014; 33:12–17. PMID: 24583653.
Article23. Riva D, Vago C, Franceschetti S, Pantaleoni C, D'Arrigo S, Granata T, et al. Intellectual and language findings and their relationship to EEG characteristics in benign childhood epilepsy with centrotemporal spikes. Epilepsy Behav. 2007; 10:278–285. PMID: 17267289.
Article24. Engel J Jr. International League Against Epilepsy (ILAE). A proposed diagnostic scheme for people with epileptic seizures and with epilepsy: report of the ILAE Task Force on Classification and Terminology. Epilepsia. 2001; 42:796–803. PMID: 11422340.
Article25. Engel J Jr. Classification of epileptic disorders. Epilepsia. 2001; 42:316. PMID: 11442146.26. Kwak KJ, Park HW, Kim CT. A study for the standardization of Korean WISC-3(1). Korean J Ind Organ Psychol. 2002; 15:19–33.27. Vakil E, Greenstein Y, Blachstein H. Normative data for composite scores for children and adults derived from the Rey Auditory Verbal Learning Test. Clin Neuropsychol. 2010; 24:662–677. PMID: 20155574.
Article28. Kirkwood MW, Weiler MD, Bernstein JH, Forbes PW, Waber DP. Sources of poor performance on the Rey-Osterrieth Complex Figure Test among children with learning difficulties: a dynamic assessment approach. Clin Neuropsychol. 2001; 15:345–356. PMID: 11778773.
Article29. Lee JB, Kim JS, Seo WS, Shin HJ, Bai DS, Lee HR. The validity and reliability of ‘Computerized Neurocognitive Function Test’ in the elementary school child. Korean J Psychosom Med. 2003; 11:97–117.30. Shin MS, Park MJ. Stroop Color and Word Test. Seoul: Hakjisa;2007.31. Verly M, Verhoeven J, Zink I, Mantini D, Peeters R, Deprez S, et al. Altered functional connectivity of the language network in ASD: role of classical language areas and cerebellum. Neuroimage Clin. 2014; 4:374–382. PMID: 24567909.
Article32. Shirer WR, Ryali S, Rykhlevskaia E, Menon V, Greicius MD. Decoding subject-driven cognitive states with whole-brain connectivity patterns. Cereb Cortex. 2012; 22:158–165. PMID: 21616982.
Article33. Price CJ. The anatomy of language: a review of 100 fMRI studies published in 2009. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010; 1191:62–88. PMID: 20392276.
Article34. Smith SM, Fox PT, Miller KL, Glahn DC, Fox PM, Mackay CE, et al. Correspondence of the brain's functional architecture during activation and rest. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009; 106:13040–13045. PMID: 19620724.
Article35. Wechsler D. WISC-III: Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children. San Antonio: Psychological Corporation;1991.36. Verrotti A, Filippini M, Matricardi S, Agostinelli MF, Gobbi G. Memory impairment and benign epilepsy with centrotemporal spike (BECTS): a growing suspicion. Brain Cogn. 2014; 84:123–131. PMID: 24362071.
Article37. Vannest J, Szaflarski JP, Eaton KP, Henkel DM, Morita D, Glauser TA, et al. Functional magnetic resonance imaging reveals changes in language localization in children with benign childhood epilepsy with centrotemporal spikes. J Child Neurol. 2013; 28:435–445. PMID: 22761402.
Article38. Papavasiliou A, Mattheou D, Bazigou H, Kotsalis C, Paraskevoulakos E. Written language skills in children with benign childhood epilepsy with centrotemporal spikes. Epilepsy Behav. 2005; 6:50–58. PMID: 15652734.
Article39. Xiao F, An D, Lei D, Li L, Chen S, Wu X, et al. Real-time effects of centrotemporal spikes on cognition in rolandic epilepsy: An EEG-fMRI study. Neurology. 2016; 86:544–551. PMID: 26747882.40. Bromley RL, Leeman BA, Baker GA, Meador KJ. Cognitive and neurodevelopmental effects of antiepileptic drugs. Epilepsy Behav. 2011; 22:9–16. PMID: 21684214.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effects of Antiepileptic Drugs on Language Abilities in Benign Epilepsy of Childhood with Centrotemporal Spikes
- A Case of a Coincidence of Rolandic and Childhood Absence Epilepsy
- Electroencephalographic Resting-State Functional Connectivity of Benign Epilepsy with Centrotemporal Spikes
- Cognitive and Behavioral Problems and the Effectiveness of Topiramate Once per Day in the Control of Benign Childhood Epilepsy with Centrotemporal Spikes
- Concomitance of Childhood Absence Epilepsy and Benign Rolandic Spikes