Ann Dermatol.
2017 Dec;29(6):826-827. 10.5021/ad.2017.29.6.826.
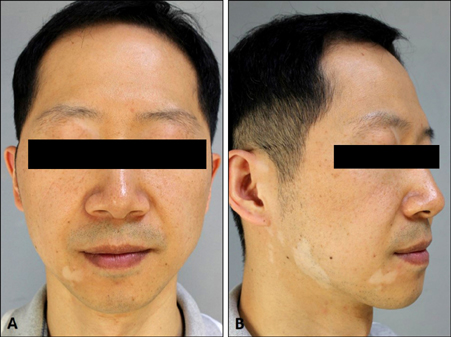
A Type II Segmental Vitiligo Developed under Infliximab Treatment for Ulcerative Colitis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. drsshong@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2395206
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2017.29.6.826
Abstract
- No abstract available.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Webb KC, Tung R, Winterfield LS, Gottlieb AB, Eby JM, Henning SW, et al. Tumour necrosis factor-α inhibition can stabilize disease in progressive vitiligo. Br J Dermatol. 2015; 173:641–650.
Article2. Toussirot É, Aubin F. Paradoxical reactions under TNF-α blocking agents and other biological agents given for chronic immune-mediated diseases: an analytical and comprehensive overview. RMD Open. 2016; 2:e000239.
Article3. Ramírez-Hernández M, Marras C, Martínez-Escribano JA. Infliximab-induced vitiligo. Dermatology. 2005; 210:79–80.
Article4. Snook JA, de Silva HJ, Jewell DP. The association of autoimmune disorders with inflammatory bowel disease. Q J Med. 1989; 72:835–840.5. Song MS, Hann SK, Ahn PS, Im S, Park YK. Clinical study of vitiligo. Ann Dermatol. 1994; 6:22–30.
Article