Nutr Res Pract.
2017 Dec;11(6):461-469. 10.4162/nrp.2017.11.6.461.
Novel glutathione-containing dry-yeast extracts inhibit eosinophilia and mucus overproduction in a murine model of asthma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Food and Nutrition, Hallym University, 1, Hallymdaehak-gil, Chuncheon, Gangwon 24252, Korea. yhkang@hallym.ac.kr
- 2Mediense Co. Ltd., 32 Soyanggang-ro, Chuncheon, Gangwon 24232, Korea.
- KMID: 2395300
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4162/nrp.2017.11.6.461
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
/OBSECTIVE: Airway inflammation by eosinophils, neutrophils and alveolar macrophages is a characteristic feature of asthma that leads to pathological subepithelial thickening and remodeling. Our previous study showed that oxidative stress in airways resulted in eosinophilia and epithelial apoptosis. The current study investigated whether glutathione-containing dry yeast extract (dry-YE) ameliorated eosinophilia, goblet cell hyperplasia and mucus overproduction. MATERIALS/METHOD: This study employed 2 µg/mL lipopolysaccharide (LPS)- or 20 ng/mL eotaxin-1-exposed human bronchial epithelial cells and ovalbumin (OVA)-challenged mice. Dry-YE employed in this study contained a significant amount of glutathione (140 mg in 100 g dry yeast).
RESULTS
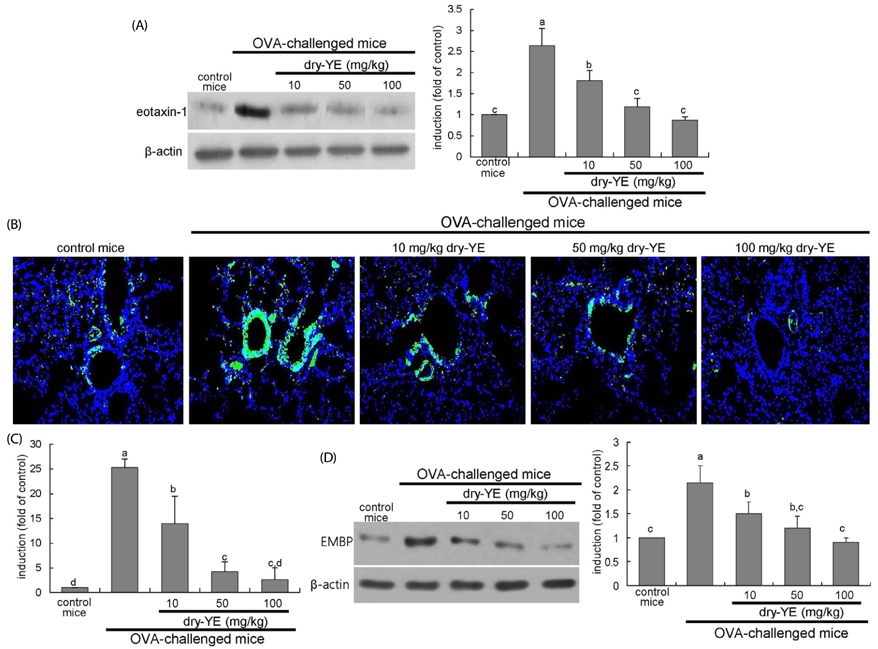
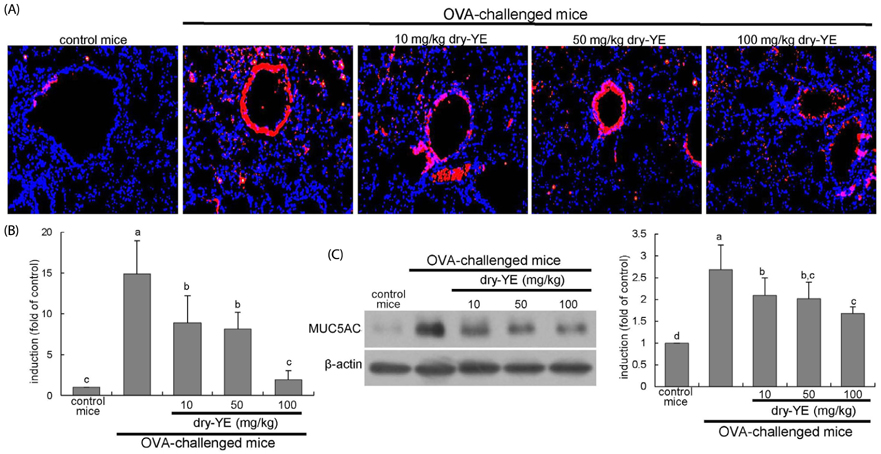
Human bronchial epithelial cell eotaxin-1 and mucin 5AC (MUC5AC) were markedly induced by the endotoxin LPS, which was dose-dependently attenuated by nontoxic dry-YE at 10-50 µg/mL. Moreover, dry-YE inhibited the MUC5AC induction enhanced by eotaxin-1, indicating that eotaxin-1-mediated eosinophilia may prompt the MUC5AC induction. Oral supplementation with 10-100 mg/kg dry-YE inhibited inflammatory cell accumulation in airway subepithelial regions with a reduction of lung tissue level of intracellular adhesion molecule-1. In addition, ≥ 50 mg/kg dry-YE diminished the lung tissue levels of eotaxin-1, eosinophil major basic protein and MUC5AC in OVA-exposed mice. Alcian blue/periodic acid schiff staining revealed that the dry-YE supplementation inhibited goblet cell hyperplasia and mucus overproduction in the trachea and bronchiolar airways of OVA-challenged mice.
