J Vet Sci.
2012 Dec;13(4):355-362.
Distribution of red-spotted grouper nervous necrosis virus (RGNNV) antigens in nervous and non-nervous organs of European seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax) during the course of an experimental challenge
- Affiliations
-
- 1IFAPA Centro El Toruno, Junta de Andalucia, El Puerto de Santa Maria, Cadiz, Spain.
- 2Departamento de Microbiologia, Facultad de Ciencias, Universidad de Malaga, 29071 Malaga, Spain. mdalonso@uma.es
- 3Institute of Aquaculture, University of Stirling, Stirling FK9 4LA, UK.
Abstract
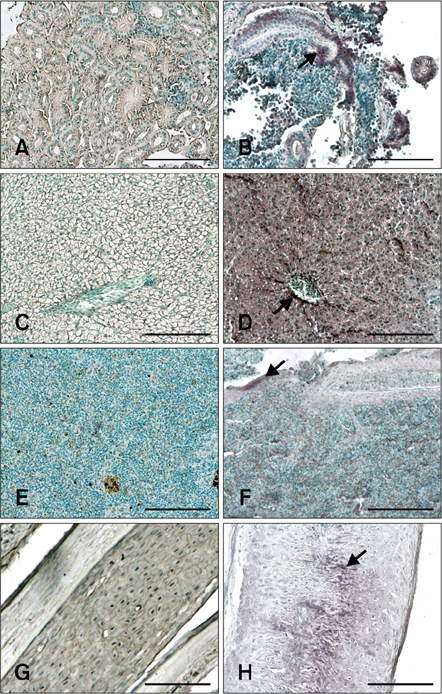
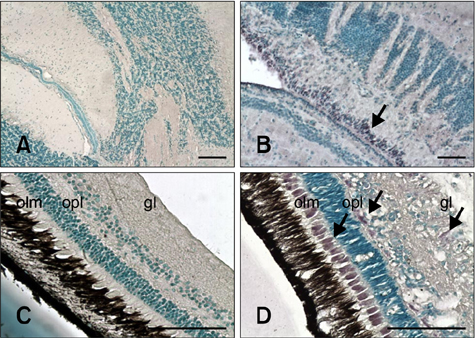
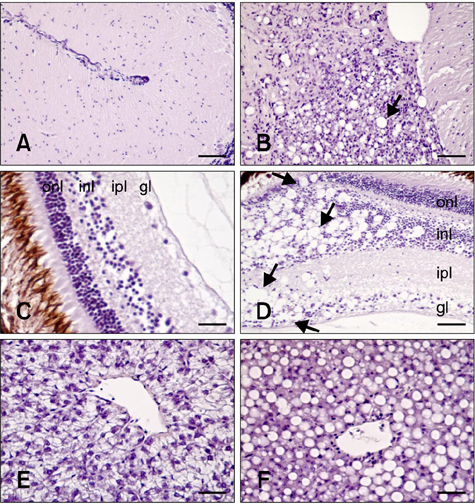
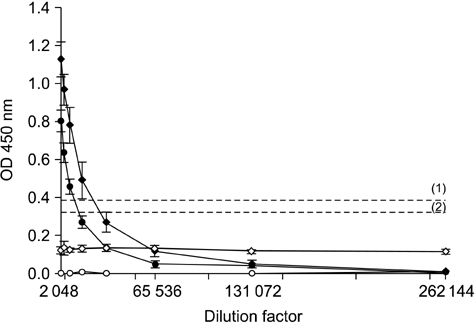
- The distribution of red-spotted grouper nervous necrosis virus (RGNNV) antigens was examined by immunohistochemistry in the nervous and non-nervous organs of juvenile European seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax) during the course of an intramuscular infection. Histological changes resulting from the infection were evaluated from 3 days to 2 months post-infection. The specific antibody response was also studied 2 months post-challenge. Viral proteins were present throughout the experimental period in the retina (inner nuclear layer, ganglion layer, outer limiting membrane, and outer plexiform layer), brain (cerebellum and tectum opticum), and liver (hepatocytes and endothelial cells). These proteins were also observed in the renal tubular cells, white pulp of spleen, and in fibroblasts and cartilage of caudal fin. This is the first report of RGNNV proteins appearing in these organs, where the immunostaining was only detected at certain sampling times after the onset of mortality. Brain and retina of virus-exposed fish showed high levels of vacuolation, while accumulation of fat vacuoles was observed in the liver. RGNNV infection also induced a specific antibody response as measured by an ELISA. In summary, this is the first study demonstrating the presence of viral proteins in cells of caudal fin, kidney and spleen of European seabass.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Alonso MC, Cano I, Garcia-Rosado E, Castro D, Lamas J, Barja JL, Borrego JJ, Bergmann SM. Isolation of lymphocystis disease virus from sole, Solea senegalensis Kaup, and blackspot sea bream, Pagellus bogaraveo (Brünnich). J Fish Dis. 2005. 28:221–228.
