Asia Pac Allergy.
2012 Jul;2(3):203-209. 10.5415/apallergy.2012.2.3.203.
Recent progress of elucidating the mechanisms of drug hypersensitivity
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, Shimada Municipal Hospital, Shimada, Shizuoka 427-8502, Japan. hihashiz0001@mac.com
- KMID: 2397483
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5415/apallergy.2012.2.3.203
Abstract
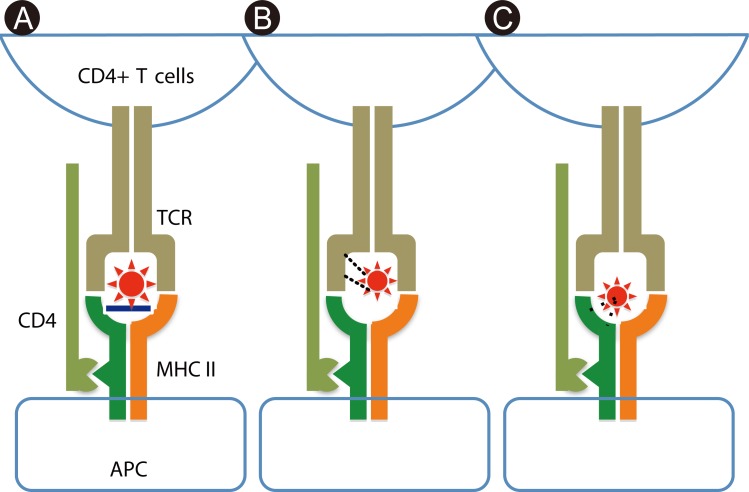
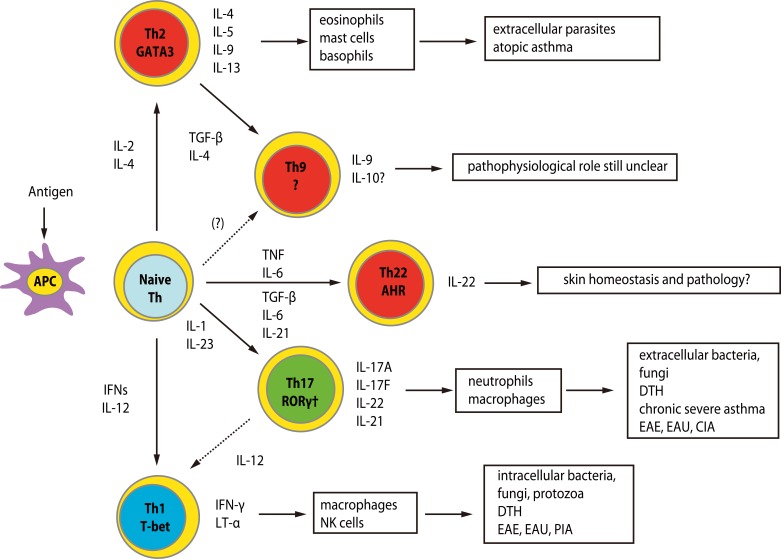
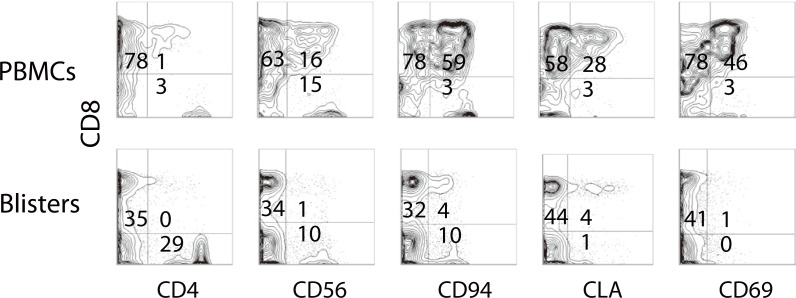
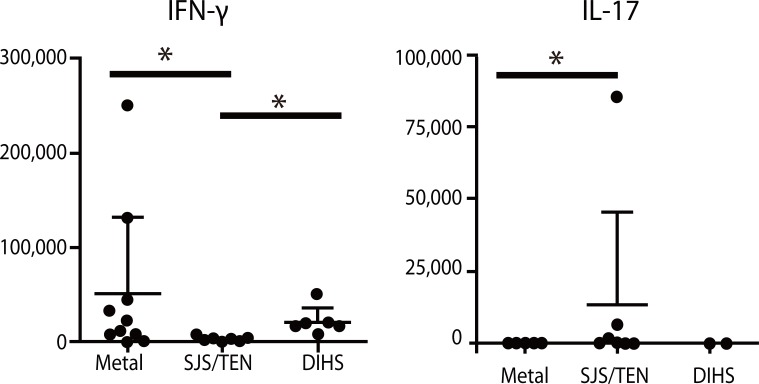
- Recent technical approaches to investigating drug hypersensitivity have provided a great deal of information to solve the mechanisms that remain poorly understood. First, immunological investigations and in silico analysis have revealed that a novel interaction between T cells and antigen-presenting cells, namely the pharmacological interaction concept, is involved in drug recognition and the hapten theory. Second, progress in immunology has provided a new concept of CD4+ T cell subsets. Th17 cells have proven to be a critical player in acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis. Our recent findings suggest that this subset might contribute to the pathogenesis of Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis. Third, alarmins, molecules associated with innate immunity, are also associated with exaggeration and the persistence of severe drug hypersensitivity. The latest innovative techniques are providing a new landscape to examine drug hypersensitivity.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
In this issue of Asia Pacific Allergy
Sang-Heon Cho
Asia Pac Allergy. 2012;2(3):165-166. doi: 10.5415/apallergy.2012.2.3.165.Lamotrigine-induced toxic epidermal necrolysis confirmed by in vitro granulysin and cytokine assays
Ha-Kyeong Won, Ji-Won Lee, Woo-Jung Song, Jettanong Klaewsongkram, Min-Gyu Kang, Han-Ki Park, Hyun-Seung Lee, Min-Hye Kim, Yoon-Seok Chang, Sang-Heon Cho, Kyung-Up Min
Asia Pac Allergy. 2014;4(4):253-256. doi: 10.5415/apallergy.2014.4.4.253.
Reference
-
