Korean J Physiol Pharmacol.
2018 Jan;22(1):91-99. 10.4196/kjpp.2018.22.1.91.
Functional identification of protein phosphatase 1-binding consensus residues in NBCe1-B
- Affiliations
-
- 1Laboratory of Physiology, College of Veterinary Medicine, Chungnam National University, Daejeon 34134, Korea.
- 2Department of Physiology, School of Medicine, Sungkyunkwan University, Suwon 16419, Korea. kimhyunjin@skku.edu
- 3Department of Physiology, College of Medicine, Gachon University, Incheon 21999, Korea. dkyang@gachon.ac.kr
- KMID: 2398559
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4196/kjpp.2018.22.1.91
Abstract
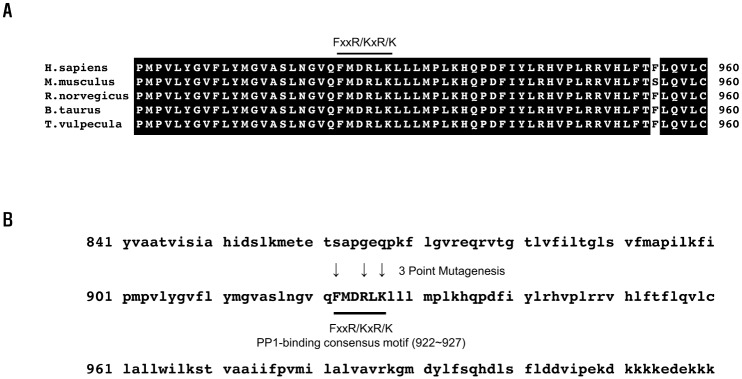
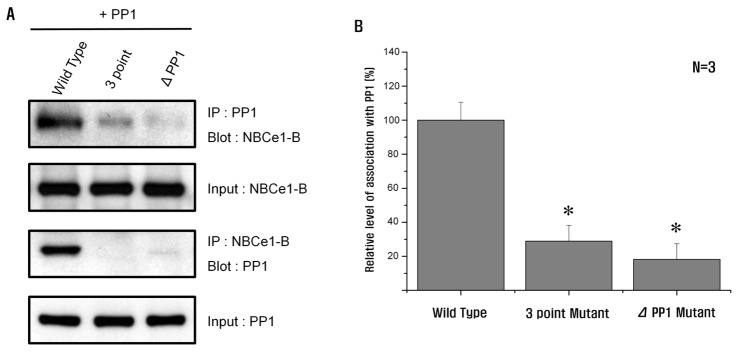
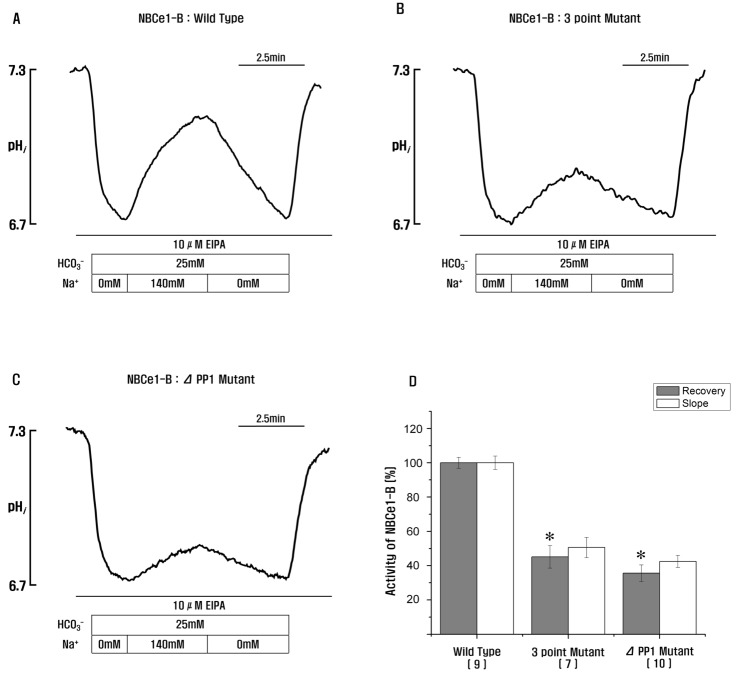
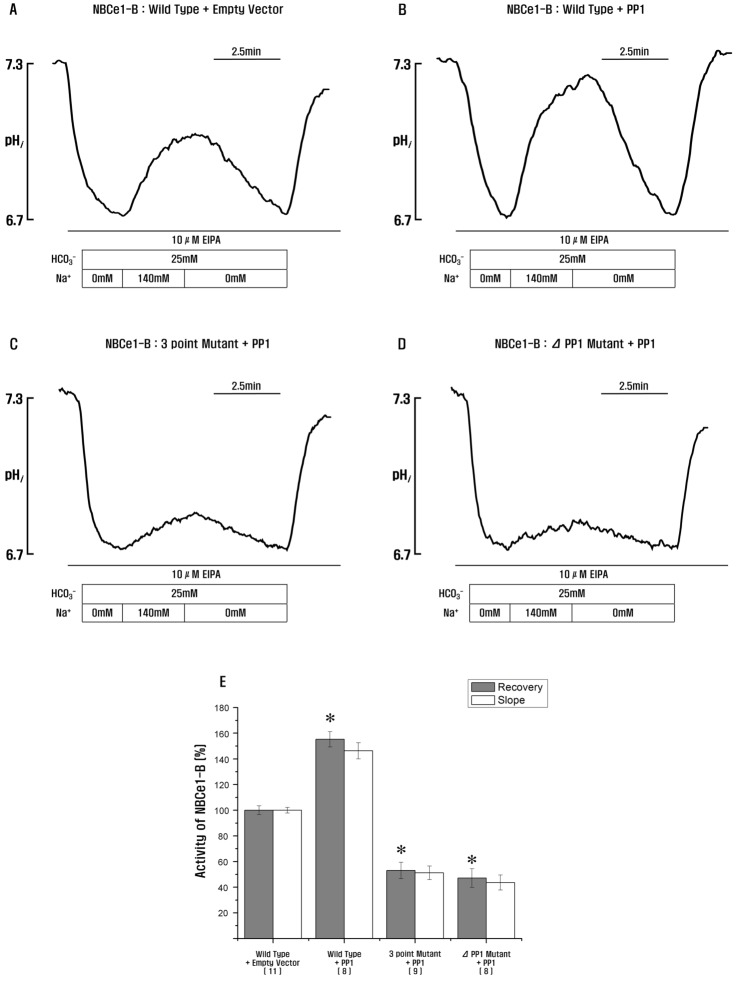
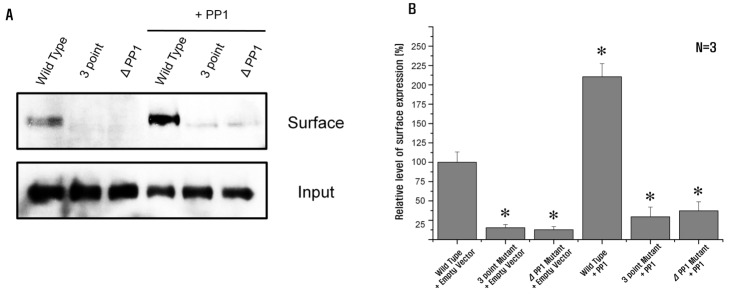
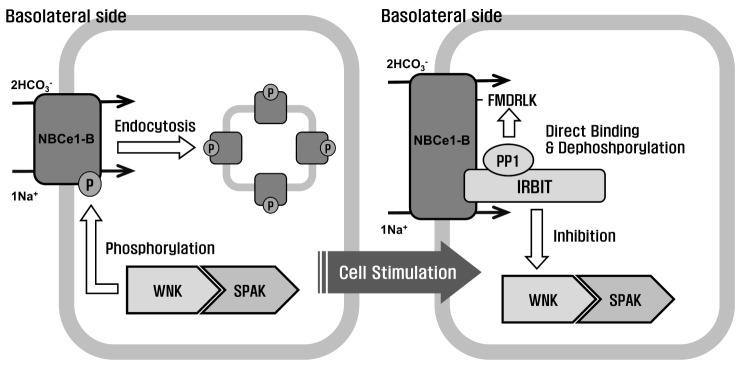
- Protein phosphatase 1 (PP1) is involved in various signal transduction mechanisms as an extensive regulator. The PP1 catalytic subunit (PP1c) recognizes and binds to PP1-binding consensus residues (FxxR/KxR/K) in NBCe1-B. Consequently, we focused on identifying the function of the PP1-binding consensus residue, â¹²²FMDRLK⹲ⷠ, in NBCe1-B. Using site-directed mutagenesis and co-immunoprecipitation assays, we revealed that in cases where the residues were substituted (F922A, R925A, and