Transl Clin Pharmacol.
2017 Sep;25(3):141-146. 10.12793/tcp.2017.25.3.141.
Caffsim: simulation of plasma caffeine concentrations implemented as an R package and Web-applications
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan, Seoul 05505, Republic of Korea. ksbae@amc.seoul.kr
- KMID: 2390934
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12793/tcp.2017.25.3.141
Abstract
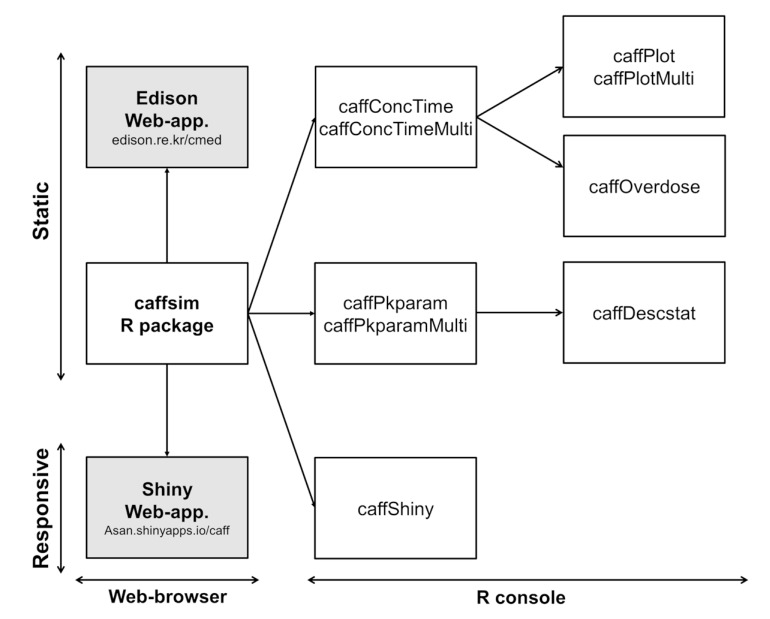
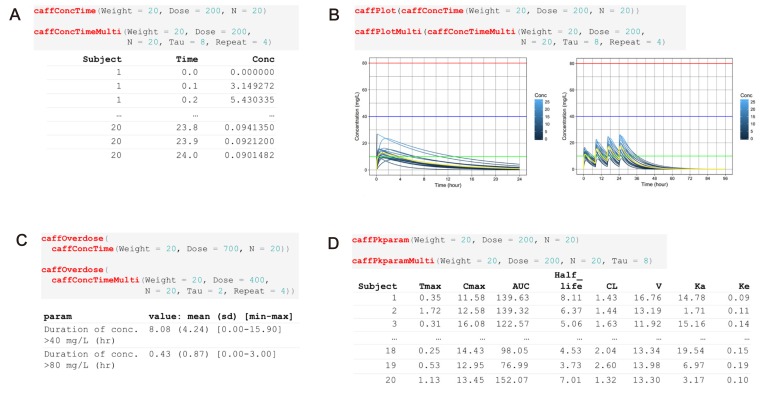
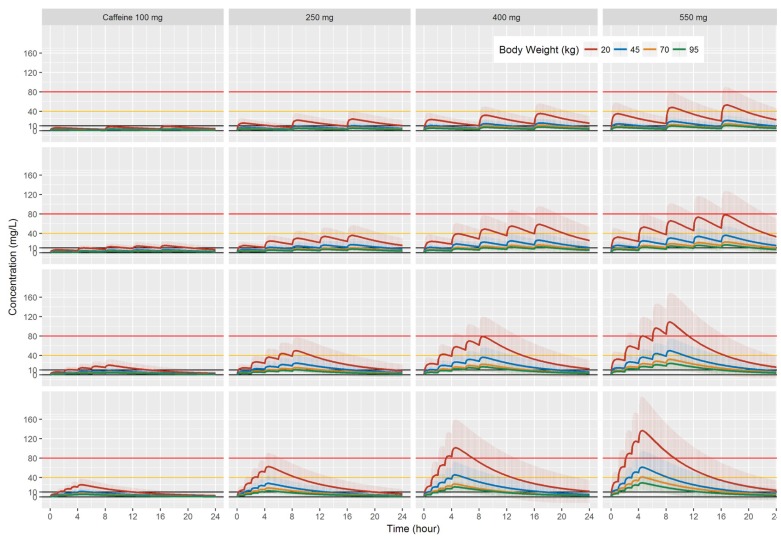
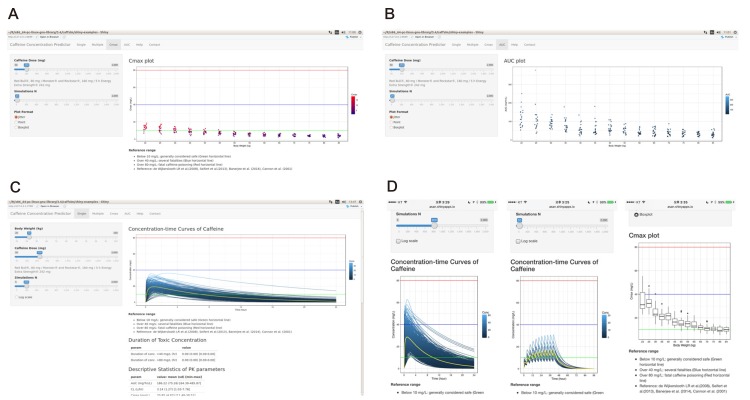
- Caffeine is a naturally-occurring central nervous system stimulant found in plant constituents including coffee, cocoa beans, and tea leaves. Consumption of caffeine through imbibing caffeinated drinks is rapidly growing among children, adolescents, and young adults, who tend to be more caffeine-sensitive than the rest of the general public; consequently, caffeine-related toxicities among these groups are also growing in number. However, a quantitative and interactive tool for predicting the plasma caffeine concentration that may lead to caffeine intoxication has yet to be developed. Using the previously established population-pharmacokinetic model, we developed "caffsim" R package and its web-based applications using Shiny and EDISON (EDucation-research Integration through Simulation On the Net). The primary aim of the software is to easily predict and calculate plasma caffeine concentration and pharmacokinetic parameters and visualize their changes after single or multiple ingestions of caffeine. The caffsim R package helps understand how plasma caffeine concentration changes over time and how long toxic concentration of caffeine can last in caffeine-sensitive groups. It may also help clinical evaluation of relationship between caffeine intake and toxicities when suspicious acute symptoms occur.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. EFSA Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition and Allergies (NDA). Scientific Opinion on the safety of caffeine: Safety of caffeine. EFSA J. 2015; 13:4102. DOI: 10.2903/j.efsa.2015.4102.2. Reissig CJ, Strain EC, Griffiths RR. Caffeinated energy drinks--A growing problem. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2009; 99:1–10. DOI: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2008.08.001. PMID: 18809264.
