J Pathol Transl Med.
2017 Sep;51(5):471-481. 10.4132/jptm.2017.06.02.
Diverse Immunoprofile of Ductal Adenocarcinoma of the Prostate with an Emphasis on the Prognostic Factors
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pathology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. yongcho@amc.seoul.kr
- 2Asan Institute for Life Sciences, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Clinical Epidemiology and Biostatistics, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2392566
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2017.06.02
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Ductal adenocarcinoma (DAC) of the prostate is an uncommon histologic subtype whose prognostic factors and immunoprofile have not been fully defined.
METHODS
To define its prognostic factors and immunoprofile, the clinicopathological features, including biochemical recurrence (BCR), of 61 cases of DAC were analyzed. Immunohistochemistry was performed on tissue microarray constructs to assess the expression of prostate cancer-related and mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling-related proteins.
RESULTS
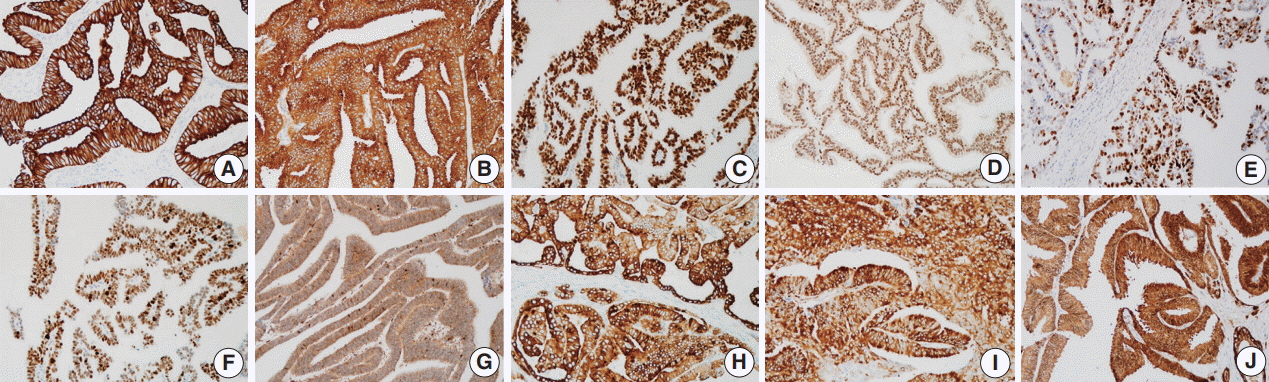
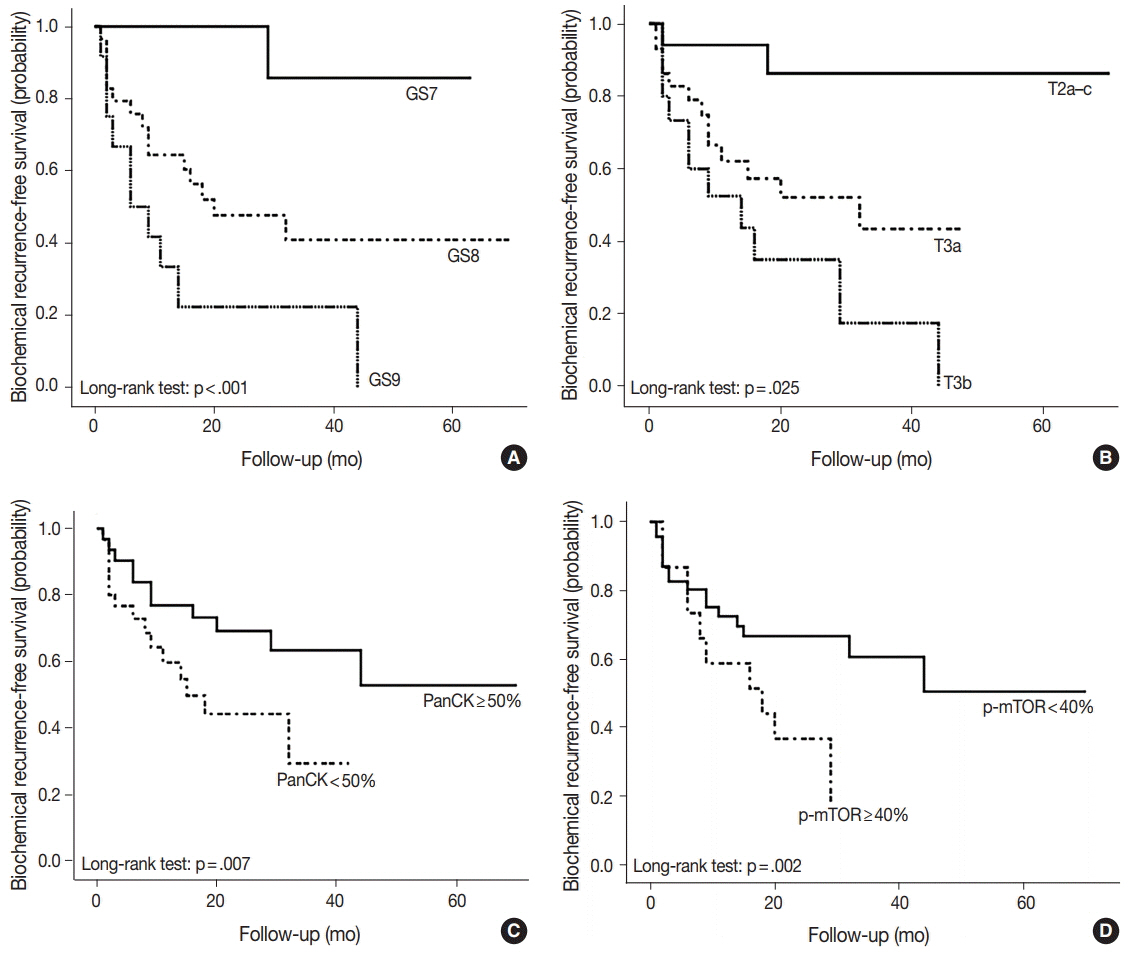
During the median follow-up period of 19.3 months, BCR occurred in 26 cases (42.6%). DAC demonstrated a wide expression range of prostate cancer-related proteins, including nine cases (14.8%) that were totally negative for pan-cytokeratin (PanCK) immunostaining. The mTOR signaling-related proteins also showed diverse expression. On univariate analysis, BCR was associated with high preoperative serum levels of prostate-specific antigen (PSA), large tumor volume, predominant ductal component, high Gleason score (GS), comedo-necrosis, high tumor stage (pT), lymphovascular invasion, and positive surgical margin. High expressions of phospho-mTOR (p-mTOR) as well as low expressions of PSA, phospho-S6 ribosomal protein (pS6) and PanCK were associated with BCR. On multivariable analysis, GS, pT, and immunohistochemical expressions of PanCK and p-mTOR remained independent prognostic factors for BCR.
CONCLUSIONS