K927A) or deleted (deletion of amino acids 922-927), NBCe1-B mutants inhibited PP1 binding to NBCe1-B. Additionally, by recording the intracellular pH, we found that PP1-binding consensus residues in NBCe1-B were not only critical for NBCe1-B activity, but also relevant to its surface expression level. Therefore, we reported that NBCe1-B, as a substrate of PP1, contains these residues in the C-terminal region and that the direct interaction between NBCe1-B and PP1 is functionally critical in controlling the regulation of the HCO₃⻠transport. These results suggested that like IRBIT, PP1 was another novel regulator of HCO₃⻠secretion in several types of epithelia.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Williams JA. Regulation of pancreatic acinar cell function. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2006; 22:498–504. PMID: 16891880.
Article2. Choi JY, Muallem D, Kiselyov K, Lee MG, Thomas PJ, Muallem S. Aberrant CFTR-dependent HCO3− transport in mutations associated with cystic fibrosis. Nature. 2001; 410:94–97. PMID: 11242048.3. Abuladze N, Lee I, Newman D, Hwang J, Boorer K, Pushkin A, Kurtz I. Molecular cloning, chromosomal localization, tissue distribution, and functional expression of the human pancreatic sodium bicarbonate cotransporter. J Biol Chem. 1998; 273:17689–17695. PMID: 9651366.
