Clin Endosc.
2017 Sep;50(5):437-445. 10.5946/ce.2017.132.
Endoscopic Therapeutic Approach for Dysplasia in Inflammatory Bowel Disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. sungnoh.hong@samsung.com
- KMID: 2394743
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2017.132
Abstract
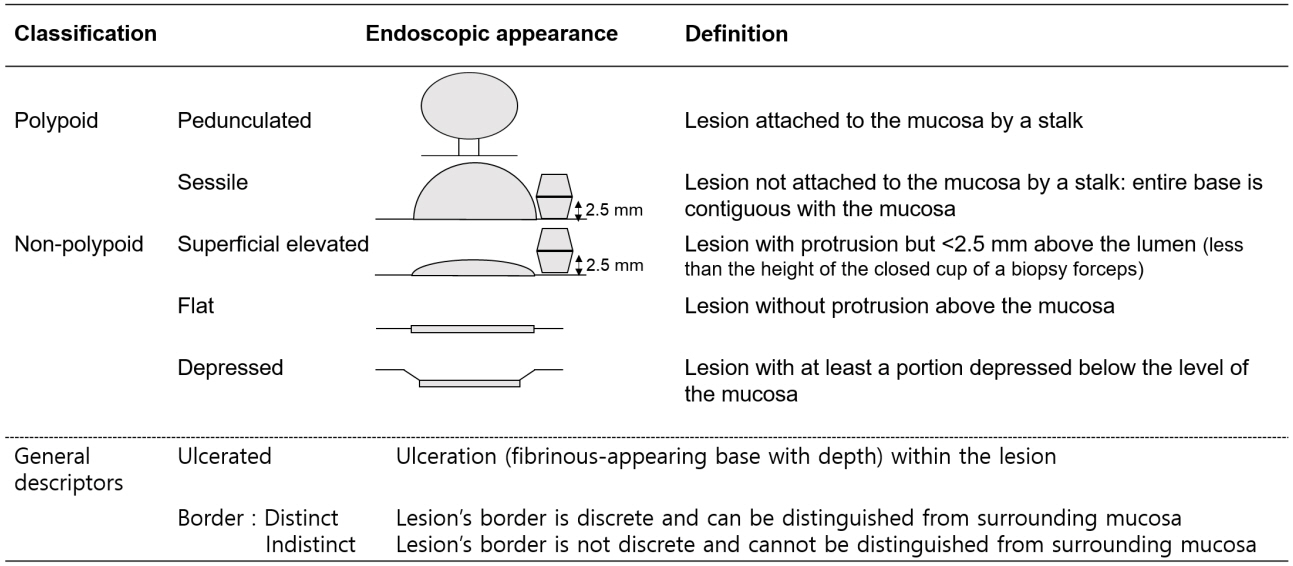
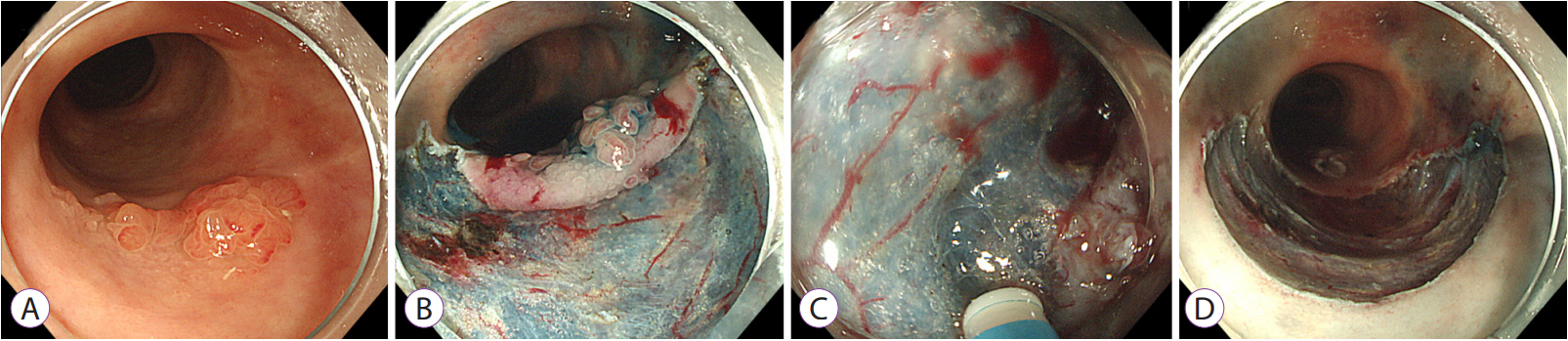
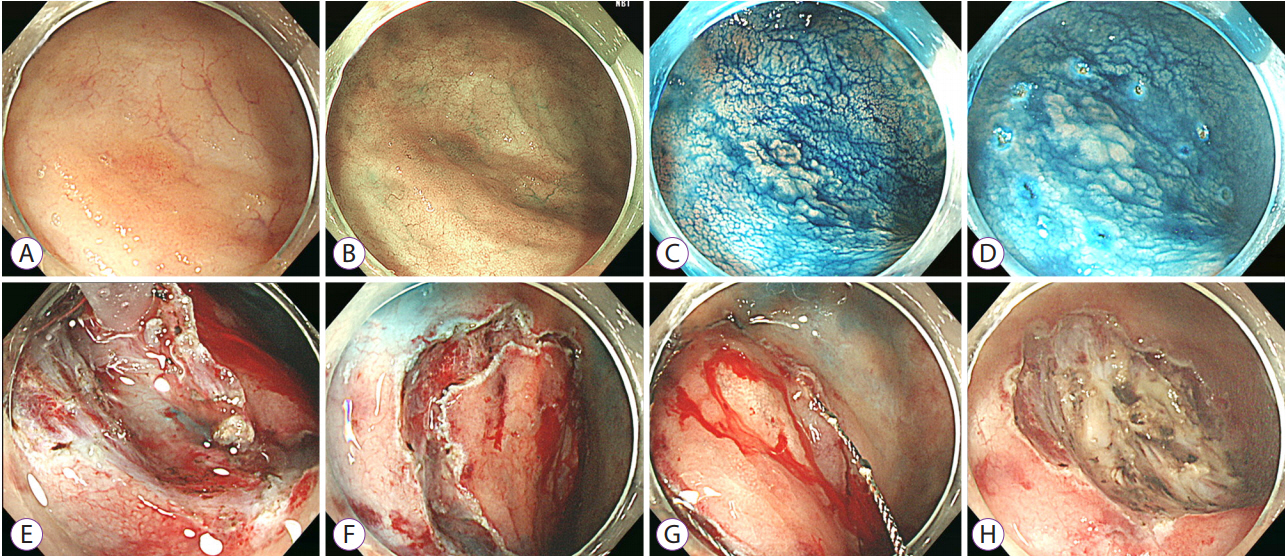
- Long-standing intestinal inflammation in patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) induces dysplastic change in the intestinal mucosa and increases the risk of subsequent colorectal cancer. The evolving endoscopic techniques and technologies, including dye spraying methods and high-definition images, have been replacing random biopsies and have been revealed as more practical and efficient for detection of dysplasia in IBD patients. In addition, they have potential usefulness in detailed characterization of lesions and in the assessment of endoscopic resectability. Most dysplastic lesions without an unclear margin, definite ulceration, non-lifting sign, and high index of malignant change with suspicion for lymph node or distant metastases can be removed endoscopically. However, endoscopic resection of dysplasia in chronic IBD patients is usually difficult because it is often complicated by submucosal fibrosis. In patients with dysplasias that demonstrate submucosa fibrosis or a large size (≥20 mm), endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) or ESD with snaring (simplified or hybrid ESD) is an alternative option and may avoid a colectomy. However, a standardized endoscopic therapeutic approach for dysplasia in IBD has not been established yet, and dedicated specialized endoscopists with interest in IBD are needed to fully investigate recent emerging techniques and technologies.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ekbom A, Helmick C, Zack M, Adami HO. Ulcerative colitis and colorectal cancer. A population-based study. N Engl J Med. 1990; 323:1228–1233.2. Ekbom A, Helmick C, Zack M, Adami HO. Increased risk of large-bowel cancer in Crohn’s disease with colonic involvement. Lancet. 1990; 336:357–359.
