Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab.
2017 Sep;22(3):189-196. 10.6065/apem.2017.22.3.189.
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in long-term survivors of childhood-onset craniopharyngioma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Seoul National University Children’s Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. chshinpd@snu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2396139
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.6065/apem.2017.22.3.189
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Hypothalamic obesity in childhood-onset (CO-) craniopharyngioma patients may predispose to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). This study reviewed the characteristics of NAFLD associated with CO-craniopharyngioma.
METHODS
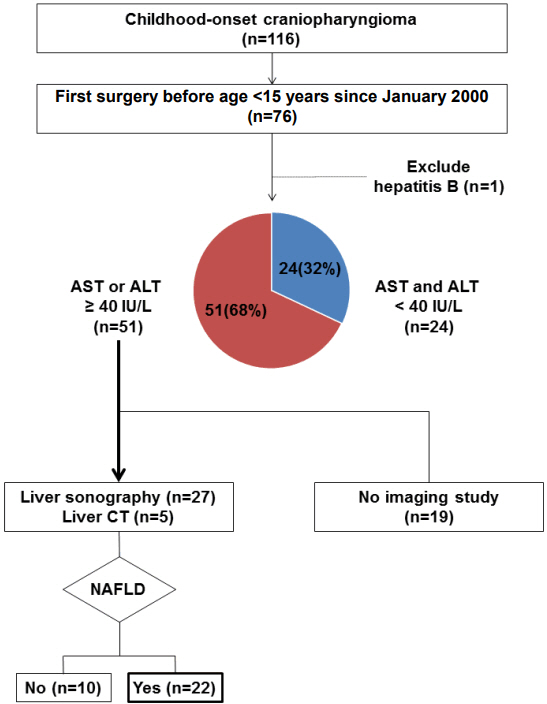
This study retrospectively reviewed 75 patients who underwent surgery for craniopharyngioma while younger than 15 years of age between 2000 and 2016.
RESULTS
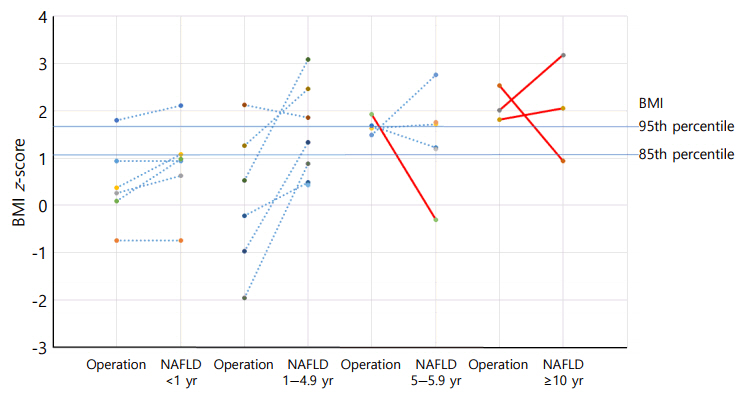
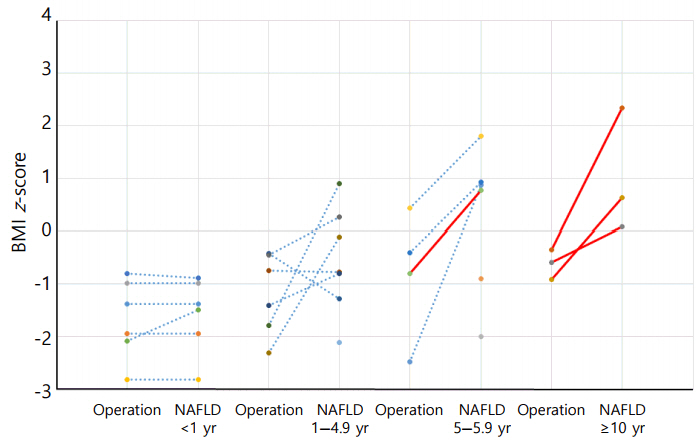
Elevated aspartate aminotransferase (AST) or alanine aminotransferase (ALT) above 40 IU/L was observed in 51 of the 75 (68%) CO-craniopharyngioma patients. Imaging studies were performed in 32 patients with elevated liver enzymes. The estimated prevalence of NAFLD in CO-craniopharyngioma was 47%. NAFLD was detected in 22 patients (male 59%, 4.3±4.0 years after first surgery). The mean age at the time of the initial operation was 9.1±2.9 years. Six patients (27.3%) were diagnosed within 1 year. Among the 19 patients with initial height and weight data, the body mass index (BMI) z-score (BMI_Z) at the time of diagnosis with NAFLD was 1.37±1.01 (range, -0.75 to 3.18), with 4 patients (18.2%) being overweight and 9 (40.9%) being obese. BMI_Z increased above BMI_Z at the time of the operation in 13 patients (68.4%). The increment in BMI_Z was 1.13 (range, 0.10-2.84). Seventeen patients did not receive growth hormone. An insulin-like growth factor-I level < 3rd percentile was observed in 19 patients.
