Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol.
2017 Sep;10(3):254-258. 10.21053/ceo.2016.01137.
Usefulness of Allerkin House Dust Mite Extract for Nasal Provocation Testing
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Inha University College of Medicine, Incheon, Korea. inhaorl@inha.ac.kr
- KMID: 2395740
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.21053/ceo.2016.01137
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
We evaluated the clinical usefulness of Allerkin (Lofarma) for nasal provocation testing (NPT) in patients with rhinitis symptoms, by examining changes in nasal symptoms and acoustic parameters after exposure to house dust mite (HDM) extract.
METHODS
Twenty patients (16 males and 4 females, mean age: 29.6±14.6 years) were enrolled. We performed skin prick test (SPT) before and 15 and 30 minutes after intranasal challenge with Allerkin HDM extract, and we evaluated symptom changes (nasal obstruction, rhinorrhea, sneezing, and itching) using a visual analogue scale. We also evaluated changes in acoustic parameters such as total nasal volume (TNV) and minimal cross-sectional area (MCA) before and after challenge.
RESULTS
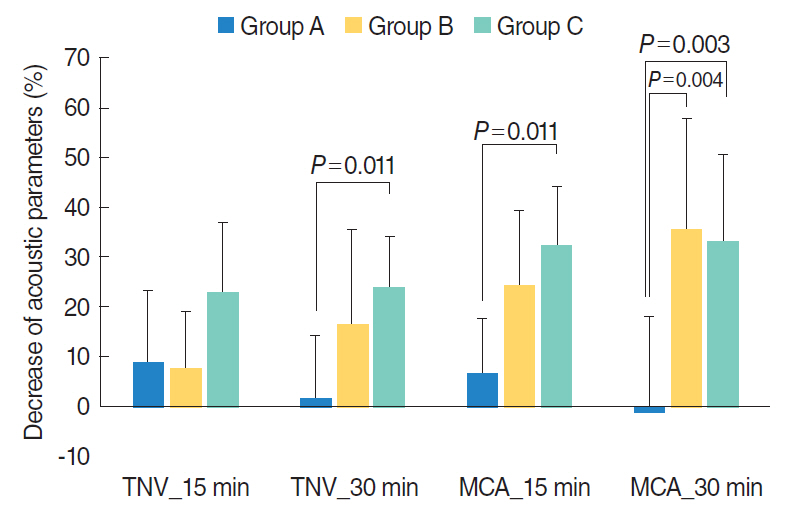
Group A (the nonallergic group, n=8) showed negative results for all tested aeroallergens in SPT and nonprovocative results ( < 25% decrease of TNV and MCA from the baseline value) in NPT. Group B (the allergic group, n=7) exhibited strongly positive results (wheal size larger than that of histamine) for HDM allergens on SPT. Group C (the local allergic group, n=5) showed negative results on SPT, but a provocative response on NPT (>29% decrease in TNV/MCA from the baseline value). Patients in group C showed significant aggravation of nasal obstruction compared to those in group A (P < 0.05). Thirty minutes after HDM challenge, patients in groups B and C showed significantly greater decreases in MCA compared to those in group A (P < 0.01).
CONCLUSION
Allerkin HDM extract can be a useful provocative agent in NPT for diagnosing allergic rhinitis and local allergic rhinitis.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Korean Modification of the Nasal Provocation Test With House Dust Mite Antigen Following the EAACI Guidelines
Soo Hyun Joo, Ki Jong Hyun, Young Hyo Kim
Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 2021;14(4):382-389. doi: 10.21053/ceo.2020.00563.
Reference
-
1. Bousquet J, Khaltaev N, Cruz AA, Denburg J, Fokkens WJ, Togias A, et al. Allergic Rhinitis and its Impact on Asthma (ARIA) 2008 update (in collaboration with the World Health Organization, GA(2)LEN and AllerGen). Allergy. 2008; Apr. 63 Suppl 86:8–160.2. Kim JH, Yoon MG, Seo DH, Kim BS, Ban GY, Ye YM, et al. Detection of allergen specific antibodies from nasal secretion of allergic rhinitis patients. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2016; Jul. 8(4):329–37.