1. Hung SI, Chung WH, Liou LB, Chu CC, Lin M, Huang HP, Lin YL, Lan JL, Yang LC, Hong HS, Chen MJ, Lai PC, Wu MS, Chu CY, Wang KH, Chen CH, Fann CS, Wu JY, Chen YT. HLA-B*5801 allele as a genetic marker for severe cutaneous adverse reactions caused by allopurinol. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005; 102:4134–4139. PMID: 15743917.
Article2. Martin AM, Nolan D, Gaudieri S, Almeida CA, Nolan R, James I, Carvalho F, Phillips E, Christiansen FT, Purcell AW, McCluskey J, Mallal S. Predisposition to abacavir hypersensitivity conferred by HLA-B*5701 and a haplotypic Hsp70-Hom variant. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004; 101:4180–4185. PMID: 15024131.
Article3. Ozeki T, Mushiroda T, Yowang A, Takahashi A, Kubo M, Shirakata Y, Ikezawa Z, Iijima M, Shiohara T, Hashimoto K, Kamatani N, Nakamura Y. Genome-wide association study identifies HLA-A*3101 allele as a genetic risk factor for carbamazepine-induced cutaneous adverse drug reactions in Japanese population. Hum Mol Genet. 2011; 20:1034–1041. PMID: 21149285.
Article4. Chung WH, Hung SI, Hong HS, Hsih MS, Yang LC, Ho HC, Wu JY, Chen YT. Medical genetics: a marker for Stevens-Johnson syndrome. Nature. 2004; 428:486. PMID: 15057820.5. Wei CY, Chung WH, Huang HW, Chen YT, Hung SI. Direct interaction between HLA-B and carbamazepine activates T cells in patients with Stevens-Johnson syndrome. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012; 129:1562–1569.e5. PMID: 22322005.
Article6. Bellón T, Alvarez L, Mayorga C, Morel E, Torres MJ, Martín-Díaz MA, Díaz R, Radial A, Carballo M, Blanca M. Differential gene expression in drug hypersensitivity reactions: induction of alarmins in severe bullous diseases. Br J Dermatol. 2010; 162:1014–1022. PMID: 20030638.
Article7. Jenkinson C, Jenkins RE, Aleksic M, Pirmohamed M, Naisbitt DJ, Park BK. Characterization of p-phenylenediamine-albumin binding sites and T-cell responses to hapten-modified protein. J Invest Dermatol. 2010; 130:732–742. PMID: 19710686.
Article8. Adam J, Pichler WJ, Yerly D. Delayed drug hypersensitivity: models of T-cell stimulation. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2011; 71:701–707. PMID: 21480949.
Article9. Pichler WJ, Beeler A, Keller M, Lerch M, Posadas S, Schmid D, Spanou Z, Zawodniak A, Gerber B. Pharmacological interaction of drugs with immune receptors: the p-i concept. Allergol Int. 2006; 55:17–25. PMID: 17075282.