CONCLUSION
NAFLD is common in survivors of CO-craniopharyngioma and may develop earlier. If the ALT or AST is above 40 IU/L, a diagnostic work-up should be started.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Müller HL. Craniopharyngioma. Endocr Rev. 2014; 35:513–43.
Article2. Sterkenburg AS, Hoffmann A, Gebhardt U, Warmuth-Metz M, Daubenbüchel AM, Müller HL. Survival, hypothalamic obesity, and neuropsychological/psychosocial status after childhood-onset craniopharyngioma: newly reported longterm outcomes. Neuro Oncol. 2015; 17:1029–38.
Article3. Kim JH, Choi JH. Pathophysiology and clinical characteristics of hypothalamic obesity in children and adolescents. Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2013; 18:161–7.
Article4. Iughetti L, Bruzzi P. Obesity and craniopharyngioma. Ital J Pediatr. 2011; 37:38.
Article5. Lustig RH. Hypothalamic obesity after craniopharyngioma: mechanisms, diagnosis, and treatment. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2011; 2:60.
Article6. Della Corte C, Mazzotta AR, Nobili V. Fatty liver disease and obesity in youth. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2016; 23:66–71.
Article7. Hoffmann A, Bootsveld K, Gebhardt U, Daubenbüchel AM, Sterkenburg AS, Müller HL. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and fatigue in long-term survivors of childhood-onset craniopharyngioma. Eur J Endocrinol. 2015; 173:389–97.
Article8. Ko JS. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2010; 56:6–14.
Article9. Lang IA, Galloway TS, Scarlett A, Henley WE, Depledge M, Wallace RB, et al. Association of urinary bisphenol A concentration with medical disorders and laboratory abnormalities in adults. JAMA. 2008; 300:1303–10.
Article10. Yoon JM, Ko JS, Seo JK, Shin CH, Yang SW, Moon JS, et al. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Children with Hypopituitarism. Korean J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2010; 13:51–7.
Article11. Marino L, Jornayvaz FR. Endocrine causes of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. World J Gastroenterol. 2015; 21:11053–76.
Article12. Müller HL, Gebhardt U, Teske C, Faldum A, Zwiener I, Warmuth-Metz M, et al. Post-operative hypothalamic lesions and obesity in childhood craniopharyngioma: results of the multinational prospective trial KRANIOPHARYNGEOM 2000 after 3-year follow-up. Eur J Endocrinol. 2011; 165:17–24.
Article13. Kendall-Taylor P, Jönsson PJ, Abs R, Erfurth EM, Koltowska-Häggström M, Price DA, et al. The clinical, metabolic and endocrine features and the quality of life in adults with childhood-onset craniopharyngioma compared with adult-onset craniopharyngioma. Eur J Endocrinol. 2005; 152:557–67.
Article14. Park SW, Jung HW, Lee YA, Shin CH, Yang SW, Cheon JE, et al. Tumor origin and growth pattern at diagnosis and surgical hypothalamic damage predict obesity in pediatric craniopharyngioma. J Neurooncol. 2013; 113:417–24.
Article15. Moon JS, Lee SY, Nam CM, Choi JM, Choe BK, Seo JW, et al. 2007 Korean National Growth Charts: review of developmental process and an outlook. Korean J Pediatr. 2008; 51:1–25.
Article16. Hyun SE, Lee BC, Suh BK, Chung SC, Ko CW, Kim HS, et al. Reference values for serum levels of insulin-like growth factor-I and insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 in Korean children and adolescents. Clin Biochem. 2012; 45:16–21.
Article17. Park JH, Kim SH, Park S, Park MJ. Alanine aminotransferase and metabolic syndrome in adolescents: the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey Study. Pediatr Obes. 2014; 9:411–8.18. Berardis S, Sokal E. Pediatric non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: an increasing public health issue. Eur J Pediatr. 2014; 173:131–9.