Article4. Boron WF, Chen L, Parker MD. Modular structure of sodiumcoupled bicarbonate transporters. J Exp Biol. 2009; 212:1697–1706. PMID: 19448079.
Article5. Pushkin A, Kurtz I. SLC4 base (HCO3−, CO32−) transporters: classification, function, structure, genetic diseases, and knockout models. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2006; 290:F580–F599. PMID: 16461757.6. Zhao H, Star RA, Muallem S. Membrane localization of H+ and HCO3− transporters in the rat pancreatic duct. J Gen Physiol. 1994; 104:57–85. PMID: 7964596.7. Ishiguro H, Steward MC, Lindsay AR, Case RM. Accumulation of intracellular HCO3− by Na+-HCO3− cotransport in interlobular ducts from guinea-pig pancreas. J Physiol. 1996; 495:169–178. PMID: 8866360.8. Ishiguro H, Naruse S, Kitagawa M, Suzuki A, Yamamoto A, Hayakawa T, Case RM, Steward MC. CO2 permeability and bicarbonate transport in microperfused interlobular ducts isolated from guineapig pancreas. J Physiol. 2000; 528:305–315. PMID: 11034620.9. Gross E, Abuladze N, Pushkin A, Kurtz I, Cotton CU. The stoichiometry of the electrogenic sodium bicarbonate cotransporter pNBC1 in mouse pancreatic duct cells is 2 HCO3−:1 Na+. J Physiol. 2001; 531:375–382. PMID: 11230510.10. Steward MC, Ishiguro H, Case RM. Mechanisms of bicarbonate secretion in the pancreatic duct. Annu Rev Physiol. 2005; 67:377–409. PMID: 15709963.