Article10. Naisbitt DJ, Farrell J, Wong G, Depta JP, Dodd CC, Hopkins JE, Gibney CA, Chadwick DW, Pichler WJ, Pirmohamed M, Park BK. Characterization of drug-specific T cells in lamotrigine hypersensitivity. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003; 111:1393–1403. PMID: 12789244.
Article11. Naisbitt DJ, Britschgi M, Wong G, Farrell J, Depta JP, Chadwick DW, Pichler WJ, Pirmohamed M, Park BK. Hypersensitivity reactions to carbamazepine: characterization of the specificity, phenotype, and cytokine profile of drug-specific T cell clones. Mol Pharmacol. 2003; 63:732–741. PMID: 12606784.
Article12. Hashizume H, Takigawa M, Tokura Y. Characterization of drug-specific T cells in phenobarbital-induced eruption. J Immunol. 2002; 168:5359–5368. PMID: 11994495.13. Krivoy N, Taer M, Neuman MG. Antiepileptic drug-induced hypersensitivity syndrome reactions. Curr Drug Saf. 2006; 1:289–299. PMID: 18690940.
Article14. Hashizume H, Seo N, Ito T, Takigawa M, Yagi H. Promiscuous interaction between gold-specific T cells and APCs in gold allergy. J Immunol. 2008; 181:8096–8102. PMID: 19018002.
Article15. Annunziato F, Romagnani S. Heterogeneity of human effector CD4+ T cells. Arthritis Res Ther. 2009; 11:257. PMID: 20053303.
Article16. Morel E, Escamochero S, Cabañas R, Díaz R, Fiandor A, Bellón T. CD94/NKG2C is a killer effector molecule in patients with Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010; 125:703–710. 710.e1–710.e8. PMID: 20132973.
Article17. Brugnolo F, Annunziato F, Sampognaro S, Campi P, Manfredi M, Matucci A, Blanca M, Romagnani S, Maggi E, Parronchi P. Highly Th2-skewed cytokine profile of beta-lactam-specific T cells from nonatopic subjects with adverse drug reactions. J Immunol. 1999; 163:1053–1059. PMID: 10395704.19. Schaerli P, Britschgi M, Keller M, Steiner UC, Steinmann LS, Moser B, Pichler WJ. Characterization of human T cells that regulate neutrophilic skin inflammation. J Immunol. 2004; 173:2151–2158. PMID: 15265952.
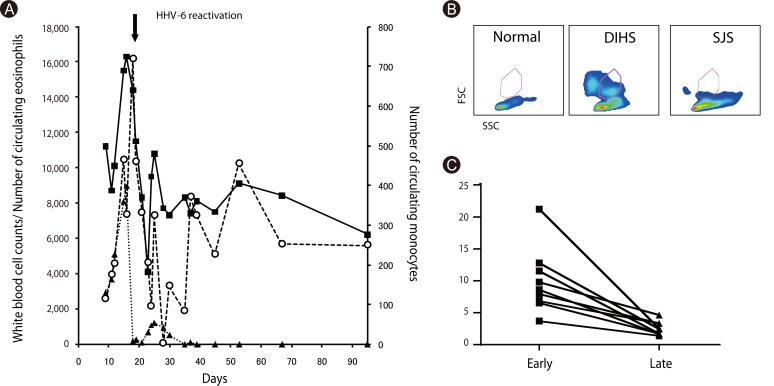
Article20. Britschgi M, Steiner UC, Schmid S, Depta JP, Senti G, Bircher A, Burkhart C, Yawalkar N, Pichler WJ. T-cell involvement in drug-induced acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis. J Clin Invest. 2001; 107:1433–1441. PMID: 11390425.
Article21. Matsumoto Y, Sakuma H, Kohyama K, Park IK. Paralysis of CD4(+) CD25(+) regulatory T cell response in chronic autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Neuroimmunol. 2007; 187:44–54. PMID: 17499858.22. Kelchtermans H, De Klerck B, Mitera T, Van Balen M, Bullens D, Billiau A, Leclercq G, Matthys P. Defective CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cell functioning in collagen-induced arthritis: an important factor in pathogenesis, counter-regulated by endogenous IFN-gamma. Arthritis Res Ther. 2005; 7:R402–R415. PMID: 15743488.23. Balandina A, Lécart S, Dartevelle P, Saoudi A, Berrih-Aknin S. Functional defect of regulatory CD4(+)CD25+ T cells in the thymus of patients with autoimmune myasthenia gravis. Blood. 2005; 105:735–741. PMID: 15454488.