Article3. Söderlund S, Brandt L, Lapidus A, et al. Decreasing time-trends of colorectal cancer in a large cohort of patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology. 2009; 136:1561–1567. quiz 1818-1819.
Article4. Bernstein CN, Blanchard JF, Kliewer E, Wajda A. Cancer risk in patients with inflammatory bowel disease: a population-based study. Cancer. 2001; 91:854–862.5. Jess T, Simonsen J, Jørgensen KT, Pedersen BV, Nielsen NM, Frisch M. Decreasing risk of colorectal cancer in patients with inflammatory bowel disease over 30 years. Gastroenterology. 2012; 143:375–381.e1. quiz e13-e14.
Article6. Jess T, Rungoe C, Peyrin-Biroulet L. Risk of colorectal cancer in patients with ulcerative colitis: a meta-analysis of population-based cohort studies. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012; 10:639–645.
Article7. Devroede G, Taylor WF. On calculating cancer risk and survival of ulcerative colitis patients with the life table method. Gastroenterology. 1976; 71:505–509.
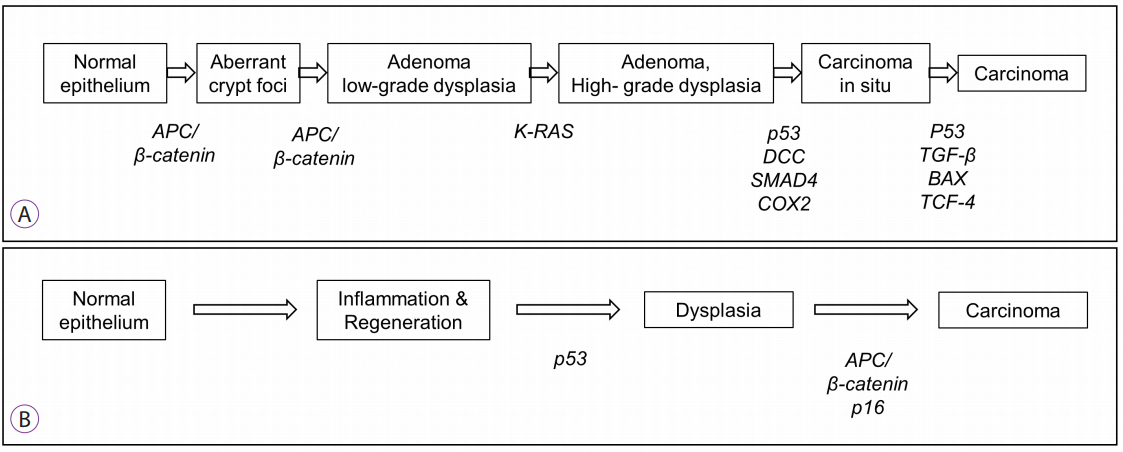
Article8. Matkowskyj KA, Chen ZE, Rao MS, Yang GY. Dysplastic lesions in inflammatory bowel disease: molecular pathogenesis to morphology. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2013; 137:338–350.
Article9. Lutgens MW, van Oijen MG, van der Heijden GJ, Vleggaar FP, Siersema PD, Oldenburg B. Declining risk of colorectal cancer in inflammatory bowel disease: an updated meta-analysis of population-based cohort studies. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2013; 19:789–799.10. Magro F, Gionchetti P, Eliakim R, et al. Third European evidence-based consensus on diagnosis and management of ulcerative colitis. Part 1: definitions, diagnosis, extra-intestinal manifestations, pregnancy, cancer surveillance, surgery, and ileo-anal pouch disorders. J Crohns Colitis. 2017; 11:649–670.
Article11. Farraye FA, Odze RD, Eaden J, et al. AGA medical position statement on the diagnosis and management of colorectal neoplasia in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology. 2010; 138:738–745.
Article12. Rutter MD, Saunders BP, Wilkinson KH, Kamm MA, Williams CB, Forbes A. Most dysplasia in ulcerative colitis is visible at colonoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2004; 60:334–339.