Article3. Greiner AN, Hellings PW, Rotiroti G, Scadding GK. Allergic rhinitis. Lancet. 2011; Dec. 378(9809):2112–22.
Article4. Cibella F, Ferrante G, Cuttitta G, Bucchieri S, Melis MR, La Grutta S, et al. The burden of rhinitis and rhinoconjunctivitis in adolescents. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2015; Jan. 7(1):44–50.
Article5. Gosepath J, Amedee RG, Mann WJ. Nasal provocation testing as an international standard for evaluation of allergic and nonallergic rhinitis. Laryngoscope. 2005; Mar. 115(3):512–6.
Article6. Kim YH, Yang TY, Lee DY, Ko KJ, Shin SH, Jang TY. Evaluation of acoustic rhinometry in a nasal provocation test with allergic rhinitis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2008; Jul. 139(1):120–3.
Article7. Rondon C, Romero JJ, Lopez S, Antunez C, Martin-Casanez E, Torres MJ, et al. Local IgE production and positive nasal provocation test in patients with persistent nonallergic rhinitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007; Apr. 119(4):899–905.8. Rondon C, Fernandez J, Lopez S, Campo P, Dona I, Torres MJ, et al. Nasal inflammatory mediators and specific IgE production after nasal challenge with grass pollen in local allergic rhinitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009; 124(5):1005–11. e1.9. Kim YH, Jang TY. Proposed diagnostic standard using visual analogue scale and acoustic rhinometry in nasal provocation test in allergic patients. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2011; Jun. 38(3):340–6.
Article10. Senna GE, Andri G, Dama AR, Falagiani P, Andri L. Local nasal immunotherapy: efficacy and tolerability of two different administration schedules in grass pollen rhinitis. Allergol Immunopathol (Madr). 2000; Jul-Aug. 28(4):238–42.11. Palma-Carlos AG, Santos AS, Pregal A. Short-term efficacy of nasal immunotherapy. Allerg Immunol (Paris). 1998; Jan. 30(1):14–7.12. Cserhati E, Mezei G. Nasal immunotherapy in pollen-sensitive children. Allergy. 1997; 52(33 Suppl):40–4.13. Powe DG, Jagger C, Kleinjan A, Carney AS, Jenkins D, Jones NS. ‘Entopy’: localized mucosal allergic disease in the absence of systemic responses for atopy. Clin Exp Allergy. 2003; Oct. 33(10):1374–9.
Article14. Rondon C, Canto G, Blanca M. Local allergic rhinitis: a new entity, characterization and further studies. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010; Feb. 10(1):1–7.15. Huggins KG, Brostoff J. Local production of specific IgE antibodies in allergic-rhinitis patients with negative skin tests. Lancet. 1975; Jul. 2(7926):148–50.16. Rondon C, Dona I, Lopez S, Campo P, Romero JJ, Torres MJ, et al. Seasonal idiopathic rhinitis with local inflammatory response and specific IgE in absence of systemic response. Allergy. 2008; Oct. 63(10):1352–8.17. Jang TY, Kim YH. Nasal provocation test is useful for discriminating allergic, nonallergic, and local allergic rhinitis. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2015; Jul-Aug. 29(4):e100–4.
Article18. Litvyakova LI, Baraniuk JN. Nasal provocation testing: a review. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2001; Apr. 86(4):355–64.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Correlation of Appearance of Nasal Eosinophils with Levels of Total Eosinophil Counts, Total IgE, and House Dust Mite Specific IgE in Children with Symptoms of Rhinitis
- Distribution of House Dust Mites in the Bedroom of Patients with Allergic Rhinitis in Pusan Area
- House Dust Mite Allergic Rhinitis Model in C57BL/6 Mice
- Usefulness of House Dust Mite Nasal Provocation Test in Asthma
- Local production of specific IgE antibody to house dust mite in nasal polyp tissues