Article3. Pray L. Caffeine in food and dietary supplements: examining safety: workshop summary. Washington D.C: The National Academies Press;2014.4. Seifert SM, Schaechter JL, Hershorin ER, Lipshultz SE. Health Effects of Energy Drinks on Children, Adolescents, and Young Adults. Pediatrics. 2011; 127:511–528. PMID: 21321035.
Article5. Banerjee P, Ali Z, Levine B, Fowler DR. Fatal Caffeine Intoxication: A Series of Eight Cases from 1999 to 2009. J Forensic Sci. 2014; 59:865–868. PMID: 24502704.
Article6. Trabulo D, Marques S, Pedroso E. Caffeinated energy drink intoxication. BMJ Case Rep. 2011; 2011:pii:bcr0920103322. DOI: 10.1136/bcr.09.2010.3322.
Article7. Jun N, Lee A, Baik I. Associations of Caffeinated Beverage Consumption and Screen Time with Excessive Daytime Sleepiness in Korean High School Students. Clin Nutr Res. 2017; 6:55–60. PMID: 28168182.
Article8. Temple JL, Ziegler AM, Graczyk AM, Crandall A. Effects of acute and chronic caffeine on risk-taking behavior in children and adolescents. J Psychopharmacol. 2017; 31:561–568. DOI: 10.1177/0269881117691568. PMID: 28198658.
Article9. Perera V, Gross AS, Xu H, McLachlan AJ. Pharmacokinetics of caffeine in plasma and saliva, and the influence of caffeine abstinence on CYP1A2 metrics. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2011; 63:1161–1168. DOI: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.2011.01326.x. PMID: 21827488.
Article10. Perera V, Gross AS, Forrest A, Landersdorfer CB, Xu H, Ait-Oudhia S, et al. A Pharmacometric Approach to Investigate the Impact of Methylxanthine Abstinence and Caffeine Consumption on CYP1A2 Activity. Drug Metab Dispos. 2013; 41:1957–1966. DOI: 10.1124/dmd.113.053074. PMID: 23996078.
Article11. Lee JW, Kim Y, Perera V, McLachlan AJ, Bae KS. Prediction of plasma caffeine concentrations in young adolescents following ingestion of caffeinated energy drinks: a Monte Carlo simulation. Eur J Pediatr. 2015; 174:1671–1678. DOI: 10.1007/s00431-015-2581-x. PMID: 26113286.
Article12. Wickham H. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis. New York: Springer-Verlag;2016.13. Cannon ME, Cooke CT, McCarthy JS. Caffeine-induced cardiac arrhythmi a: an unrecognised danger of healthfood products. Med J Aust. 2001; 174:520–521. PMID: 11419773.14. Holmgren P, Nordén-Pettersson L, Ahlner J. Caffeine fatalities--four case reports. Forensic Sci Int. 2004; 139:71–73. PMID: 14687776.
Article15. Kerrigan S, Lindsey T. Fatal caffeine overdose: two case reports. Forensic Sci Int. 2005; 153:67–69. PMID: 15935584.
Article16. Thelander G, Jönsson AK, Personne M, Forsberg GS, Lundqvist KM, Ahlner J. Caffeine fatalities--Do sales restrictions prevent intentional intoxications? Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2010; 48:354–358. DOI: 10.3109/15563650903586752. PMID: 20170393.17. de Wijkerslooth LR, Koch BC, Malingré MM, Smits P, Bartelink AKM. Lifethreatening hypokalaemia and lactate accumulation after autointoxication with Stacker 2®, a “powerful slimming agent. ” Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2008; 66:728–731. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2008.03279.x. PMID: 18823307.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effects of Web-based Simulation and High-fidelity Simulation of Acute Heart Disease Patient Care
- Effect of caffeine on the Ca2+ pool affecting contractility and actomyosin ATPase activity in vascular smooth muscle of rabbit
- Effects of caffeine and calcium on the activities of the mouse osteoblastic cells
- Histomorphological study of the potentiation effects of caffeine in pregnant mice with mitomycin V treatment
- Development of a user-friendly training software for pharmacokinetic concepts and models