Diabetes Metab J.
2017 Jun;41(3):205-212. 10.4093/dmj.2017.41.3.205.
The Effect of 12 Weeks Aerobic, Resistance, and Combined Exercises on Omentin-1 Levels and Insulin Resistance among Type 2 Diabetic Middle-Aged Women
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Clinical Epidemiology and Biostatistics, McMaster University, Hamilton, ON, Canada.
- 2Shiraz HIV/AIDS Research Center, Institute of Health, Shiraz University of Medical Sciences, Shiraz, Iran. dianati.epid@gmail.com, fararooei@gmail.com
- 3Department of Nutrition, Shiraz University of Medical Sciences School of Nutrition and Food Sciences, Shiraz, Iran.
- 4Department of Physical Therapy, Shiraz University of Medical Sciences School of Rehabilitation Sciences, Shiraz, Iran.
- 5Department of Epidemiology, Student Research Committee, Shiraz University of Medical Sciences School of Health, Shiraz, Iran.
- KMID: 2392495
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2017.41.3.205
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Recent studies have shown that omentin-1 derived from adipokines can affect physiological regulations and some metabolic dis-eases such as type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
METHODS
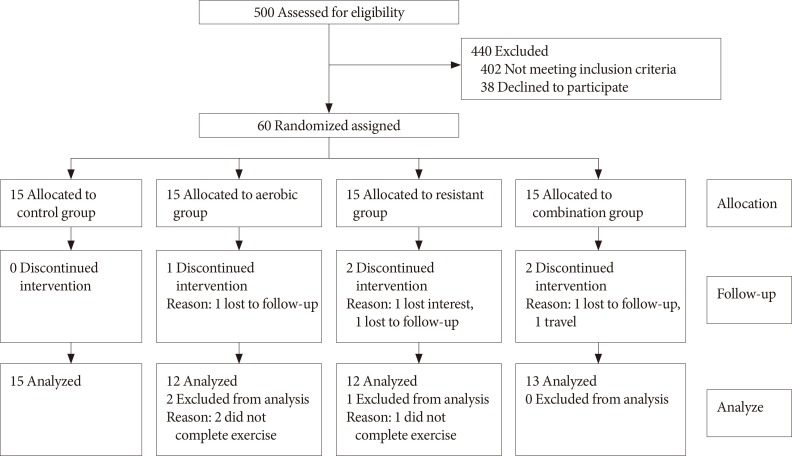
The purpose of this study was to examine the impact of 12 weeks of aerobic (cycle ergometer), resistance, and combined exercises on omentin-1 level, glucose and insulin resistance indices in overweight middle age women with T2DM. In this study, 60 overweight middle age diabetic women were selected using simple random sampling and they were assigned to three groups of aerobic exercise (n=12), resistant exercise (n=12) and combined exercise (n=13), and one control group (n=15). Exercises were done in a three times per week sessions for a total of 12 weeks. Blood samples were collected before each exercise session and 24 hours after of the last session.
RESULTS
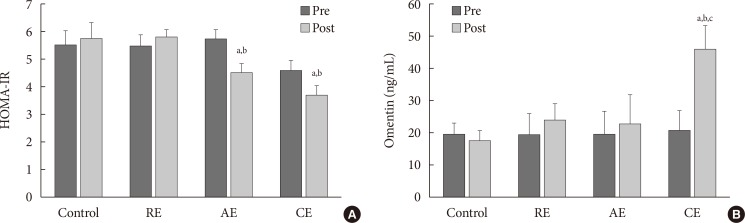
Present study showed that fasting blood sugar decreased significantly in all intervention groups, while homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) decreased only in the aerobic and combined exercises groups. Furthermore, there was a significant increase in the omentin-1 level only in the combined exercise group.
CONCLUSION
Compared to aerobic and resistance exercises, 12 weeks of combined exercise was more efficient in improving HOMA-IR and increasing serum omentin-1 among women with T2DM.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Joint Association of Relative Grip Strength and Resting Heart Rate with the Risk of Developing Diabetes in Middle-Aged Adults
DooYong Park, YeonSoo Kim, Eunkyung Kim
Korean J Sports Med. 2023;41(4):216-224. doi: 10.5763/kjsm.2023.41.4.216.
Reference
-
1. Galic S, Oakhill JS, Steinberg GR. Adipose tissue as an endocrine organ. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2010; 316:129–139. PMID: 19723556.
Article2. Sturm R. Childhood obesity: what we can learn from existing data on societal trends, part 2. Prev Chronic Dis. 2005; 2:A20.3. Granger DN, Granger JP. Chapter 5, Cardiovascular responses to exercise. Colloquium series on integrated systems physiology: from molecule to function. San Rafael: Morgan & Claypool Life Sciences;2011. p. 1–124.4. Kang J. Nutrition and metabolism in sports, exercise and health. Abingdon: Routledge;2013.5. Berg AH, Scherer PE. Adipose tissue, inflammation, and cardiovascular disease. Circ Res. 2005; 96:939–949. PMID: 15890981.
Article6. Uchiyama Y, Suzuki T, Mochizuki K, Goda T. Dietary supplementation with (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate reduces inflammatory response in adipose tissue of non-obese type 2 diabetic Goto-Kakizaki (GK) rats. J Agric Food Chem. 2013; 61:11410–11417. PMID: 24206061.
Article7. Rabe K, Lehrke M, Parhofer KG, Broedl UC. Adipokines and insulin resistance. Mol Med. 2008; 14:741–751. PMID: 19009016.
