Korean J Neurotrauma.
2012 Oct;8(2):110-114. 10.13004/kjnt.2012.8.2.110.
Risk Factors for the Post-Traumatic Hydrocephalus Following Decompressive Craniectomy in Severe Traumatic Injury Patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Daejeon St. Mary's Hospital, Daejeon, Korea. kope95@hanmail.net
- KMID: 1427722
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.13004/kjnt.2012.8.2.110
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
The goal of this study was to assess the incidence and risk factors for post-traumatic hydrocephalus (PTH) following decompressive craniectomy (DC). An additional objective was to investigate the relationship between hydrocephalus and subdural hygroma (SDG) after DC.
METHODS
We conducted a retrospective study of 94 patients who were admitted to our department between 2007 and 2010 with severe head injury requiring DC. Post-traumatic hydrocephalus was defined as: frontal horn index (FHI) > or =0.4 or modified FHI > or =0.33 accompanying transependymal edema; the presence of either clinical worsening or failure to make neurological improvement over time; and clinical improvement after ventriculoperitoneal shunt. Post-traumatic SDG was defined as the presence of low density at computerized tomography (CT) of more than 5mm thickness.
RESULTS
Among the 94 patients, we could follow up more than 3 months and obtain more than 4 serial CT scans in 41 patients. PTH developed in 29.3% (12/41) and SDG developed in 48.8% (20/41) of these patients. The development of PTH was significantly associated with delayed craniplasty after DC and with interhemispheric SDG. No relationship was found between PTH and age, sex, Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) score, intraventricular hemorrhage, subarachnoid hemorrhage, midline shift, basal cistern effacement, or cortical opening during DC.
CONCLUSION
Hydrocephalus occurred in 29.3% of the patients with severe traumatic brain injury who required DC. Delayed cranioplasty and interhemispheric SDG after DC were risk factors for the development of PTH.
MeSH Terms
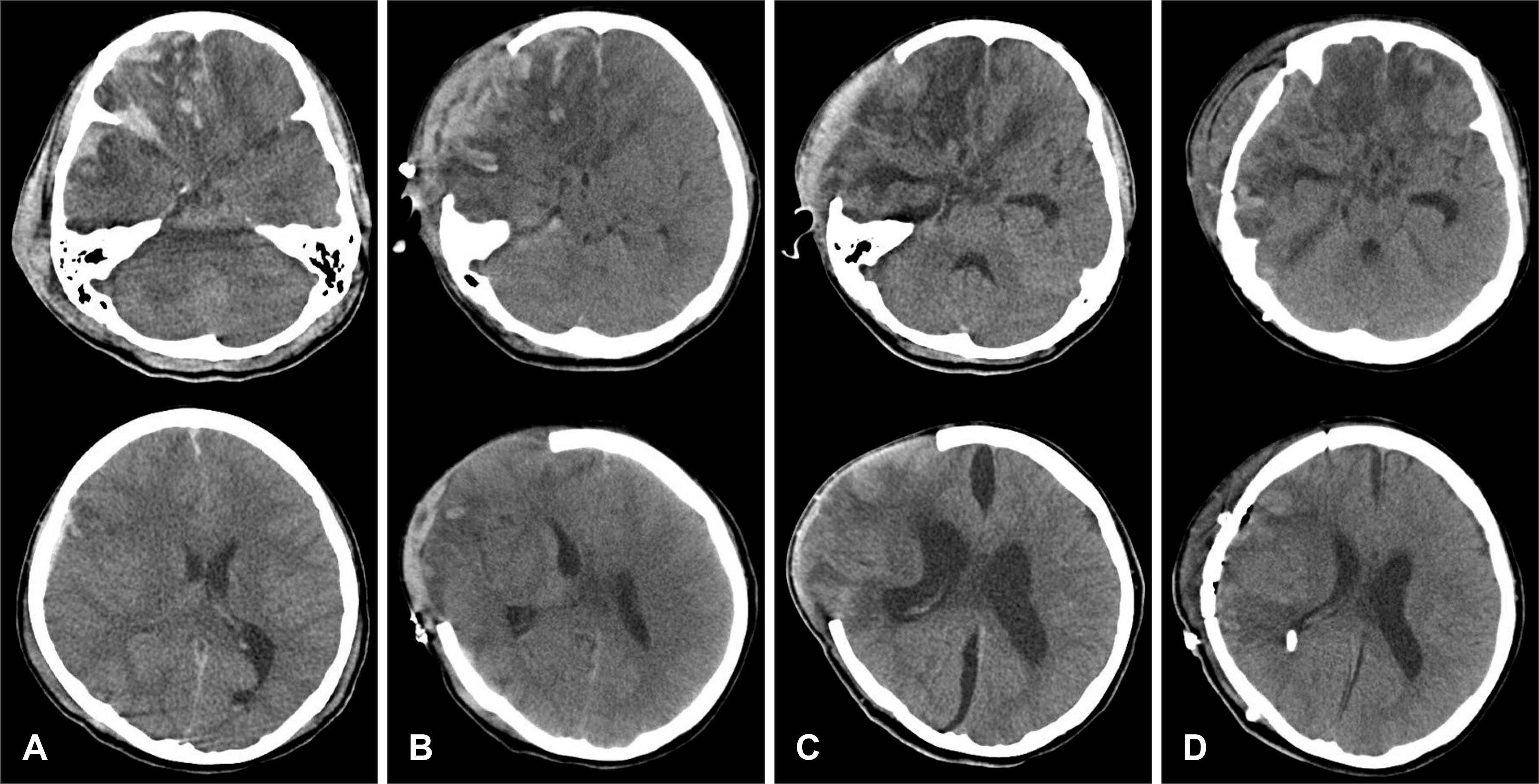
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
The Risk Factors for Hydrocephalus and Subdural Hygroma after Decompressive Craniectomy in Head Injured Patients
Hee Jong Ki, Hyung-Jin Lee, Hong-Jae Lee, Jin-Seok Yi, Ji-Ho Yang, Il-Woo Lee
J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2015;58(3):254-261. doi: 10.3340/jkns.2015.58.3.254.