Article13. Laine L, Kaltenbach T, Barkun A, McQuaid KR, Subramanian V, Soetikno R. SCENIC international consensus statement on surveillance and management of dysplasia in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology. 2015; 148:639–651.e28.
Article14. Leedham SJ, Graham TA, Oukrif D, et al. Clonality, founder mutations, and field cancerization in human ulcerative colitis-associated neoplasia. Gastroenterology. 2009; 136:542–550.e6.
Article15. Issa JP, Ahuja N, Toyota M, Bronner MP, Brentnall TA. Accelerated age-related CpG island methylation in ulcerative colitis. Cancer Res. 2001; 61:3573–3577.16. Lyda MH, Noffsinger A, Belli J, Fischer J, Fenoglio-Preiser CM. Multifocal neoplasia involving the colon and appendix in ulcerative colitis: pathological and molecular features. Gastroenterology. 1998; 115:1566–1573.
Article17. Graham TA, McDonald SA, Wright NA. Field cancerization in the GI tract. Future Oncol. 2011; 7:981–993.
Article18. Marcellin P, Gane E, Buti M, et al. Regression of cirrhosis during treatment with tenofovir disoproxil fumarate for chronic hepatitis B: a 5-year open-label follow-up study. Lancet. 2013; 381:468–475.
Article19. Blackstone MO, Riddell RH, Rogers BH, Levin B. Dysplasia-associated lesion or mass (DALM) detected by colonoscopy in long-standing ulcerative colitis: an indication for colectomy. Gastroenterology. 1981; 80:366–374.
Article20. ASGE Technology Committee. High-definition and high-magnification endoscopes. Gastrointest Endosc. 2014; 80:919–927.21. Odze R. Diagnostic problems and advances in inflammatory bowel disease. Mod Pathol. 2003; 16:347–358.
Article22. Soetikno R, Kaltenbach T, McQuaid KR, et al. Paradigm shift in the surveillance and management of dysplasia in inflammatory bowel disease (West). Dig Endosc. 2016; 28:266–273.
Article23. Imai K, Hotta K, Yamaguchi Y, et al. Should laterally spreading tumors granular type be resected en bloc in endoscopic resections? Surg Endosc. 2014; 28:2167–2173.
Article24. Kudo S, Kashida H, Tamura T, et al. Colonoscopic diagnosis and management of nonpolypoid early colorectal cancer. World J Surg. 2000; 24:1081–1090.
Article25. Hayashi N, Tanaka S, Hewett DG, et al. Endoscopic prediction of deep submucosal invasive carcinoma: validation of the narrow-band imaging international colorectal endoscopic (NICE) classification. Gastrointest Endosc. 2013; 78:625–632.
Article26. Ikematsu H, Matsuda T, Emura F, et al. Efficacy of capillary pattern type IIIA/IIIB by magnifying narrow band imaging for estimating depth of invasion of early colorectal neoplasms. BMC Gastroenterol. 2010; 10:33.
Article27. American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy Standards of Practice Committee, Shergill AK, Lightdale JR, et al. The role of endoscopy in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastrointest Endosc. 2015; 81:1101–1121. e1-e13.
Article28. Rubin DT, Rothe JA, Hetzel JT, Cohen RD, Hanauer SB. Are dysplasia and colorectal cancer endoscopically visible in patients with ulcerative colitis? Gastrointest Endosc. 2007; 65:998–1004.
Article29. Mowat C, Cole A, Windsor A, et al. Guidelines for the management of inflammatory bowel disease in adults. Gut. 2011; 60:571–607.
Article30. Uraoka T, Parra-Blanco A, Yahagi N. Colorectal endoscopic submucosal dissection: is it suitable in western countries? J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013; 28:406–414.
Article31. Repici A, Hassan C, De Paula Pessoa D, et al. Efficacy and safety of endoscopic submucosal dissection for colorectal neoplasia: a systematic review. Endoscopy. 2012; 44:137–150.
Article32. Kuroki Y, Hoteya S, Mitani T, et al. Endoscopic submucosal dissection for residual/locally recurrent lesions after endoscopic therapy for colorectal tumors. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010; 25:1747–1753.
