Ann Dermatol.
2017 Apr;29(2):219-222. 10.5021/ad.2017.29.2.219.
Paraneoplastic Pemphigus Associated with a Malignant Thymoma: A Case of Persistent and Refractory Oral Ulcerations Following Thymectomy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Cutaneous Biology Research Institute, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. kimsc@yuhs.ac
- 2Department of Dermatology, Severance Hospital, Cutaneous Biology Research Institute, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Dermatology, Kurume University School of Medicine, and Kurume University Institute of Cutaneous Cell Biology, Kurume, Japan.
- KMID: 2394848
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2017.29.2.219
Abstract
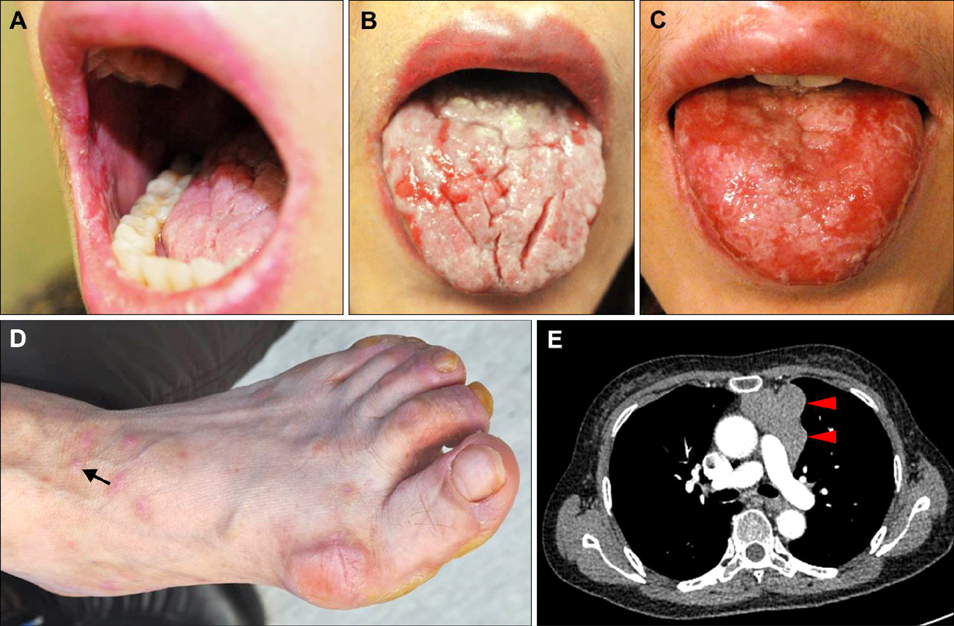
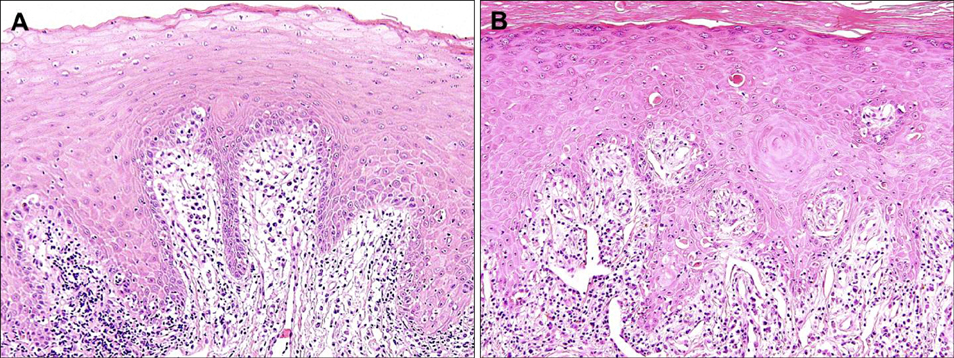
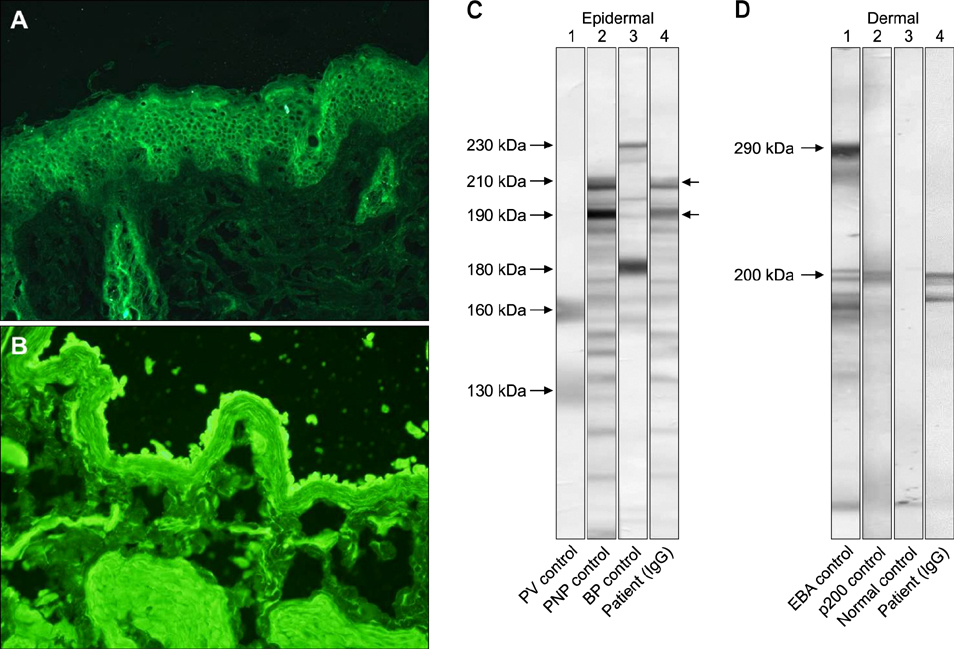
- Paraneoplastic pemphigus is a rare, life-threatening autoimmune mucocutaneous blistering disease associated with underlying neoplasia, commonly lymphoproliferative tumors. Herein we report a case of paraneoplastic pemphigus with a unique autoantibody profile associated with a malignant thymoma. A 56-year-old female patient presented with relapsing oral ulcerations accompanied by erythematous papules and patches on her extremities for 2 months. Skin and mucosal biopsies identified interface dermatitis with lichenoid lymphocytic infiltration in the upper dermis. Immunoblotting and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays revealed that the patient had multiple autoantibodies against desmoglein 1, desmocollin 1, 2, 3, laminin gamma-1, envoplakin, and periplakin. The skin lesions completely healed following thymectomy and systemic corticosteroid therapy, but the oral ulcerations persisted through a follow-up period of over 2 years.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Anhalt GJ, Kim SC, Stanley JR, Korman NJ, Jabs DA, Kory M, et al. Paraneoplastic pemphigus. An autoimmune mucocutaneous disease associated with neoplasia. N Engl J Med. 1990; 323:1729–1735.