These results suggest GS, pT, and immunohistochemical expressions of PanCK and p-mTOR as independent prognostic factors for BCR in DAC. Since DAC showed diverse expression of prostate cancer-related proteins, this should be recognized in interpreting the immunoprofile of DAC. The diverse expression of mTOR-related proteins implicates their potential utility as predictive markers for mTOR targeted therapy.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Moch H, Humphrey PA, Ulbright TM, Reuter VE. WHO classification of tumours of the urinary system and male genital organs. 4th ed. Lyon: International Agency for Research on Cancer;2016.2. Melicow MM, Pachter M. Endometrial carcinoma of proxtatic utricle (uterus masculinus). Cancer. 1967; 20:1715–22.3. Tarjan M, Lenngren A, Hellberg D, Tot T. Immunohistochemical verification of ductal differentiation in prostate cancer. APMIS. 2012; 120:510–8.4. Meeks JJ, Zhao LC, Cashy J, Kundu S. Incidence and outcomes of ductal carcinoma of the prostate in the USA: analysis of data from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results program. BJU Int. 2012; 109:831–4.
Article5. Tu SM, Lopez A, Leibovici D, et al. Ductal adenocarcinoma of the prostate: clinical features and implications after local therapy. Cancer. 2009; 115:2872–80.6. Statz CM, Patterson SE, Mockus SM. mTOR inhibitors in castration-resistant prostate cancer: a systematic review. Target Oncol. 2017; 12:47–59.
Article7. Jung WY, Sung CO, Han SH, et al. AZGP-1 immunohistochemical marker in prostate cancer: potential predictive marker of biochemical recurrence in post radical prostatectomy specimens. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 2014; 22:652–7.8. Edge SB, Compton CC. The American Joint Committee on Cancer: the 7th edition of the AJCC cancer staging manual and the future of TNM. Ann Surg Oncol. 2010; 17:1471–4.
Article9. Bostwick DG, Kindrachuk RW, Rouse RV. Prostatic adenocarcinoma with endometrioid features: clinical, pathologic, and ultrastructural findings. Am J Surg Pathol. 1985; 9:595–609.10. Ro JY, Ayala AG, Wishnow KI, Ordóñez NG. Prostatic duct adenocarcinoma with endometrioid features: immunohistochemical and electron microscopic study. Semin Diagn Pathol. 1988; 5:301–11.11. Gong Y, Caraway N, Stewart J, Staerkel G. Metastatic ductal adenocarcinoma of the prostate: cytologic features and clinical findings. Am J Clin Pathol. 2006; 126:302–9.12. Leite KR, Mitteldorf CA, Srougi M, et al. Cdx2, cytokeratin 20, thyroid transcription factor 1, and prostate-specific antigen expression in unusual subtypes of prostate cancer. Ann Diagn Pathol. 2008; 12:260–6.