Article8. Tan BK, Adya R, Farhatullah S, Lewandowski KC, O'Hare P, Lehnert H, Randeva HS. Omentin-1, a novel adipokine, is decreased in overweight insulin-resistant women with polycystic ovary syndrome: ex vivo and in vivo regulation of omentin-1 by insulin and glucose. Diabetes. 2008; 57:801–808. PMID: 18174521.9. de Souza Batista CM, Yang RZ, Lee MJ, Glynn NM, Yu DZ, Pray J, Ndubuizu K, Patil S, Schwartz A, Kligman M, Fried SK, Gong DW, Shuldiner AR, Pollin TI, McLenithan JC. Omentin plasma levels and gene expression are decreased in obesity. Diabetes. 2007; 56:1655–1661. PMID: 17329619.
Article10. Cai RC, Wei L, Di JZ, Yu HY, Bao YQ, Jia WP. Expression of omentin in adipose tissues in obese and type 2 diabetic patients. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2009; 89:381–384. PMID: 19567114.11. Gursoy G, Kirnap NG, Esbah O, Acar Y, Demirbas B, Akcayoz S, Ozturk A. The relationship between plasma omentin-1 levels and insulin resistance in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetıc women. Clin Rev Opin. 2010; 2:49–54.12. Pan HY, Guo L, Li Q. Changes of serum omentin-1 levels in normal subjects and in patients with impaired glucose regulation and with newly diagnosed and untreated type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2010; 88:29–33. PMID: 20129687.
Article13. Moreno-Navarrete JM, Catalan V, Ortega F, Gomez-Ambrosi J, Ricart W, Fruhbeck G, Fernandez-Real JM. Circulating omentin concentration increases after weight loss. Nutr Metab (Lond). 2010; 7:27. PMID: 20380714.
Article14. Saremi A, Asghari M, Ghorbani A. Effects of aerobic training on serum omentin-1 and cardiometabolic risk factors in overweight and obese men. J Sports Sci. 2010; 28:993–998. PMID: 20544489.
Article15. World Health Organization. Definition and diagnosis of diabetes mellitus and intermediate hyperglycemia. Geneva: World Health Organization;2006.16. Wilms B, Ernst B, Gerig R, Schultes B. Plasma omentin-1 levels are related to exercise performance in obese women and increase upon aerobic endurance training. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2015; 123:187–192. PMID: 25789872.
Article17. Cauza E, Hanusch-Enserer U, Strasser B, Ludvik B, Metz-Schimmerl S, Pacini G, Wagner O, Georg P, Prager R, Kostner K, Dunky A, Haber P. The relative benefits of endurance and strength training on the metabolic factors and muscle function of people with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2005; 86:1527–1533. PMID: 16084803.
Article18. Jorge ML, de Oliveira VN, Resende NM, Paraiso LF, Calixto A, Diniz AL, Resende ES, Ropelle ER, Carvalheira JB, Espindola FS, Jorge PT, Geloneze B. The effects of aerobic, resistance, and combined exercise on metabolic control, inflammatory markers, adipocytokines, and muscle insulin signaling in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Metabolism. 2011; 60:1244–1252. PMID: 21377179.
Article19. Abd-Elbaky AE, Abo-ElMatty DM, Mesbah NM, Ibrahim SM. Omentin and apelin concentrations in relation to obesity, diabetes mellitus type two, and cardiovascular diseases in Egyptian population. Int J Diabetes Dev Ctries. 2016; 36:52–58.
Article20. Bremer AA, Jialal I. Adipose tissue dysfunction in nascent metabolic syndrome. J Obes. 2013; 2013:393192. PMID: 23653857.
Article21. Ho SS, Dhaliwal SS, Hills AP, Pal S. The effect of 12 weeks of aerobic, resistance or combination exercise training on cardiovascular risk factors in the overweight and obese in a randomized trial. BMC Public Health. 2012; 12:704. PMID: 23006411.
Article22. Park DH, Ransone JW. Effects of submaximal exercise on high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol subfractions. Int J Sports Med. 2003; 24:245–251. PMID: 12784165.
Article23. Davidson LE, Hudson R, Kilpatrick K, Kuk JL, McMillan K, Janiszewski PM, Lee S, Lam M, Ross R. Effects of exercise modality on insulin resistance and functional limitation in older adults: a randomized controlled trial. Arch Intern Med. 2009; 169:122–131. PMID: 19171808.24. O'Leary VB, Marchetti CM, Krishnan RK, Stetzer BP, Gonzalez F, Kirwan JP. Exercise-induced reversal of insulin resistance in obese elderly is associated with reduced visceral fat. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2006; 100:1584–1589. PMID: 16373444.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Letter: The Effect of 12 Weeks Aerobic, Resistance, and Combined Exercises on Omentin-1 Levels and Insulin Resistance among Type 2 Diabetic Middle-Aged Women (Diabetes Metab J 2017;41:205-12)
- Response: The Effect of 12 Weeks Aerobic, Resistance, and Combined Exercises on Omentin-1 Levels and Insulin Resistance among Type 2 Diabetic Middle-Aged Women (Diabetes Metab J 2017;41:205-12)
- Corrigendum: Author's Name and Affiliation Correction: The Effect of 12 Weeks Aerobic, Resistance, and Combined Exercises on Omentin-1 Levels and Insulin Resistance among Type 2 Diabetic Middle-Aged Women
- Effect of Exercise on Glucose Metabolism
- The Effects of Aerobic/Resistance Exercise on Body Fat Mass, Muscle Strength and Endothelial Function in Korean Type 2 Diabetes mellitus Patients