J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2017 Nov;60(6):730-737. 10.3340/jkns.2017.0210.
Factors Associated Postoperative Hydrocephalus in Patients with Traumatic Acute Subdural Hemorrhage
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Myongji Hospital, Goyang, Korea. antanatia@gmail.com
- KMID: 2395794
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2017.0210
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
Postoperative hydrocephalus is a common complication following craniectomy in patients with traumatic brain injury, and affects patients' long-term outcomes. This study aimed to verify the risk factors associated with the development of hydrocephalus after craniectomy in patients with acute traumatic subdural hemorrhage (tSDH).
METHODS
Patients with acute traumatic SDH who had received a craniectomy between December 2005 and January 2016 were retrospectively assessed by reviewing the coexistence of other types of hemorrahges, measurable variables on computed tomography (CT) scans, and the development of hydrocephalus during the follow-up period.
RESULTS
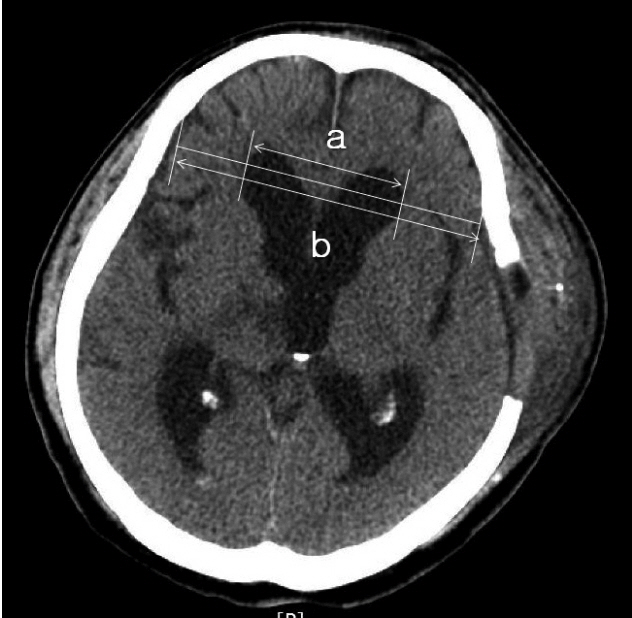
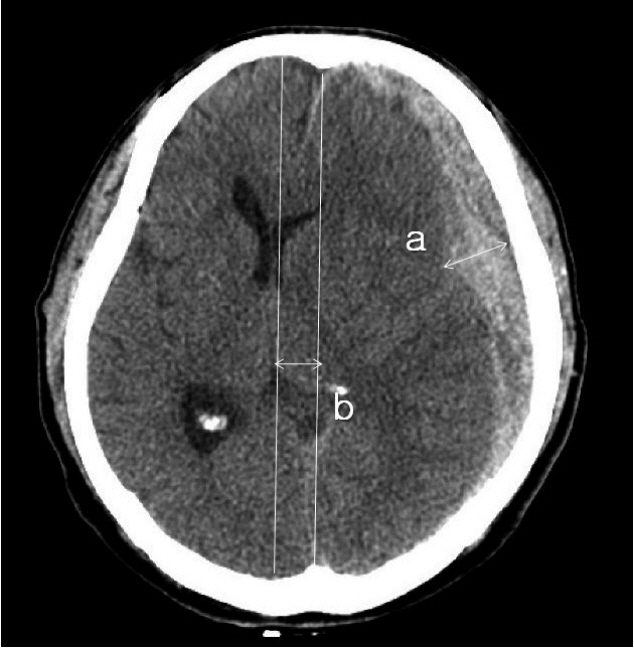
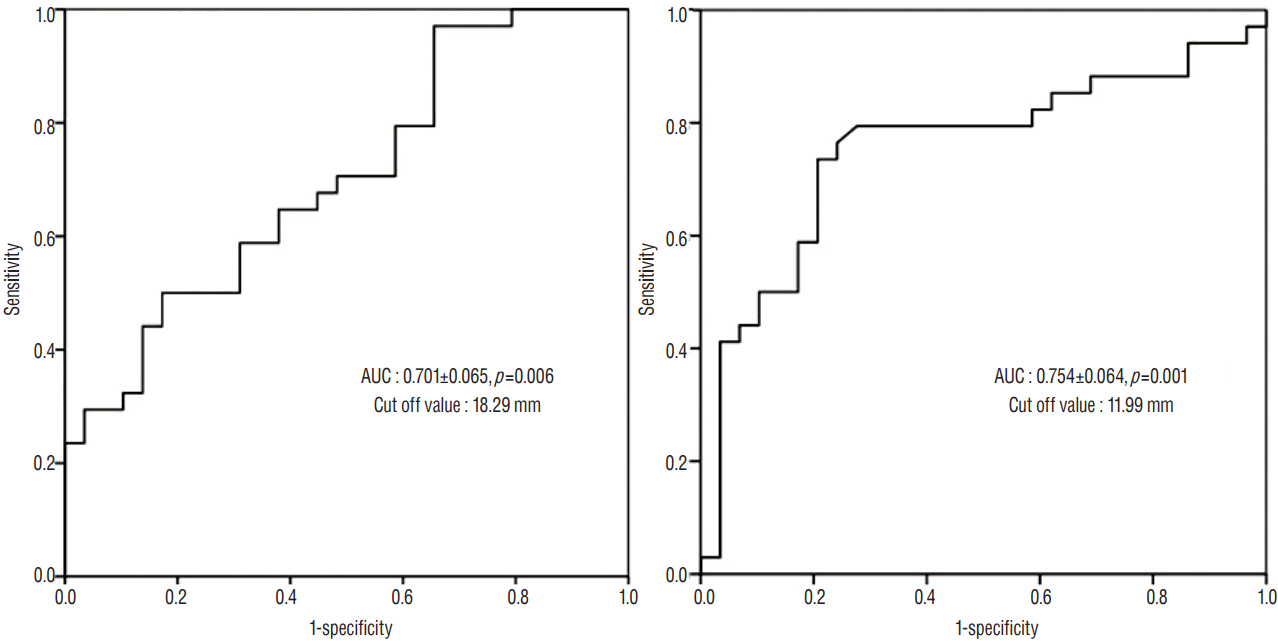