Article11. Yang D, Li Q, So I, Huang CL, Ando H, Mizutani A, Seki G, Mikoshiba K, Thomas PJ, Muallem S. IRBIT governs epithelial secretion in mice by antagonizing the WNK/SPAK kinase pathway. J Clin Invest. 2011; 121:956–965. PMID: 21317537.
Article12. Lee SK, Boron WF, Parker MD. Relief of autoinhibition of the electrogenic Na-HCO3 [corrected] cotransporter NBCe1-B: role of IRBIT vs.amino-terminal truncation. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2012; 302:C518–C526. PMID: 22012331.13. Shirakabe K, Priori G, Yamada H, Ando H, Horita S, Fujita T, Fujimoto I, Mizutani A, Seki G, Mikoshiba K. IRBIT, an inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor-binding protein, specifically binds to and activates pancreas-type Na+/HCO3− cotransporter 1 (pNBC1). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006; 103:9542–9547. PMID: 16769890.14. Yang D, Shcheynikov N, Zeng W, Ohana E, So I, Ando H, Mizutani A, Mikoshiba K, Muallem S. IRBIT coordinates epithelial fluid and HCO3− secretion by stimulating the transporters pNBC1 and CFTR in the murine pancreatic duct. J Clin Invest. 2009; 119:193–202. PMID: 19033647.15. Shenolikar S, Nairn AC. Protein phosphatases: recent progress. Adv Second Messenger Phosphoprotein Res. 1991; 23:1–121. PMID: 1847640.16. Shenolikar S. Protein serine/threonine phosphatases?new avenues for cell regulation. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1994; 10:55–86. PMID: 7888183.
Article17. Wera S, Hemmings BA. Serine/threonine protein phosphatases. Biochem J. 1995; 311:17–29. PMID: 7575450.
Article18. Aggen JB, Nairn AC, Chamberlin R. Regulation of protein phosphatase-1. Chem Biol. 2000; 7:R13–R23. PMID: 10662690.
Article19. Marx SO, Kurokawa J, Reiken S, Motoike H, D'Armiento J, Marks AR, Kass RS. Requirement of a macromolecular signaling complex for beta adrenergic receptor modulation of the KCNQ1-KCNE1 potassium channel. Science. 2002; 295:496–499. PMID: 11799244.20. Darman RB, Flemmer A, Forbush B. Modulation of ion transport by direct targeting of protein phosphatase type 1 to the Na-K-Cl cotransporter. J Biol Chem. 2001; 276:34359–34362. PMID: 11466303.
Article21. Flores-Hernandez J, Hernandez S, Snyder GL, Yan Z, Fienberg AA, Moss SJ, Greengard P, Surmeier DJ. D1 dopamine receptor activation reduces GABAA receptor currents in neostriatal neurons through a PKA/DARPP-32/PP1 signaling cascade. J Neurophysiol. 2000; 83:2996–3004. PMID: 10805695.22. Furukawa T, Ogura T, Zheng YJ, Tsuchiya H, Nakaya H, Katayama Y, Inagaki N. Phosphorylation and functional regulation of ClC-2 chloride channels expressed in Xenopus oocytes by M cyclindependent protein kinase. J Physiol. 2002; 540:883–893. PMID: 11986377.23. Rutledge E, Denton J, Strange K. Cell cycle- and swelling-induced activation of a Caenorhabditis elegans ClC channel is mediated by CeGLC-7alpha/beta phosphatases. J Cell Biol. 2002; 158:435–444. PMID: 12163466.24. Ayllón V, Cayla X, García A, Fleischer A, Rebollo A. The anti-apoptotic molecules Bcl-xL and Bcl-w target protein phosphatase 1α to Bad. Eur J Immunol. 2002; 32:1847–1855. PMID: 12115603.