Article13. Copeland JN, Amin MB, Humphrey PA, Tamboli P, Ro JY, Gal AA. The morphologic spectrum of metastatic prostatic adenocarcinoma to the lung: special emphasis on histologic features overlapping with other pulmonary neoplasms. Am J Clin Pathol. 2002; 117:552–7.14. Oxley JD, Abbott CD, Gillatt DA, MacIver AG. Ductal carcinomas of the prostate: a clinicopathological and immunohistochemical study. Br J Urol. 1998; 81:109–15.
Article15. Lee SS. Endometrioid adenocarcinoma of the prostate: a clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical study. J Surg Oncol. 1994; 55:235–8.
Article16. Millar EK, Sharma NK, Lessells AM. Ductal (endometrioid) adenocarcinoma of the prostate: a clinicopathological study of 16 cases. Histopathology. 1996; 29:11–9.
Article17. Tulunay O, Orhan D, Baltaci S, Gögüş C, Müftüoglu YZ. Prostatic ductal adenocarcinoma showing Bcl-2 expression. Int J Urol. 2004; 11:805–8.
Article18. Seipel AH, Samaratunga H, Delahunt B, Wiklund P, Clements M, Egevad L. Immunohistochemistry of ductal adenocarcinoma of the prostate and adenocarcinomas of non-prostatic origin: a comparative study. APMIS. 2016; 124:263–70.
Article19. Sanati S, Watson MA, Salavaggione AL, Humphrey PA. Gene expression profiles of ductal versus acinar adenocarcinoma of the prostate. Mod Pathol. 2009; 22:1273–9.
Article20. Ruizeveld de Winter JA, Janssen PJ, Sleddens HM, et al. Androgen receptor status in localized and locally progressive hormone refractory human prostate cancer. Am J Pathol. 1994; 144:735–46.21. Henshall SM, Quinn DI, Lee CS, et al. Altered expression of androgen receptor in the malignant epithelium and adjacent stroma is associated with early relapse in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2001; 61:423–7.22. Schlomm T, Iwers L, Kirstein P, et al. Clinical significance of p53 alterations in surgically treated prostate cancers. Mod Pathol. 2008; 21:1371–8.
Article23. Lee K, Chae JY, Kwak C, Ku JH, Moon KC. TMPRSS2-ERG gene fusion and clinicopathologic characteristics of Korean prostate cancer patients. Urology. 2010; 76:1268. e7-13.
Article24. Epstein JI, Egevad L, Humphrey PA, Montironi R, Members of the IIiDUPG. Best practices recommendations in the application of immunohistochemistry in the prostate: report from the International Society of Urologic Pathology consensus conference. Am J Surg Pathol. 2014; 38:e6–19.25. Berner A, Harvei S, Tretli S, Fosså SD, Nesland JM. Prostatic carcinoma: a multivariate analysis of prognostic factors. Br J Cancer. 1994; 69:924–30.
Article26. Morais CL, Herawi M, Toubaji A, et al. PTEN loss and ERG protein expression are infrequent in prostatic ductal adenocarcinomas and concurrent acinar carcinomas. Prostate. 2015; 75:1610–9.
Article27. Suh JH, Park JW, Lee C, Moon KC. ERG immunohistochemistry and clinicopathologic characteristics in Korean prostate adenocarcinoma patients. Korean J Pathol. 2012; 46:423–8.
Article28. Bachmann IM, Halvorsen OJ, Collett K, et al. EZH2 expression is associated with high proliferation rate and aggressive tumor subgroups in cutaneous melanoma and cancers of the endometrium, prostate, and breast. J Clin Oncol. 2006; 24:268–73.
Article29. van Leenders GJ, Dukers D, Hessels D, et al. Polycomb-group oncogenes EZH2, BMI1, and RING1 are overexpressed in prostate cancer with adverse pathologic and clinical features. Eur Urol. 2007; 52:455–63.
Article30. Laplante M, Sabatini DM. mTOR signaling in growth control and disease. Cell. 2012; 149:274–93.
Article31. Xu K, Liu P, Wei W. mTOR signaling in tumorigenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014; 1846:638–54.
Article32. Giannico GA, Arnold SA, Gellert LL. New and emerging diagnostic and prognostic immunohistochemical biomarkers in prostate pathology. Adv Anat Pathol. 2017; 24:35–44.
Article33. Sabatini DM. mTOR and cancer: insights into a complex relationship. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006; 6:729–34.
Article34. Morrison DK. The 14-3-3 proteins: integrators of diverse signaling cues that impact cell fate and cancer development. Trends Cell Biol. 2009; 19:16–23.
Article35. Templeton AJ, Dutoit V, Cathomas R, et al. Phase 2 trial of single-agent everolimus in chemotherapy-naive patients with castration-resistant prostate cancer (SAKK 08/08). Eur Urol. 2013; 64:150–8.
Article36. Vaishampayan U, Shevrin D, Stein M, et al. Phase II trial of carboplatin, everolimus, and prednisone in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer pretreated with docetaxel chemotherapy: a prostate cancer clinical trial consortium study. Urology. 2015; 86:1206–11.
Article