Data from a total of 63 patients who underwent unilateral craniectomy were analyzed. Postoperative hydrocephalus was identified in 34 patients (54%) via brain CT scans. Preoperative intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH) was associated with the development of hydrocephalus. Furthermore, the thickness of SDH (p=0.006) and the extent of midline shift before craniectomy (p=0.001) were significantly larger in patients with postoperative hydrocephalus. Indeed, multivariate analyses showed that the thickness of SDH (p=0.019), the extent of midline shift (p<0.001) and the coexistence of IVH (p=0.012) were significant risk factors for the development of postoperative hydrocephalus. However, the distance from the midline to the craniectomy margin was not an associated risk factor for postoperative hydrocephalus.
CONCLUSION
In patients with acute traumatic SDH with coexisting IVH, a large amount of SDH, and a larger midline shift, close follow-up is necessary for the early prediction of postoperative hydrocephalus. Furthermore, craniectomy margin need not be limited in acute traumatic SDH patients for the reason of postoperative hydrocephalus.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
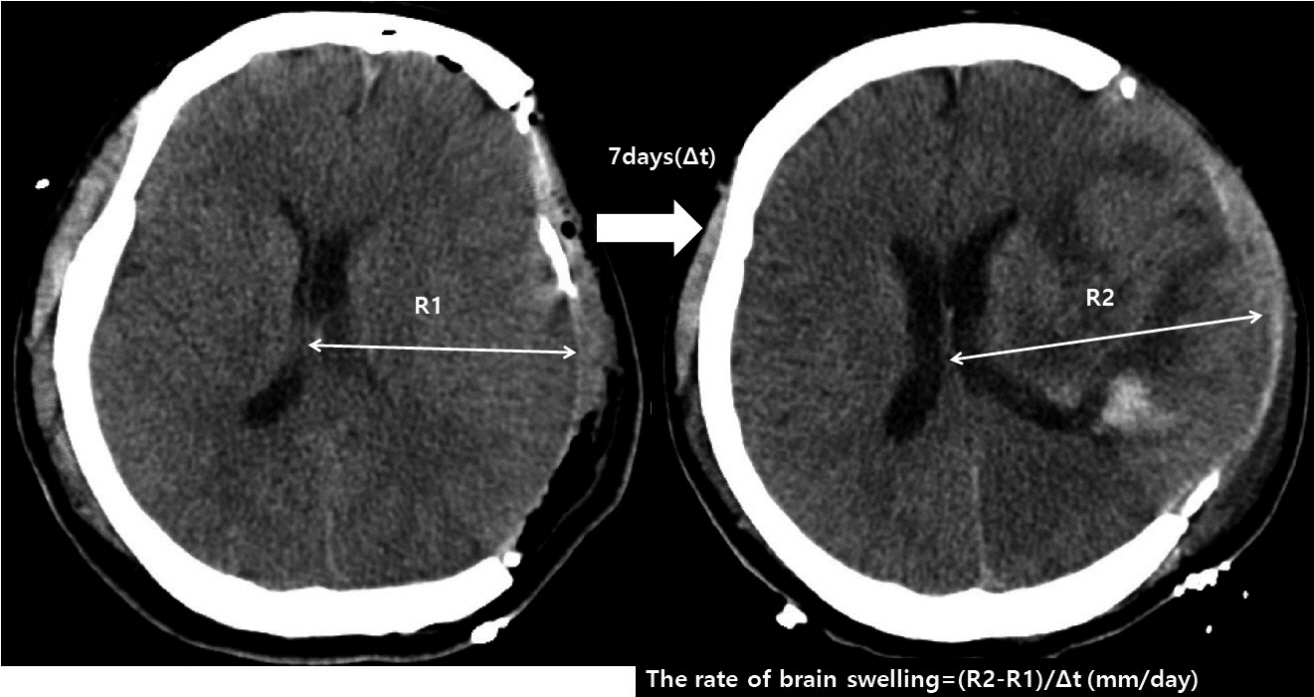
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Cardoso ER, Galbraith S. Posttraumatic hydrocephalus--a retrospective review. Surg Neurol. 23:261–264. 1985.