Article24. Nishibori T, Tanabe Y, Su L, David M. Impaired development of CD4+ CD25+ regulatory T cells in the absence of STAT1: increased susceptibility to autoimmune disease. J Exp Med. 2004; 199:25–34. PMID: 14699080.25. Longhi MS, Ma Y, Bogdanos DP, Cheeseman P, Mieli-Vergani G, Vergani D. Impairment of CD4(+)CD25(+) regulatory T-cells in autoimmune liver disease. J Hepatol. 2004; 41:31–37. PMID: 15246204.
Article26. Mao C, Wang S, Xiao Y, Xu J, Jiang Q, Jin M, Jiang X, Guo H, Ning G, Zhang Y. Impairment of regulatory capacity of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells mediated by dendritic cell polarization and hyperthyroidism in Graves' disease. J Immunol. 2011; 186:4734–4743. PMID: 21398613.
Article27. Takahashi R, Kano Y, Yamazaki Y, Kimishima M, Mizukawa Y, Shiohara T. Defective regulatory T cells in patients with severe drug eruptions: timing of the dysfunction is associated with the pathological phenotype and outcome. J Immunol. 2009; 182:8071–8079. PMID: 19494333.
Article28. Oppenheim JJ, Tewary P, de la Rosa G, Yang D. Alarmins initiate host defense. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007; 601:185–194. PMID: 17713005.
Article29. Piccinini AM, Midwood KS. DAMPening inflammation by modulating TLR signalling. Mediators Inflamm. 2010; 2010:672395. PMID: 20706656.
Article30. Nakajima S, Watanabe H, Tohyama M, Sugita K, Iijima M, Hashimoto K, Tokura Y, Nishimura Y, Doi H, Tanioka M, Miyachi Y, Kabashima K. High-mobility group box 1 protein (HMGB1) as a novel diagnostic tool for toxic epidermal necrolysis and Stevens-Johnson syndrome. Arch Dermatol. 2011; 147:1110–1112. PMID: 21931056.
Article31. Chung WH, Hung SI, Yang JY, Su SC, Huang SP, Wei CY, Chin SW, Chiou CC, Chu SC, Ho HC, Yang CH, Lu CF, Wu JY, Liao YD, Chen YT. Granulysin is a key mediator for disseminated keratinocyte death in Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis. Nat Med. 2008; 14:1343–1350. PMID: 19029983.
Article32. Clayberger C, Finn MW, Wang T, Saini R, Wilson C, Barr VA, Sabatino M, Castiello L, Stroncek D, Krensky AM. 15 kDa granulysin causes differentiation of monocytes to dendritic cells but lacks cytotoxic activity. J Immunol. 2012; 188:6119–6126. PMID: 22586033.
Article33. Tewary P, Yang D, de la Rosa G, Li Y, Finn MW, Krensky AM, Clayberger C, Oppenheim JJ. Granulysin activates antigen-presenting cells through TLR4 and acts as an immune alarmin. Blood. 2010; 116:3465–3474. PMID: 20660289.
Article34. Seishima M, Yamanaka S, Fujisawa T, Tohyama M, Hashimoto K. Reactivation of human herpesvirus (HHV) family members other than HHV-6 in drug-induced hypersensitivity syndrome. Br J Dermatol. 2006; 155:344–349. PMID: 16882173.
Article35. Kano Y, Hiraharas K, Sakuma K, Shiohara T. Several herpesviruses can reactivate in a severe drug-induced multiorgan reaction in the same sequential order as in graft-versus-host disease. Br J Dermatol. 2006; 155:301–306. PMID: 16882166.
Article36. Tohyama M, Hashimoto K, Yasukawa M, Kimura H, Horikawa T, Nakajima K, Urano Y, Matsumoto K, Iijima M, Shear NH. Association of human herpesvirus 6 reactivation with the flaring and severity of drug-induced hypersensitivity syndrome. Br J Dermatol. 2007; 157:934–940. PMID: 17854362.
Article37. Hashizume H, Aoshima M, Ito T, Seo N, Takigawa M, Yagi H. Emergence of circulating monomyeloid precursors predicts reactivation of human herpesvirus-6 in drug-induced hypersensitivity syndrome. Br J Dermatol. 2009; 161:486–488. PMID: 19485994.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- An Overview of Multiple Drug Hypersensitivity Syndrome
- Hypersensitivity Reactions to Antineoplastic Agents: Characteristics and Premedication Strategies
- Radiocontrast media hypersensitivity in the Asia Pacific region
- Update on the Management of Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug Hypersensitivity
- T-cell-mediated drug hypersensitivity: immune mechanisms and their clinical relevance