CONCLUSIONS
Oxidative stress may be involved in the induction of eotaxin-1 and MUC5AC by endotoxin episode and OVA challenge. Dry-YE effectively ameliorated oxidative stress-responsive epithelial eosinophilia and mucus-secreting goblet cell hyperplasia in cellular and murine models of asthma.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
Apoptosis
Asthma*
Chemokine CCL11
Eosinophil Major Basic Protein
Eosinophilia*
Eosinophils
Epithelial Cells
Glutathione
Goblet Cells
Humans
Hyperplasia
Inflammation
Lung
Macrophages, Alveolar
Mice
Mucin 5AC
Mucins
Mucus*
Neutrophils
Ovalbumin
Ovum
Oxidative Stress
Trachea
Yeasts
Chemokine CCL11
Eosinophil Major Basic Protein
Glutathione
Mucin 5AC
Mucins
Ovalbumin
Figure
Reference
-
1. Holgate ST. The sentinel role of the airway epithelium in asthma pathogenesis. Immunol Rev. 2011; 242:205–219.
Article2. Pelaia G, Vatrella A, Busceti MT, Gallelli L, Calabrese C, Terracciano R, Maselli R. Cellular mechanisms underlying eosinophilic and neutrophilic airway inflammation in asthma. Mediators Inflamm. 2015; 2015:879783.
Article3. Possa SS, Leick EA, Prado CM, Martins MA, Tibério IF. Eosinophilic inflammation in allergic asthma. Front Pharmacol. 2013; 4:46.
Article4. Ohashi Y, Motojima S, Fukuda T, Makino S. Airway hyperresponsiveness, increased intracellular spaces of bronchial epithelium, and increased infiltration of eosinophils and lymphocytes in bronchial mucosa in asthma. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1992; 145:1469–1476.
Article5. Saitoh T, Kusunoki T, Yao T, Kawano K, Kojima Y, Miyahara K, Onoda J, Yokoi H, Ikeda K. Relationship between epithelial damage or basement membrane thickness and eosinophilic infiltration in nasal polyps with chronic rhinosinusitis. Rhinology. 2009; 47:275–279.
Article6. Pease JE. Asthma, allergy and chemokines. Curr Drug Targets. 2006; 7:3–12.
Article7. Pope SM, Zimmermann N, Stringer KF, Karow ML, Rothenberg ME. The eotaxin chemokines and CCR3 are fundamental regulators of allergen-induced pulmonary eosinophilia. J Immunol. 2005; 175:5341–5350.
Article8. Kew KM, Quinn M, Quon BS, Ducharme FM. Increased versus stable doses of inhaled corticosteroids for exacerbations of chronic asthma in adults and children. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016; CD007524.
Article9. Beeh KM. The Role of Bronchodilators in preventing exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Tuberc Respir Dis (Seoul). 2016; 79:241–247.
Article10. Papathanassiou E, Loukides S, Bakakos P. Severe asthma: anti-IgE or anti-IL-5? Eur Clin Respir J. 2016; 3:31813.
Article11. Patel TR, Sur S. IgE and eosinophils as therapeutic targets in asthma. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017; 17:42–49.
Article12. Hosoki K, Itazawa T, Boldogh I, Sur S. Neutrophil recruitment by allergens contributes to allergic sensitization and allergic inflammation. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016; 16:45–50.
Article13. Thomson NC. Novel approaches to the management of noneosinophilic asthma. Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2016; 10:211–234.
Article14. Rose MC, Nickola TJ, Voynow JA. Airway mucus obstruction: Mucin glycoproteins, MUC gene regulation and goblet cell hyperplasia. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2001; 25:533–537.
Article15. Kim V, Criner GJ. Chronic bronchitis and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2013; 187:228–237.
Article16. Boucherat O, Boczkowski J, Jeannotte L, Delacourt C. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of goblet cell metaplasia in the respiratory airways. Exp Lung Res. 2013; 39:207–216.
Article17. Lambrecht BN, Hammad H. The airway epithelium in asthma. Nat Med. 2012; 18:684–692.
Article18. Lai H, Rogers DF. New pharmacotherapy for airway mucus hypersecretion in asthma and COPD: targeting intracellular signaling pathways. J Aerosol Med Pulm Drug Deliv. 2010; 23:219–231.
Article19. Takeyama K, Tamaoki J, Kondo M, Isono K, Nagai A. Role of epidermal growth factor receptor in maintaining airway goblet cell hyperplasia in rats sensitized to allergen. Clin Exp Allergy. 2008; 38:857–865.