Article33. Wanders LK, Dekker E, Pullens B, Bassett P, Travis SP, East JE. Cancer risk after resection of polypoid dysplasia in patients with longstanding ulcerative colitis: a meta-analysis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014; 12:756–764.
Article34. Iacucci M, Uraoka T, Fort Gasia M, Yahagi N. Novel diagnostic and therapeutic techniques for surveillance of dysplasia in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014; 28:361–370.
Article35. Smith LA, Baraza W, Tiffin N, Cross SS, Hurlstone DP. Endoscopic resection of adenoma-like mass in chronic ulcerative colitis using a combined endoscopic mucosal resection and cap assisted submucosal dissection technique. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2008; 14:1380–1386.
Article36. Leighton JA, Shen B, Baron TH, et al. ASGE guideline: endoscopy in the diagnosis and treatment of inflammatory bowel disease. Gastrointest Endosc. 2006; 63:558–565.
Article37. Kornbluth A, Sachar DB; Practice Parameters Committee of the American College of Gastroenterology. Ulcerative colitis practice guidelines in adults: American college of gastroenterology, practice parameters committee. Am J Gastroenterol. 2010; 105:501–523. quiz 524.
Article38. Velayos FS, et al. Incidence and prognosis of colorectal dysplasia in inflammatory bowel disease: a population-based study from Olmsted County, Minnesota. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2006; 12:669–676.39. Rubin PH, Friedman S, Harpaz N, et al. Colonoscopic polypectomy in chronic colitis: conservative management after endoscopic resection of dysplastic polyps. Gastroenterology. 1999; 117:1295–1300.
Article40. Blonski W, Kundu R, Furth EF, Lewis J, Aberra F, Lichtenstein GR. High-grade dysplastic adenoma-like mass lesions are not an indication for colectomy in patients with ulcerative colitis. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2008; 43:817–820.
Article41. Goldstone R, Itzkowitz S, Harpaz N, Ullman T. Progression of lowgrade dysplasia in ulcerative colitis: effect of colonic location. Gastrointest Endosc. 2011; 74:1087–1093.
Article42. Kisiel JB, Loftus EV Jr, Harmsen WS, Zinsmeister AR, Sandborn WJ. Outcome of sporadic adenomas and adenoma-like dysplasia in patients with ulcerative colitis undergoing polypectomy. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2012; 18:226–235.
Article43. Medlicott SA, Jewell LD, Price L, Fedorak RN, Sherbaniuk RW, Urbanski SJ. Conservative management of small adenomata in ulcerative colitis. Am J Gastroenterol. 1997; 92:2094–2098.44. Odze RD, Farraye FA, Hecht JL, Hornick JL. Long-term follow-up after polypectomy treatment for adenoma-like dysplastic lesions in ulcerative colitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2004; 2:534–541.
Article45. Pekow JR, Hetzel JT, Rothe JA, et al. Outcome after surveillance of low-grade and indefinite dysplasia in patients with ulcerative colitis. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2010; 16:1352–1356.
Article46. Rozen P, Baratz M, Fefer F, Gilat T. Low incidence of significant dysplasia in a successful endoscopic surveillance program of patients with ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology. 1995; 108:1361–1370.
Article47. Vieth M, Behrens H, Stolte M. Sporadic adenoma in ulcerative colitis: endoscopic resection is an adequate treatment. Gut. 2006; 55:1151–1155.
Article48. Harbord M, Eliakim R, Bettenworth D, et al. Third European evidence-based consensus on diagnosis and management of ulcerative colitis. Part 2: current management. J Crohns Colitis. 2017; 11:769–784.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection for Colitis-Associated Dysplasia
- Role of Advanced Endoscopic Imaging Techniques in the Management of Inflammatory Bowel Disease
- Non-conventional dysplastic subtypes in inflammatory bowel disease: a review of their diagnostic characteristics and potential clinical implications
- Endoscopic molecular imaging in inflammatory bowel disease
- Diagnostic Tips for Making the Diagnosis of Inflammatory Bowel Disease