Lack of efficacy of a herbal preparation (RCM-102) for seasonal allergic rhinitis: a double blind, randomised, placebo-controlled trial
- Affiliations
-
- 1Traditional & Complementary Medicine Research Program, Health Innovations Research Institute, Discipline of Chinese Medicine, School of Health Sciences, RMIT University, Bundoora Campus, Victoria 3083, Australia. george.lenon@rmit.edu.au
- 2Department of Respiratory Medicine, Box Hill Hospital & Monash University, Box Hill, Victoria 3128, Australia.
- KMID: 2397481
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5415/apallergy.2012.2.3.187
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
A herbal preparation, known as RMIT Chinese Medicine 102 (RCM-102) consisting of eight herbs which demonstrates inhibition of the release of key inflammatory mediators associated with seasonal allergic rhinitis (SAR) was used. This study evaluated the efficacy and safety of RCM-102 for SAR.
OBJECTIVE
This study evaluated the efficacy and safety of RCM-102 for SAR.
METHODS
This randomised placebo-controlled trial involved subjects aged between 18 and 65 who were randomly assigned to either RCM-102 or a placebo group. After a two-week baseline period, all subjects took either RCM-102 or placebo capsules (two capsules each time, three times daily with a four hour interval) for a period of eight weeks. The primary end-points were the Five-Point Scale symptom scores. Rhinoconjunctivitis Quality of Life Questionnaire, relief medication usage, adverse events, kidney and liver function tests and full blood examination were secondary end-points. Intention-to-treat analysis was applied.
RESULTS
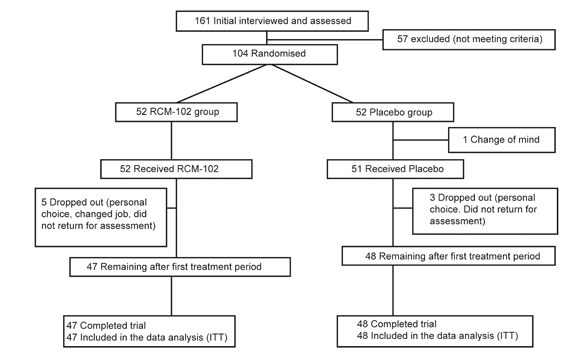
One hundred and four subjects were randomised with 52 in each group. Ninety-five subjects (47 and 48 subjects in RCM-102 and placebo groups) completed the trial. Nine subjects withdrew from the study prior to the end of the second treatment week. At the end of the trial, there were no significant differences between the two groups with respect to all outcome measures. There were no liver or kidney function abnormalities reported.
CONCLUSION
This mechanism-based RCM-102 was safe but not more beneficial than placebo for patients with SAR.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
In this issue of Asia Pacific Allergy
Sang-Heon Cho
Asia Pac Allergy. 2012;2(3):165-166. doi: 10.5415/apallergy.2012.2.3.165.Chinese Herbal Medicine to Treat Allergic Rhinitis: Evidence From a Meta-Analysis
Xu Zhang, Feng Lan, Yuan Zhang, Luo Zhang
Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2018;10(1):34-42. doi: 10.4168/aair.2018.10.1.34.Chinese Society of Allergy Guidelines for Diagnosis and Treatment of Allergic Rhinitis
Lei Cheng, Jianjun Chen, Qingling Fu, Shaoheng He, Huabin Li, Zheng Liu, Guolin Tan, Zezhang Tao, Dehui Wang, Weiping Wen, Rui Xu, Yu Xu, Qintai Yang, Chonghua Zhang, Gehua Zhang, Ruxin Zhang, Yuan Zhang, Bing Zhou, Dongdong Zhu, Luquan Chen, Xinyan Cui, Yuqin Deng, Zhiqiang Guo, Zhenxiao Huang, Zizhen Huang, Houyong Li, Jingyun Li, Wenting Li, Yanqing Li, Lin Xi, Hongfei Lou, Meiping Lu, Yuhui Ouyang, Wendan Shi, Xiaoyao Tao, Huiqin Tian, Chengshuo Wang, Min Wang, Nan Wang, Xiangdong Wang, Hui Xie, Shaoqing Yu, Renwu Zhao, Ming Zheng, Han Zhou, Luping Zhu, Luo Zhang
Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2018;10(4):300-353. doi: 10.4168/aair.2018.10.4.300.
Reference
-
1. Xue CC, Hügel HM, Li CG, Story DF. Efficacy, chemistry and pharmacology of Chinese herbal medicine for allergic rhinitis. Curr Med Chem. 2004. 11:1403–1421.
Article2. Xue CC, Li CG, Hügel HM, Story DF. Does acupuncture or Chinese herbal medicine have a role in the treatment of allergic rhinitis? Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006. 6:175–179.
Article3. Yuan R, Lin Y. Traditional Chinese medicine: an approach to scientific proof and clinical validation. Pharmacol Ther. 2000. 86:191–198.
Article4. Wang M, Lamers RJ, Korthout HA, van Nesselrooij JH, Witkamp RF, van der Heijden R, Voshol PJ, Havekes LM, Verpoorte R, van der Greef J. Metabolomics in the context of systems biology: bridging traditional Chinese medicine and molecular pharmacology. Phytother Res. 2005. 19:173–182.
