Korean Circ J.
2017 Jul;47(4):490-500. 10.4070/kcj.2016.0320.
Experience with Mechanical Circulatory Support for Medically Intractable Low Cardiac Output in a Pediatric Intensive Care Unit
- Affiliations
-
- 1Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea. hongklim@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2392887
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4070/kcj.2016.0320
Abstract
- BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES
Mechanical circulatory support with extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) and ventricular assist device has always been the optimal choice for treating the majority of medically intractable low cardiac output case. We retrospectively investigated our institution's outcomes and variables associated with a high risk of mortality.
SUBJECTS AND METHODS
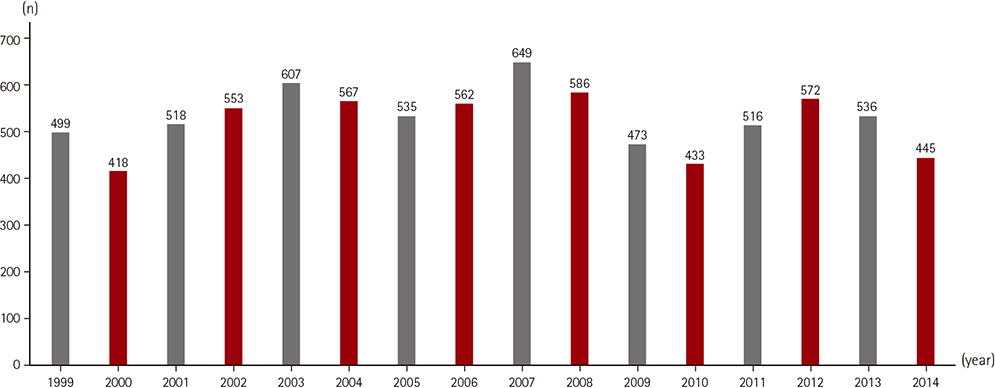
From 1999 to 2014, 86 patients who were of pediatric age or had grown-up congenital heart disease underwent mechanical circulatory support for medically intractable low cardiac output in our pediatric intensive care unit. Of these, 9 grown-up congenital heart disease patients were over 18 years of age, and the median age of the subject group was 5.82 years (range: 1 day to 41.6 years). A review of all demographic, clinical, and surgical data and survival analysis were performed.
RESULTS
A total of 45 (52.3%) patients were successfully weaned from the mechanical assist device, and 25 (29.1%) survivors were able to be discharged. There was no significant difference in results between patients over 18 years and under 18 years of age. Risk factors for mortality were younger age (<30 days), functional single ventricle anatomy, support after cardiac operations, longer support duration, and deteriorated pre-ECMO status (severe metabolic acidosis and increased levels of lactate, creatinine, bilirubin, or liver enzyme). The survival rate has improved since 2010 (from 25% before 2010 to 35% after 2010), when we introduced an upgraded oxygenator, activated heart transplantation, and also began to apply ECMO before the end-stage of cardiac dysfunction, even though we could not reveal significant correlations between survival rate and changed strategies associated with ECMO.