Reference
-
1). Aarabi B., Chesler D., Maulucci C., Blacklock T., Alexander M. Dynamics of subdural hygroma following decompressive craniectomy: a comparative study. Neurosurg Focus 26: E8. 2009.
Article2). Aarabi B., Hesdorffer DC., Ahn ES., Aresco C., Scalea TM., Eisenberg HM. Outcome following decompressive craniectomy for malignant swelling due to severe head injury. J Neurosurg. 104:469–479. 2006.
Article3). Choi I., Park HK., Chang JC., Cho SJ., Choi SK., Byun BJ. Clinical factors for the development of posttraumatic hydrocephalus after decompressive craniectomy. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 43:227–231. 2008.
Article4). De Bonis P., Pompucci A., Mangiola A., Rigante L., Anile C. Posttraumatic hydrocephalus after decompressive craniectomy: an underestimated risk factor. J Neurotrauma. 27:1965–1970. 2010.
Article5). Foltz EL., Ward AA Jr. Communicating hydrocephalus from subarachnoid bleeding. J Neurosurg. 13:546–566. 1956.
Article6). Greene KA., Marciano FF., Johnson BA., Jacobowitz R., Spetzler RF., Harrington TR. Impact of traumatic subarachnoid hemorrhage on outcome in nonpenetrating head injury. Part I: A proposed computerized tomography grading scale. J Neurosurg. 83:445–452. 1995.7). Honeybul S. Complications of decompressive craniectomy for head injury. J Clin Neurosci. 17:430–435. 2010.
Article8). Honeybul S., Ho KM. Incidence and risk factors for post-traumatic hydrocephalus following decompressive craniectomy for intractable intracranial hypertension and evacuation of mass lesions. J Neurotrauma. 29:1872–1878. 2012.
Article9). Honeybul S., Ho KM. Long-term complications of decompressive craniectomy for head injury. J Neurotrauma. 28:929–935. 2011.
Article10). Huh PW., Yoo DS., Cho KS., Park CK., Kang SG., Park YS, et al. Diagnostic method for differentiating external hydrocephalus from simple subdural hygroma. J Neurosurg. 105:65–70. 2006.
Article11). Jeon SW., Choi JH., Jang TW., Moon SM., Hwang HS., Jeong JH. Risk factors associated with subdural hygroma after decompressive craniectomy in patients with traumatic brain injury: a comparative study. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 49:355–358. 2011.12). Kaen A., Jimenez-Roldan L., Alday R., Gomez PA., Lagares A., Alén JF, et al. Interhemispheric hygroma after decompressive craniectomy: does it predict posttraumatic hydrocephalus? J Neurosurg. 113:1287–1293. 2010.
Article13). Lee KS. The pathogenesis and clinical significance of traumatic subdural hygroma. Brain Inj. 12:595–603. 1998.
Article14). Lee KS., Bae WK., Bae HG., Yun IG. The fate of traumatic subdural hygroma in serial computed tomographic scans. J Korean Med Sci. 15:560–568. 2000.
Article15). Lee KS., Bae WK., Park YT., Yun IG. The pathogenesis and fate of traumatic subdural hygroma. Br J Neurosurg. 8:551–558. 1994.
Article16). Ohno K., Suzuki R., Masaoka H., Matsushima Y., Inaba Y., Monma S. Chronic subdural haematoma preceded by persistent traumatic subdural fluid collection. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 50:1694–1697. 1987.
Article17). Stiver SI. Complications of decompressive craniectomy for traumatic brain injury. Neurosurg Focus 26: E7. 2009.
Article18). Tian HL., Xu T., Hu J., Cui YH., Chen H., Zhou LF. Risk factors related to hydrocephalus after traumatic subarachnoid hemorrhage. Surg Neurol. 69:241–246. discussion 246. 2008.
Article19). Vanneste J., Augustijn P., Davies GA., Dirven C., Tan WF. Normal-pressure hydrocephalus. Is cisternography still useful in selecting patients for a shunt? Arch Neurol. 49:366–370. 1992.
Article20). Waziri A., Fusco D., Mayer SA., McKhann GM 2nd., Connolly ES Jr. Postoperative hydrocephalus in patients undergoing decompressive hemicraniectomy for ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke. Neurosurgery. 61:489–493. discussion 493-494. 2007.
Article21). Yang XF., Wen L., Shen F., Li G., Lou R., Liu WG, et al. Surgical complications secondary to decompressive craniectomy in patients with a head injury: a series of 108 consecutive cases. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 150:1241–1247. discussion 1248. 2008.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Pushed-out Scrylic Bone Flap n Post-traumatic Hydrocephalus
- Middle Cerebral Artery Compromise Associated With Post-traumatic Hydrocephalus: A Case Report
- Decompressive Craniectomy in Traumatic Brain Injury: A Review Article
- A Reappraisal of the Necessity of a Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt After Decompressive Craniectomy in Traumatic Brain Injury
- Factors Associated Postoperative Hydrocephalus in Patients with Traumatic Acute Subdural Hemorrhage