Article5. Tang JL, Leung PC. An efficacy-driven approach to the research and development of traditional Chinese medicine. Hong Kong Med J. 2001. 7:375–380.6. Xue CC, Thien FC, Zhang JJ, Da Costa C, Li CG. Treatment for seasonal allergic rhinitis by Chinese herbal medicine: a randomized placebo controlled trial. Altern Ther Health Med. 2003. 9:80–87.7. Lenon GB, Li CG, Xue CC, Thien FC, Story DF. Inhibition of release of vasoactive and inflammatory mediators in airway and vascular tissues and macrophages by a chinese herbal medicine formula for allergic rhinitis. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2007. 4:209–217.
Article8. Lenon GB, Li CG, Xue CC, Thien FC, Story DF. Inhibition of inducible nitric oxide production and iNOS protein expression in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated rat aorta and Raw 264.7 macrophages by ethanol extract of a Chinese herbal medicine formula (RCM-101) for allergic rhinitis. J Ethnopharmacol. 2008. 116:547–553.
Article9. Lenon GB, Xue CC, Story DF, Thien FC, McPhee S, Li CG. Inhibition of release of inflammatory mediators in primary and cultured cells by a Chinese herbal medicine formula for allergic rhinitis. Chin Med. 2007. 2:2.10. Lenon GB, Xue CC, Story DF, Thien FC, Li CG. Inhibition of release of inflammatory mediators in rat peritoneal mast cells and murine macrophages by a Chinese herbal medicine formula (RCM-102). Phytother Res. 2009. 23:1270–1275.
Article11. Whitcup SM, Bradford R, Lue J, Schiffman RM, Abelson MB. Efficacy and tolerability of ophthalmic epinastine: a randomized, double-masked, parallel-group, active- and vehicle-controlled environmental trial in patients with seasonal allergic conjunctivitis. Clin Ther. 2004. 26:29–34.
Article12. Juniper EF, Thompson AK, Ferrie PJ, Roberts JN. Development and validation of the mini Rhinoconjunctivitis Quality of Life Questionnaire. Clin Exp Allergy. 2000. 30:132–140.
Article13. Lenon GB, Xue CL, Li CG. Pharmacological actions of Chinese herbal formula (RCM-102). 2004. Sydney: The Australian Health & Medical Research Congress.14. Kimata M, Shichijo M, Miura T, Serizawa I, Inagaki N, Nagai H. Effects of luteolin, quercetin and baicalein on immunoglobulin E-mediated mediator release from human cultured mast cells. Clin Exp Allergy. 2000. 30:501–508.
Article15. But P, Chang C. Chinese herbal medicine in the treatment of asthma and allergies. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 1996. 14:253–269.
Article16. Hirata JD, Swiersz LM, Zell B, Small R, Ettinger B. Does dong quai have estrogenic effects in postmenopausal women? A double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Fertil Steril. 1997. 68:981–986.
Article17. Borchers AT, Sakai S, Henderson GL, Harkey MR, Keen CL, Stern JS, Terasawa K, Gershwin ME. Shosaiko-to and other Kampo (Japanese herbal) medicines: a review of their immunomodulatory activities. J Ethnopharmacol. 2000. 73:1–13.
Article18. Chou CT, Kuo SC. The anti-inflammatory and anti-hyperuricemic effects of Chinese herbal formula danggui-nian-tong-tang on acute gouty arthritis: a comparative study with indomethacin and allopurinol. Am J Chin Med. 1995. 23:261–271.
Article19. Fung AY, Look PC, Chong LY, But PP, Wong E. A controlled trial of traditional Chinese herbal medicine in Chinese patients with recalcitrant atopic dermatitis. Int J Dermatol. 1999. 38:387–392.
Article20. Latchman Y, Banerjee P, Poulter LW, Rustin M, Brostoff J. Association of immunological changes with clinical efficacy in atopic eczema patients treated with traditional Chinese herbal therapy (Zemaphyte). Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 1996. 109:243–249.
Article21. Melchart D, Linde K, Weidenhammer W, Hager S, Shaw D, Bauer R. Liver enzyme elevations in patients treated with traditional Chinese medicine. JAMA. 1999. 282:28–29.
Article22. Lord GM, Tagore R, Cook T, Gower P, Pusey CD. Nephropathy caused by Chinese herbs in the UK. Lancet. 1999. 354:481–482.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Herbal anti-inflammatory immunomodulators as host modulators in chronic periodontitis patients: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, clinical trial
- The Effects of a Saffron Extract (affron ® ) on Menopausal Symptoms in Women during Perimenopause: A Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study
- Allergen-Specific Immunotherapy Against Allergic Respiratory Diseases
- Therapeutic Effects of Fermented Red Ginseng in Allergic Rhinitis: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study
- Efficacy and Safety of New Prokinetic Agent Benachio Q Solution(R) in Patients with Postprandial Distress Syndrome Subtype in Functional Dyspepsia: A Single-center, Randomized, Double-blind, Placebo-controlled Pilot Study