CONCLUSION
Mechanical circulatory support has played a critical role and has had a dramatic effect on survival in patients with medically intractable heart failure, particularly in recent years. Meticulous monitoring of acid-base status, laboratory findings, and early and liberal applications are recommended to improve outcomes without critical complication rates, particularly in neonates with single ventricle physiology.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Acidosis
Bilirubin
Cardiac Output, Low*
Creatinine
Critical Care*
Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation
Heart Defects, Congenital
Heart Failure
Heart Transplantation
Heart-Assist Devices
Humans
Infant, Newborn
Intensive Care Units*
Lactic Acid
Liver
Mortality
Oxygen
Oxygenators
Physiology
Resuscitation
Retrospective Studies
Risk Factors
Survival Rate
Survivors
Bilirubin
Creatinine
Lactic Acid
Oxygen
Figure
Reference
-
1. Rossano JW, Jang GY. Pediatric heart failure: current state and future possibilities. Korean Circ J. 2015; 45:1–8.2. Bakhtiary F, Keller H, Dogan S, et al. Venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for treatment of cardiogenic shock: clinical experiences in 45 adult patients. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2008; 135:382–388.3. Ko WJ, Lin CY, Chen RJ, et al. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation support for adult postcardiotomy cardiogenic shock. Ann Thorac Surg. 2002; 73:538–545.4. Fuchs A, Netz H. Ventricular assist devices in pediatrics. Images Paediatr Cardiol. 2001; 3:24–54.5. Aharon AS, Drinkwater DC Jr, Churchwell KB, et al. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in children after repair of congenital cardiac lesions. Ann Thorac Surg. 2001; 72:2095–2101.6. Alsoufi B, Al-Radi OO, Gruenwald C, et al. Extra-corporeal life support following cardiac surgery in children: analysis of risk factors and survival in a single institution. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2009; 35:1004–1011.7. del Nido PJ, Duncan BW, Mayer JE Jr, Wessel DL, LaPierre RA, Jonas RA. Left ventricular assist device improves survival in children with left ventricular dysfunction after repair of anomalous origin of the left coronary artery from the pulmonary artery. Ann Thorac Surg. 1999; 67:169–172.8. Kumar TK, Zurakowski D, Dalton H, et al. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in postcardiotomy patients: factors influencing outcome. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2010; 140:330–336.e2.9. del Nido PJ, Dalton HJ, Thompson AE, Siewers RD. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenator rescue in children during cardiac arrest after cardiac surgery. Circulation. 1992; 86:5 Suppl. II300–II304.10. Duncan BW, Ibrahim AE, Hraska V, et al. Use of rapid-deployment extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for the resuscitation of pediatric patients with heart disease after cardiac arrest. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1998; 116:305–311.11. Greason KL, Hemp JR, Maxwell JM, Fetter JE, Moreno-Cabral RJ. Prevention of distal limb ischemia during cardiopulmonary support via femoral cannulation. Ann Thorac Surg. 1995; 60:209–210.12. Morris MC, Ittenbach RF, Godinez RI, et al. Risk factors for mortality in 137 pediatric cardiac intensive care unit patients managed with extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. Crit Care Med. 2004; 32:1061–1069.13. Doll N, Kiaii B, Borger M, et al. Five-year results of 219 consecutive patients treated with extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for refractory postoperative cardiogenic shock. Ann Thorac Surg. 2004; 77:151–157.14. Fuhrman BP, Hernan LJ, Rotta AT, Heard CM, Rosenkranz ER. Pathophysiology of cardiac extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. Artif Organs. 1999; 23:966–969.15. Chow G, Koirala B, Armstrong D, et al. Predictors of mortality and neurological morbidity in children undergoing extracorporeal life support for cardiac disease. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2004; 26:38–43.16. Cengiz P, Seidel K, Rycus PT, Brogan TV, Roberts JS. Central nervous system complications during pediatric extracorporeal life support: incidence and risk factors. Crit Care Med. 2005; 33:2817–2824.17. Kolovos NS, Bratton SL, Moler FW, et al. Outcome of pediatric patients treated with extracorporeal life support after cardiac surgery. Ann Thorac Surg. 2003; 76:1435–1441.18. Polimenakos AC, Wojtyla P, Smith PJ, et al. Post-cardiotomy extracorporeal cardiopulmonary resuscitation in neonates with complex single ventricle: analysis of outcomes. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2011; 40:1396–1405.19. Lee J, Kim GB, Kwon HW, et al. Safety and efficacy of the off-label use of milrinone in pediatric patients with heart diseases. Korean Circ J. 2014; 44:320–327.20. Montgomery VL, Strotman JM, Ross MP. Impact of multiple organ system dysfunction and nosocomial infections on survival of children treated with extracorporeal membrane oxygenation after heart surgery. Crit Care Med. 2000; 28:526–531.21. Osaki S, Edwards NM, Velez M, et al. Improved survival in patients with ventricular assist device therapy: the University of Wisconsin experience. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2008; 34:281–288.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Mechanical Circulatory Support to Control Medically Intractable Arrhythmias in Pediatric Patients After Cardiac Surgery
- A Clinical Survey of Pediatric espiratory Intensive Care (1985)-The fifth report
- A Clinical Study on Resipratory Intensive Care in Critically Ill Patients - 9th report
- Successful Recovery after Cardiac Arrest from Medically Intractable Coronary Spasm Induced by Ergonovine, Using Percutaneous Cardiopulmonary Support: A Case Report
- Cardiac Complications in Patients Admitted to the Neuro-Intensive Care Unit