Article2. Lee SE, Kim SC. Paraneoplastic pemphigus. Dermatol Sin. 2010; 28:1–14.
Article3. Nguyen VT, Ndoye A, Bassler KD, Shultz LD, Shields MC, Ruben BS, et al. Classification, clinical manifestations, and immunopathological mechanisms of the epithelial variant of paraneoplastic autoimmune multiorgan syndrome: a reappraisal of paraneoplastic pemphigus. Arch Dermatol. 2001; 137:193–206.4. Liu Q, Bu DF, Li D, Zhu XJ. Genotyping of HLA-I and HLA-II alleles in Chinese patients with paraneoplastic pemphigus. Br J Dermatol. 2008; 158:587–591.
Article5. Sehgal VN, Srivastava G. Paraneoplastic pemphigus/paraneoplastic autoimmune multiorgan syndrome. Int J Dermatol. 2009; 48:162–169.
Article6. Choi Y, Nam KH, Lee JB, Lee JY, Ihm CW, Lee SE, et al. Retrospective analysis of 12 Korean patients with paraneoplastic pemphigus. J Dermatol. 2012; 39:973–981.
Article7. Ohzono A, Sogame R, Li X, Teye K, Tsuchisaka A, Numata S, et al. Clinical and immunological findings in 104 cases of paraneoplastic pemphigus. Br J Dermatol. 2015; 173:1447–1452.
Article8. Oh SJ, Lee SE, Hashimoto T, Kim SC. A case of paraneoplastic pemphigus associated with Castleman disease reacting with multiple autoantigens, including the p200 protein. Br J Dermatol. 2016; 174:930–932.
Article9. Hong WJ, Lee SE, Chang SE, Hashimoto T, Kim SC. Paraneoplastic pemphigus associated with metastatic lymphoepithelioma-like carcinoma originating from the thyroid gland. Br J Dermatol. 2015; 172:831–834.
Article10. Kelly S, Schifter M, Fulcher DA, Lin MW. Paraneoplastic pemphigus: two cases of intra-abdominal malignancy presenting solely as treatment refractory oral ulceration. J Dermatol. 2015; 42:300–304.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Paraneoplastic Pemphigus Presenting with Generalized Exfoliative Dermatitis
- Paraneoplastic Encephalitis Associated with Thymoma: A Case Report
- Minimal Change Nephrotic Syndrome Developed after Thymectomy in a Patient with Thymoma
- Pure Red Cell Aplasia Associated with Good Syndrome
- Effect of Thymectomy in Myasthenia Gravis