J Clin Neurol.
2017 Jul;13(3):287-292. 10.3988/jcn.2017.13.3.287.
Repetitive Nerve Stimulation in MuSK-Antibody-Positive Myasthenia Gravis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. hayshin@yuhs.ac
- 2Department of Neurology, Bundang Jesaeng General Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- KMID: 2391673
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3988/jcn.2017.13.3.287
Abstract
- BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE
Responses to repetitive nerve stimulation (RNS) in patients with muscle-specific tyrosine kinase (MuSK) antibody (Ab)-positive myasthenia gravis (MG) vary depending on the muscles tested. We analyzed the RNS responses of limb and facial muscles in MuSK-Ab-positive and acetylcholine receptor (AChR)-Ab-negative MG (MuSK MG) and MuSK-Ab-negative and AChR-Ab-negative [double-seronegative (DSN)] MG patients.
METHODS
We retrospectively compared RNS responses between 45 MuSK MG and 29 DSN MG. RNS was applied to the abductor digiti minimi, flexor carpi ulnaris, trapezius, orbicularis oculi, and nasalis muscles.
RESULTS
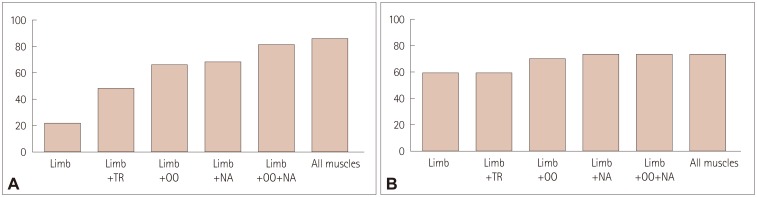
Abnormal RNS responses in limb muscles were observed in 22.2 and 58.6% of MuSK MG and DSN MG patients, respectively, with abnormal facial responses observed in 77.8 and 65.5%, and abnormal responses observed in any of the five muscles in 86.7 and 72.4%. Abnormal RNS responses in the abductor digiti minimi or flexor carpi ulnaris were less frequent in MuSK MG (8.9 and 15.6%, respectively) than in DSN MG (37.9 and 55.2%), whereas the findings for other muscles were not significantly different between the groups. Abnormal facial responses but normal limb responses were independently associated with MuSK MG (odds ratio=5.224, 95% confidence interval=1.300-20.990).
CONCLUSIONS
Abnormal RNS responses primarily in facial muscles without involvement of limb muscles were more pronounced in MuSK MG than in DSN MG. RNS of both facial and limb muscles in AChR-Ab-negative MG can increase the test sensitivity and aid in early suspicion of MuSK MG.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
2. Lee HS, Lee HS, Shin HY, Choi YC, Kim SM. The epidemiology of myasthenia gravis in Korea. Yonsei Med J. 2016; 57:419–425. PMID: 26847295.
Article3. Evoli A, Tonali PA, Padua L, Monaco ML, Scuderi F, Batocchi AP, et al. Clinical correlates with anti-MuSK antibodies in generalized seronegative myasthenia gravis. Brain. 2003; 126(Pt 10):2304–2311. PMID: 12821509.
Article4. Hoch W, McConville J, Helms S, Newsom-Davis J, Melms A, Vincent A. Auto-antibodies to the receptor tyrosine kinase MuSK in patients with myasthenia gravis without acetylcholine receptor antibodies. Nat Med. 2001; 7:365–368. PMID: 11231638.
Article5. Lavrnic D, Losen M, Vujic A, De Baets M, Hajdukovic LJ, Stojanovic V, et al. The features of myasthenia gravis with autoantibodies to MuSK. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2005; 76:1099–1102. PMID: 16024887.
Article6. Sanders DB, El-Salem K, Massey JM, McConville J, Vincent A. Clinical aspects of MuSK antibody positive seronegative MG. Neurology. 2003; 60:1978–1980. PMID: 12821744.
Article7. Padua L, Tonali P, Aprile I, Caliandro P, Bartoccioni E, Evoli A. Seronegative myasthenia gravis: comparison of neurophysiological picture in MuSK+ and MuSK- patients. Eur J Neurol. 2006; 13:273–276. PMID: 16618345.
Article8. Pasnoor M, Wolfe GI, Nations S, Trivedi J, Barohn RJ, Herbelin L, et al. Clinical findings in MuSK-antibody positive myasthenia gravis: a U.S. experience. Muscle Nerve. 2010; 41:370–374. PMID: 19882635.
Article9. Oh SJ, Hatanaka Y, Hemmi S, Young AM, Scheufele ML, Nations SP, et al. Repetitive nerve stimulation of facial muscles in MuSK antibody-positive myasthenia gravis. Muscle Nerve. 2006; 33:500–504. PMID: 16392120.
Article10. Nikolic A, Basta I, Stojanovic VR, Stevic Z, Lavrnic D. Electrophysiological profile of the patients with MuSK positive myasthenia gravis. Neurol Res. 2014; 36:945–949. PMID: 24825477.
Article11. Oh SJ. Muscle-specific receptor tyrosine kinase antibody positive myasthenia gravis current status. J Clin Neurol. 2009; 5:53–64. PMID: 19587811.
Article12. Wolfe GI, Oh SJ. Clinical phenotype of muscle-specific tyrosine kinase-antibody-positive myasthenia gravis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2008; 1132:71–75. PMID: 18567855.
Article13. Oh SJ, Eslami N, Nishihira T, Sarala PK, Kuba T, Elmore RS, et al. Electrophysiological and clinical correlation in myasthenia gravis. Ann Neurol. 1982; 12:348–354. PMID: 7149660.
Article14. Stickler DE, Massey JM, Sanders DB. MuSK-antibody positive myasthenia gravis: clinical and electrodiagnostic patterns. Clin Neurophysiol. 2005; 116:2065–2068. PMID: 16043398.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Muscle-Specific Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Antibody Positive Myasthenia Gravis Current Status
- Clinical and Electrophysiologic Responses to Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors in MuSK-Antibody-Positive Myasthenia Gravis: Evidence for Cholinergic Neuromuscular Hyperactivity
- Two Cases with Positive Ice Tests Mimicking Ocular Myasthenia Gravis
- Muscle-specific receptor tyrosine kinase (MuSK) myasthenia gravis associated with castleman disease
- A Patient with Coexisting Myasthenia Gravis and Lambert-Eaton Myasthenic Syndrome