Article19. Crom DB, Smith D, Xiong Z, Onar A, Hudson MM, Merchant TE, et al. Health status in long-term survivors of pediatric craniopharyngiomas. J Neurosci Nurs. 2010; 42:323–8.
Article20. Mofrad P, Contos MJ, Haque M, Sargeant C, Fisher RA, Luketic VA, et al. Clinical and histologic spectrum of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease associated with normal ALT values. Hepatology. 2003; 37:1286–92.
Article21. Charlton MR, Burns JM, Pedersen RA, Watt KD, Heimbach JK, Dierkhising RA. Frequency and outcomes of liver transplantation for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in the United States. Gastroenterology. 2011; 141:1249–53.
Article22. Temple JL, Cordero P, Li J, Nguyen V, Oben JA. A guide to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in childhood and adolescence. Int J Mol Sci. 2016; 17(6):pii: E947. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17060947.
Article23. Holterman A, Gurria J, Tanpure S, DiSomma N. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and bariatric surgery in adolescents. Semin Pediatr Surg. 2014; 23:49–57.
Article24. Holterman AX, Guzman G, Fantuzzi G, Wang H, Aigner K, Browne A, et al. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in severely obese adolescent and adult patients. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2013; 21:591–7.
Article25. Feldstein AE, Charatcharoenwitthaya P, Treeprasertsuk S, Benson JT, Enders FB, Angulo P. The natural history of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in children: a follow-up study for up to 20 years. Gut. 2009; 58:1538–44.
Article26. Adams LA, Feldstein A, Lindor KD, Angulo P. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease among patients with hypothalamic and pituitary dysfunction. Hepatology. 2004; 39:909–14.
Article27. Holmer H, Pozarek G, Wirfält E, Popovic V, Ekman B, Björk J, et al. Reduced energy expenditure and impaired feeding-related signals but not high energy intake reinforces hypothalamic obesity in adults with childhood onset craniopharyngioma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010; 95:5395–402.
Article28. Simoneau-Roy J, O'Gorman C, Pencharz P, Adeli K, Daneman D, Hamilton J. Insulin sensitivity and secretion in children and adolescents with hypothalamic obesity following treatment for craniopharyngioma. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2010; 72:364–70.
Article29. Srinivasan S, Ogle GD, Garnett SP, Briody JN, Lee JW, Cowell CT. Features of the metabolic syndrome after childhood craniopharyngioma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004; 89:81–6.
Article30. Sahakitrungruang T, Klomchan T, Supornsilchai V, Wacharasindhu S. Obesity, metabolic syndrome, and insulin dynamics in children after craniopharyngioma surgery. Eur J Pediatr. 2011; 170:763–9.
Article31. Wainwright P, Byrne CD. Bidirectional Relationships and Disconnects between NAFLD and Features of the Metabolic Syndrome. Int J Mol Sci. 2016; 17:367.
Article32. Hong JW, Kim JY, Kim YE, Lee EJ. Metabolic parameters and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in hypopituitary men. Horm Metab Res. 2011; 43:48–54.
Article33. Matsumoto R, Fukuoka H, Iguchi G, Nishizawa H, Bando H, Suda K, et al. Long-term effects of growth hormone replacement therapy on liver function in adult patients with growth hormone deficiency. Growth Horm IGF Res. 2014; 24:174–9.
Article34. Geffner M, Lundberg M, Koltowska-Häggström M, Abs R, Verhelst J, Erfurth EM, et al. Changes in height, weight, and body mass index in children with craniopharyngioma after three years of growth hormone therapy: analysis of KIGS (Pfizer International Growth Database). J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004; 89:5435–40.
Article35. Hribal ML, Procopio T, Petta S, Sciacqua A, Grimaudo S, Pipitone RM, et al. Insulin-like growth factor-I, inflammatory proteins, and fibrosis in subjects with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013; 98:E304–8.
Article36. Schwimmer JB. Clinical advances in pediatric nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. 2016; 63:1718–25.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Long-term follow-up study and long-term care of childhood cancer survivors
- Noninvasive serum biomarkers for liver steatosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Current and future developments
- Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: pathogenesis and treatment
- Elevated serum bilirubin levels are inversely associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
- A case of hepatopulmonary syndrome in a child with fatty liver disease secondary to hypopituitarism after craniopharyngioma resection