Article2. Aranguren R, Tafalla C, Novoa B, Figueras A. Experimental transmission of encephalopathy and retinopathy induced by nodavirus to sea bream, Sparus aurata L., using different infection models. J Fish Dis. 2002. 25:317–324.
Article3. Athanassopoulou F, Billinis C, Psychas V, Karipoglou K. Viral encephalopathy and retinopathy of Dicentrarchus labrax (L.) farmed in fresh water in Greece. J Fish Dis. 2003. 26:361–365.
Article4. Azad IS, Shekhar MS, Thirunavukkarasu AR, Jithendran KP. Viral nerve necrosis in hatchery-produced fry of Asian seabass Lates calcarifer: sequential microscopic analysis of histopathology. Dis Aquat Organ. 2006. 73:123–130.
Article5. Bigarré L, Baud M, Cabon J, Crenn K, Castric J. New PCR probes for detection and genotyping of piscine betanodaviruses. J Fish Dis. 2010. 33:907–912.
Article6. Bloch B, Gravningen K, Larsen JL. Encephalomyelitis among turbot associated with a picornavirus-like agent. Dis Aquat Organ. 1991. 10:65–70.
Article7. Bovo G, Gustinelli A, Quaglio F, Gobbo F, Panzarin V, Fusaro A, Mutinelli F, Caffara M, Fioravanti ML. Viral encephalopathy and retinopathy outbreak in freshwater fish farmed in Italy. Dis Aquat Organ. 2011. 96:45–54.
Article8. Bovo G, Nishizawa T, Maltese C, Borghesan F, Mutinelli F, Montesi F, De Mas S. Viral encephalopathy and retinopathy of farmed marine fish species in Italy. Virus Res. 1999. 63:143–146.
Article9. Breuil G, Pépin JFP, Boscher S, Thiéry R. Experimental vertical transmission of nodavirus from broodfish to eggs and larvae of the sea bass, Dicentrarchus labrax (L.). J Fish Dis. 2002. 25:697–702.
Article10. Chérif N, Thiéry R, Castric J, Biacchesi S, Brémont M, Thabti F, Limem L, Hammami S. Viral encephalopathy and retinopathy of Dicentrarchus labrax and Sparus aurata farmed in Tunisia. Vet Res Commun. 2009. 33:345–353.
Article11. Comps M, Pépin JF, Bonami JR. Purification and characterization of two fish encephalitis viruses (FEV) infecting Lates calcarifer and Dicentrarchus labrax. Aquaculture. 1994. 123:1–10.
Article12. Cunningham CH. Kruse PF, Patterson MK, editors. Quantal and enumerative titration of virus in cell cultures. Tissue Culture: Methods and Applications. 1973. New York: Academic Press;527–532.
Article13. Curtis PA, Drawbridge M, Iwamoto T, Nakai T, Hedrick RP, Gendron AP. Nodavirus infection of juvenile white sea bass, Atractoscion nobilis, cultured in Southern California: first record of viral nervous necrosis (VNN) in North America. J Fish Dis. 2001. 24:263–271.
Article14. Frerichs GN, Rodger HD, Peric Z. Cell culture isolation of piscine neuropathy nodavirus from juvenile sea bass, Dicentrarchus labrax. J Gen Virol. 1996. 77:2067–2071.
Article15. Grove S, Johansen R, Dannevig BH, Reitan LJ, Ranheim T. Experimental infection of Atlantic halibut Hippoglossus hippoglossus with nodavirus: tissue distribution and immune response. Dis Aquat Organ. 2003. 53:211–221.
Article16. Grove S, Johansen R, Reitan LJ, Press CM, Dannevig BH. Quantitative investigation of antigen and immune response in nervous and lymphoid tissues of Atlantic halibut (Hippoglossus hippoglossus) challenged with nodavirus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2006. 21:525–539.
Article17. Húsgağ S, Grotmol S, Hjeltnes BK, Rødseth OM, Biering E. Immune response to a recombinant capsid protein of striped jack nervous necrosis virus (SJNNV) in turbot Scophthalmus maximus and Atlantic halibut Hippoglossus hippoglossus, and evaluation of a vaccine against SJNNV. Dis Aquat Organ. 2001. 45:33–44.18. Iwamoto T, Mise K, Takeda A, Okinaka Y, Mori K, Arimoto M, Okuno T, Nakai T. Characterization of Striped jack nervous necrosis virus subgenomic RNA3 and biological activities of its encoded protein B2. J Gen Virol. 2005. 86:2807–2816.
Article19. Iwamoto T, Nakai T, Mori K, Arimoto M, Furusawa I. Cloning of the fish cell line SSN-1 for piscine nodaviruses. Dis Aquat Organ. 2000. 43:81–89.
Article20. Johansen R, Grove S, Svendsen AK, Modahl I, Dannevig B. A sequential study of pathological findings in Atlantic halibut, Hippoglossus hippoglossus (L), throughout one year after an acute outbreak of viral encephalopathy and retinopathy. J Fish Dis. 2004. 27:327–341.