Article20. Tanabe T, Kanoh S, Tsushima K, Yamazaki Y, Kubo K, Rubin BK. Clarithromycin inhibits interleukin-13-induced goblet cell hyperplasia in human airway cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2011; 45:1075–1083.
Article21. Davis CW, Dickey BF. Regulated airway goblet cell mucin secretion. Annu Rev Physiol. 2008; 70:487–512.
Article22. Bruse S, Petersen H, Weissfeld J, Picchi M, Willink R, Do K, Siegfried J, Belinsky SA, Tesfaigzi Y. Increased methylation of lung cancer-associated genes in sputum DNA of former smokers with chronic mucous hypersecretion. Respir Res. 2014; 15:2.
Article23. Lin CH, Shen ML, Zhou N, Lee CC, Kao ST, Wu DC. Protective effects of the polyphenol sesamin on allergen-induced T(H)2 responses and airway inflammation in mice. PLoS One. 2014; 9:e96091.
Article24. Gong JH, Shin D, Han SY, Kim JL, Kang YH. Kaempferol suppresses eosionphil infiltration and airway inflammation in airway epithelial cells and in mice with allergic asthma. J Nutr. 2012; 142:47–56.
Article25. O'Donnell R, Breen D, Wilson S, Djukanovic R. Inflammatory cells in the airways in COPD. Thorax. 2006; 61:448–454.26. Swaminathan GJ, Myszka DG, Katsamba PS, Ohnuki LE, Gleich GJ, Acharya KR. Eosinophil-granule major basic protein, a C-type lectin, binds heparin. Biochemistry. 2005; 44:14152–14158.
Article27. Cho IH, Gong JH, Kang MK, Lee EJ, Park JH, Park SJ, Kang YH. Astragalin inhibits airway eotaxin-1 induction and epithelial apoptosis through modulating oxidative stress-responsive MAPK signaling. BMC Pulm Med. 2014; 14:122.
Article28. Lee IT, Yang CM. Role of NADPH oxidase/ROS in pro-inflammatory mediators-induced airway and pulmonary diseases. Biochem Pharmacol. 2012; 84:581–590.
Article29. Qu J, Li Y, Zhong W, Gao P, Hu C. Recent developments in the role of reactive oxygen species in allergic asthma. J Thorac Dis. 2017; 9:E32–E43.
Article30. Zuo L, Otenbaker NP, Rose BA, Salisbury KS. Molecular mechanisms of reactive oxygen species-related pulmonary inflammation and asthma. Mol Immunol. 2013; 56:57–63.
Article31. Pompella A, Visvikis A, Paolicchi A, De Tata V, Casini AF. The changing faces of glutathione, a cellular protagonist. Biochem Pharmacol. 2003; 66:1499–1503.
Article32. Wood LG, Wark PA, Garg ML. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of resveratrol in airway disease. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2010; 13:1535–1548.
Article33. Shin D, Park SH, Choi YJ, Kim YH, Antika LD, Habibah NU, Kang MK, Kang YH. Dietary compound kaempferol inhibits airway thickening induced by allergic reaction in a bovine serum albumin-induced model of asthma. Int J Mol Sci. 2015; 16:29980–29995.
Article34. Hazlewood LC, Wood LG, Hansbro PM, Foster PS. Dietary lycopene supplementation suppresses Th2 responses and lung eosinophilia in a mouse model of allergic asthma. J Nutr Biochem. 2011; 22:95–100.
Article35. Ashino S, Takeda K, Li H, Taylor V, Joetham A, Pine PR, Gelfand EW. Janus kinase 1/3 signaling pathways are key initiators of TH2 differentiation and lung allergic responses. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014; 133:1162–1174.
Article36. Wijerathne CUB, Seo CS, Song JW, Park HS, Moon OS, Won YS, Kwon HJ, Son HY. Isoimperatorin attenuates airway inflammation and mucus hypersecretion in an ovalbumin-induced murine model of asthma. Int Immunopharmacol. 2017; 49:67–76.
Article37. Hao Y, Kuang Z, Xu Y, Walling BE, Lau GW. Pyocyanin-induced mucin production is associated with redox modification of FOXA2. Respir Res. 2013; 14:82.
Article38. Jung JY, Lee KY, Lee MY, Jung D, Cho ES, Son HY. Antioxidant and antiasthmatic effects of saucerneol D in a mouse model of airway inflammation. Int Immunopharmacol. 2011; 11:698–705.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effects of Korean Red Ginseng Extracts on Airway Hyperresponsiveness and Inflammation in a Murine Asthma Model
- Effect of Dexamethasone on Airway Hyperresponsiveness and Airway Inflammation in Ovalbumin-induced Murine Asthma Model
- Identification of Wild Yeast Strains and Analysis of Their beta-Glucan and Glutathione Levels for Use in Makgeolli Brewing
- Recent Advances in the Development of Novel Drug Candidates for Regulating the Secretion of Pulmonary Mucus
- Role of Matrix Metalloproteinase in the Pathogenesis of Bronchial Asthma