Article2. Carvi Y, Nievas MN, Hollerhage HG. Early combined cranioplasty and programmable shunt in patients with skull bone defects and CSF-circulation disorders. Neurol Res. 28:139–144. 2006.
Article3. Choi I, Park HK, Chang JC, Cho SJ, Choi SK, Byun BJ. Clinical factors for the development of posttraumatic hydrocephalus after decompressive craniectomy. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 43:227–231. 2008.
Article4. De Bonis P, Pompucci A, Mangiola A, Rigante L, Anile C. Post-traumatic hydrocephalus after decompressive craniectomy: an underestimated risk factor. J Neurotrauma. 27:1965–1970. 2010.
Article5. De Bonis P, Sturiale CL, Anile C, Gaudino S, Mangiola A, Martucci M, et al. Decompressive craniectomy, interhemispheric hygroma and hydrocephalus: a timeline of events? Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 115:1308–1312. 2013.
Article6. Foroglou G, Zander E. Post-traumatic hydrocephalus and measurement of cerebrospinal fluid pressure. Acta Radiol Diagn (Stockh). 13:524–530. 1972.7. Fotakopoulos G, Tsianaka E, Siasios G, Vagkopoulos K, Fountas K. Posttraumatic hydrocephalus after decompressive craniectomy in 126 patients with severe traumatic brain injury. J Neurol Surg A Cent Eur Neurosurg. 77:88–92. 2016.
Article8. Jeon SW, Choi JH, Jang TW, Moon SM, Hwang HS, Jeong JH. Risk factors associated with subdural hygroma after decompressive craniectomy in patients with traumatic brain injury: a comparative study. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 49:355–358. 2011.
Article9. Jiao QF, Liu Z, Li S, Zhou LX, Li SZ, Tian W, et al. Influencing factors for posttraumatic hydrocephalus in patients suffering from severe traumatic brain injuries. Chin J Traumatol. 10:159–162. 2007.10. Ki HJ, Lee HJ, Lee HJ, Yi JS, Yang JH, Lee IW. The risk factors for hydrocephalus and subdural hygroma after decompressive craniectomy in head injured patients. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 58:254–261. 2015.
Article11. Marmarou A, Foda MA, Bandoh K, Yoshihara M, Yamamoto T, Tsuji O, et al. Posttraumatic ventriculomegaly: hydrocephalus or atrophy? A new approach for diagnosis using CSF dynamics. J Neurosurg. 85:1026–1035. 1996.
Article12. Tian HL, Xu T, Hu J, Cui YH, Chen H, Zhou LF. Risk factors related to hydrocephalus after traumatic subarachnoid hemorrhage. Surg Neurol. 69:241–246. discussion 246. 2008.
Article13. Vedantam A, Yamal JM, Hwang H, Robertson CS, Gopinath SP. Factors associated with shunt-dependent hydrocephalus after decompressive craniectomy for traumatic brain injury. J Neurosurg. 2017. [Epub ahead of print].
Article14. Wang QP, Ma JP, Zhou ZM, You C. Impact of operation details on hydrocephalus after decompressive craniectomy. Neurosciences (Riyadh). 21:10–16. 2016.
Article15. Wani AA, Ramzan AU, Tanki H, Malik NK, Dar BA. Hydrocephalus after decompressive craniotomy: a case series. Pediatr neurosurg. 49:287–291. 2013.
Article16. Waziri A, Fusco D, Mayer SA, McKhann GM 2nd, Connolly ES Jr. Postoperative hydrocephalus in patients undergoing decompressive hemicraniectomy for ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke. Neurosurgery. 61:489–493. discussion 493–494. 2007.
Article17. Yang XF, Wen L, Shen F, Li G, Lou R, Liu WG, et al. Surgical complications secondary to decompressive craniectomy in patients with a head injury: a series of 108 consecutive cases. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 150:1241–1247. discussion 1248. 2008.
Article18. Yuan Q, Wu X, Yu J, Sun Y, Li Z, Du Z, et al. Subdural hygroma following decompressive craniectomy or non-decompressive craniectomy in patients with traumatic brain injury: clinical features and risk factors. Brain Inj. 29:971–980. 2015.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical Analysis of Post-traumatic Hydrocephalus
- Traumatic Intraventricular Hemorrhage: 2 Cases Report
- Clinical Analysis of Subdural Hematoma after Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt for Hydrocephalus
- Risk Factors for the Post-Traumatic Hydrocephalus Following Decompressive Craniectomy in Severe Traumatic Injury Patients
- Risk Factors for Development of Chronic Hydrocephalus Following Aneurysmal Subarachnoidal Hemorrhage