Article21. Le Breton A, Grisez L, Sweetman J, Ollevier F. Viral nervous necrosis (VNN) associated with mass mortalities in cage-reared sea bass, Dicentrarchus labrax (L.). J Fish Dis. 1997. 20:145–151.
Article22. Lopez-Jimena B, Alonso MC, Thompson KD, Adams A, Infante C, Castro D, Borrego JJ, Garcia-Rosado E. Tissue distribution of red spotted grouper nervous necrosis virus (RGNNV) genome in experimentally infected juvenile European seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax). Vet Microbiol. 2011. 154:86–95.
Article23. Lopez-Jimena B, Cherif N, Garcia-Rosado E, Infante C, Cano I, Castro D, Hammami S, Borrego JJ, Alonso MC. A combined RT-PCR and dot-blot hybridization method reveals the coexistence of SJNNV and RGNNV betanodavirus genotypes in wild meagre (Argyrosomus regius). J Appl Microbiol. 2010. 109:1361–1369.
Article24. Mazelet L, Dietrich J, Rolland JL. New RT-qPCR assay for viral nervous necrosis virus detection in sea bass, Dicentrarchus labrax (L.): application and limits for hatcheries sanitary control. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2011. 30:27–32.
Article25. Mladineo I. The immunohistochemical study of nodavirus changes in larval, juvenile and adult sea bass tissue. J Appl Ichthyol. 2003. 19:366–370.
Article26. Munday BL, Kwang J, Moody N. Betanodavirus infections of teleost fish: a review. J Fish Dis. 2002. 25:127–142.
Article27. Nguyen HD, Mushiake K, Nakai T, Muroga K. Tissue distribution of striped jack nervous necrosis virus (SJNNV) in adult striped jack. Dis Aquat Organ. 1997. 28:87–91.
Article28. Nguyen HD, Nakai T, Muroga K. Progression of striped jack nervous necrosis virus (SJNNV) infection in naturally and experimentally infected striped jack Pseudocaranx dentex larvae. Dis Aquat Organ. 1996. 24:99–105.
Article29. Nishizawa T, Furuhashi M, Nagai T, Nakai T, Muroga K. Genomic classification of fish nodaviruses by molecular phylogenetic analysis of the coat protein gene. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1997. 63:1633–1636.
Article30. Péducasse S, Castric J, Thiéry R, Jeffroy J, Le Ven A, Baudin Laurencin F. Comparative study of viral encephalopathy and retinopathy in juvenile sea bass Dicentrarchus labrax infected in different ways. Dis Aquat Organ. 1999. 36:11–20.
Article31. Rivers TM. Viruses and Koch's Postulates. J Bacteriol. 1937. 33:1–12.
Article32. Rodríguez-Gómez FJ, Sarasquete C, Muñoz-Cueto JA. A morphological study of the brain of Solea senegalensis. I. The telencephalon. Histol Histopathol. 2000. 15:355–364.33. Scapigliati G, Buonocore F, Randelli E, Casani D, Meloni S, Zarletti G, Tiberi M, Pietretti D, Boschi I, Manchado M, Martin-Antonio B, Jimenez-Cantizano R, Bovo G, Borghesan F, Lorenzen N, Einer-Jensen K, Adams S, Thompson K, Alonso C, Bejar J, Cano I, Borrego JJ, Alvarez MC. Cellular and molecular immune responses of the sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) experimentally infected with betanodavirus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2010. 28:303–311.
Article34. Skinner LA, LaPatra SE, Adams A, Thompson KD, Balfry SK, McKinley RS, Schulte PM. Concurrent injection of a rhabdovirus-specific DNA vaccine with a polyvalent, oil-adjuvanted vaccine delays the specific anti-viral immune response in Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar L. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2010. 28:579–586.
Article35. Skliris GP, Richards RH. Induction of nodavirus disease in seabass, Dicentrarchus labrax, using different infection models. Virus Res. 1999. 63:85–93.
Article36. Starkey WG, Ireland JH, Muir KF, Jenkins ME, Roy WJ, Richards RH, Ferguson HW. Nodavirus infection in Atlantic cod and Dover sole in the UK. Vet Rec. 2001. 149:179–181.
Article37. Thiery R, Peducasse S, Castric J, Le Ven A, Jeffroy J, Baudin Laurencin F. Experimental transmission of viral encephalopathy and retinopathy to juvenile sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax). Bull Eur Assoc Fish Pathol. 1997. 17:118–122.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Computer-aided drug design of Azadirachta indica compounds against nervous necrosis virus by targeting grouper heat shock cognate protein 70 (GHSC70): quantum mechanics calculations and molecular dynamic simulation approaches
- Immune mechanisms of Theiler's virus-induced demyelination
- The value of computerized axial tomography of the brain in children with central nervous system disorders
- A Critical Review on the Argument that the Sacral Division of the Autonomic Nervous System should be Classified as the Sympathetic Nervous System
- Treatment of pediatric central nervous system infections