Article25. Lee MG, Ahn W, Choi JY, Luo X, Seo JT, Schultheis PJ, Shull GE, Kim KH, Muallem S. Na+-dependent transporters mediate HCO3− salvage across the luminal membrane of the main pancreatic duct. J Clin Invest. 2000; 105:1651–1658. PMID: 10841524.26. Gagnon KB, Delpire E. Multiple pathways for protein phosphatase 1 (PP1) regulation of Na-K-2Cl cotransporter (NKCC1) function: the N-terminal tail of the Na-K-2Cl cotransporter serves as a regulatory scaffold for Ste20-related proline/alanine-rich kinase (SPAK) and PP1. J Biol Chem. 2010; 285:14115–14121. PMID: 20223824.27. Roy J, Cyert MS. Cracking the phosphatase code: docking interactions determine substrate specificity. Sci Signal. 2009; 2:re9. PMID: 19996458.
Article28. Villa F, Goebel J, Rafiqi FH, Deak M, Thastrup J, Alessi DR, van Aalten DM. Structural insights into the recognition of substrates and activators by the OSR1 kinase. EMBO Rep. 2007; 8:839–845. PMID: 17721439.
Article29. Gagnon KB, England R, Diehl L, Delpire E. Apoptosis-associated tyrosine kinase scaffolding of protein phosphatase 1 and SPAK reveals a novel pathway for Na-K-2C1 cotransporter regulation. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2007; 292:C1809–C1815. PMID: 17267545.
Article30. Bergeron MJ, Frenette-Cotton R, Carpentier GA, Simard MG, Caron L, Isenring P. Phosphoregulation of K+-Cl− cotransporter 4 during changes in intracellular Cl and cell volume. J Cell Physiol. 2009; 219:787–796. PMID: 19206159.31. Devogelaere B, Nadif Kasri N, Derua R, Waelkens E, Callewaert G, Missiaen L, Parys JB, De Smedt H. Binding of IRBIT to the IP3 receptor: determinants and functional effects. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006; 343:49–56. PMID: 16527252.32. Xu B, English JM, Wilsbacher JL, Stippec S, Goldsmith EJ, Cobb MH. WNK1, a novel mammalian serine/threonine protein kinase lacking the catalytic lysine in subdomain II. J Biol Chem. 2000; 275:16795–16801. PMID: 10828064.
Article33. Wilson FH, Disse-Nicodeme S, Choate KA, Ishikawa K, Nelson-Williams C, Desitter I, Gunel M, Milford DV, Lipkin GW, Achard JM, Feely MP, Dussol B, Berland Y, Unwin RJ, Mayan H, Simon DB, Farfel Z, Jeunemaitre X, Lifton RP. Human hypertension caused by mutations in WNK kinases. Science. 2001; 293:1107–1112. PMID: 11498583.
Article34. Vitari AC, Deak M, Morrice NA, Alessi DR. The WNK1 and WNK4 protein kinases that are mutated in Gordon's hypertension syndrome phosphorylate and activate SPAK and OSR1 protein kinases. Biochem J. 2005; 391:17–24. PMID: 16083423.
Article35. Gagnon KB, England R, Delpire E. Volume sensitivity of cation-Cl− cotransporters is modulated by the interaction of two kinases: Ste20-related proline-alanine-rich kinase and WNK4. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2006; 290:C134–C142. PMID: 15930150.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Ahcyl2 upregulates NBCe1-B via multiple serine residues of the PEST domain-mediated association
- Identification of determinants that mediate binding between Tembusu virus and the cellular receptor heat shock protein A9
- Characterizing affinity epitopes between prion protein and beta-amyloid using an epitope mapping immunoassay
- Phosphorylation of chicken protein tyrosine phosphatase 1 by casein kinase II in vitro
- NBCe1 Regulates Odontogenic Differentiation of Human Dental Pulp Stem Cells via NF-κB