Lab Med Online.
2017 Oct;7(4):176-181. 10.3343/lmo.2017.7.4.176.
Establishing Reference Intervals for Soluble ST2 Assay in a Korean Population
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Konkuk University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. ymyun@kuh.ac.kr
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, VHS Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2389657
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/lmo.2017.7.4.176
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Soluble ST2 (sST2) has emerged as a biomarker of heart failure. Previous studies indicated 35 ng/mL of sST2 as the clinically prognostic cut-off value. This study aims to establish reference intervals in a Korean population using an sST2 assay and to evaluate the applicability of the cut-off value.
METHODS
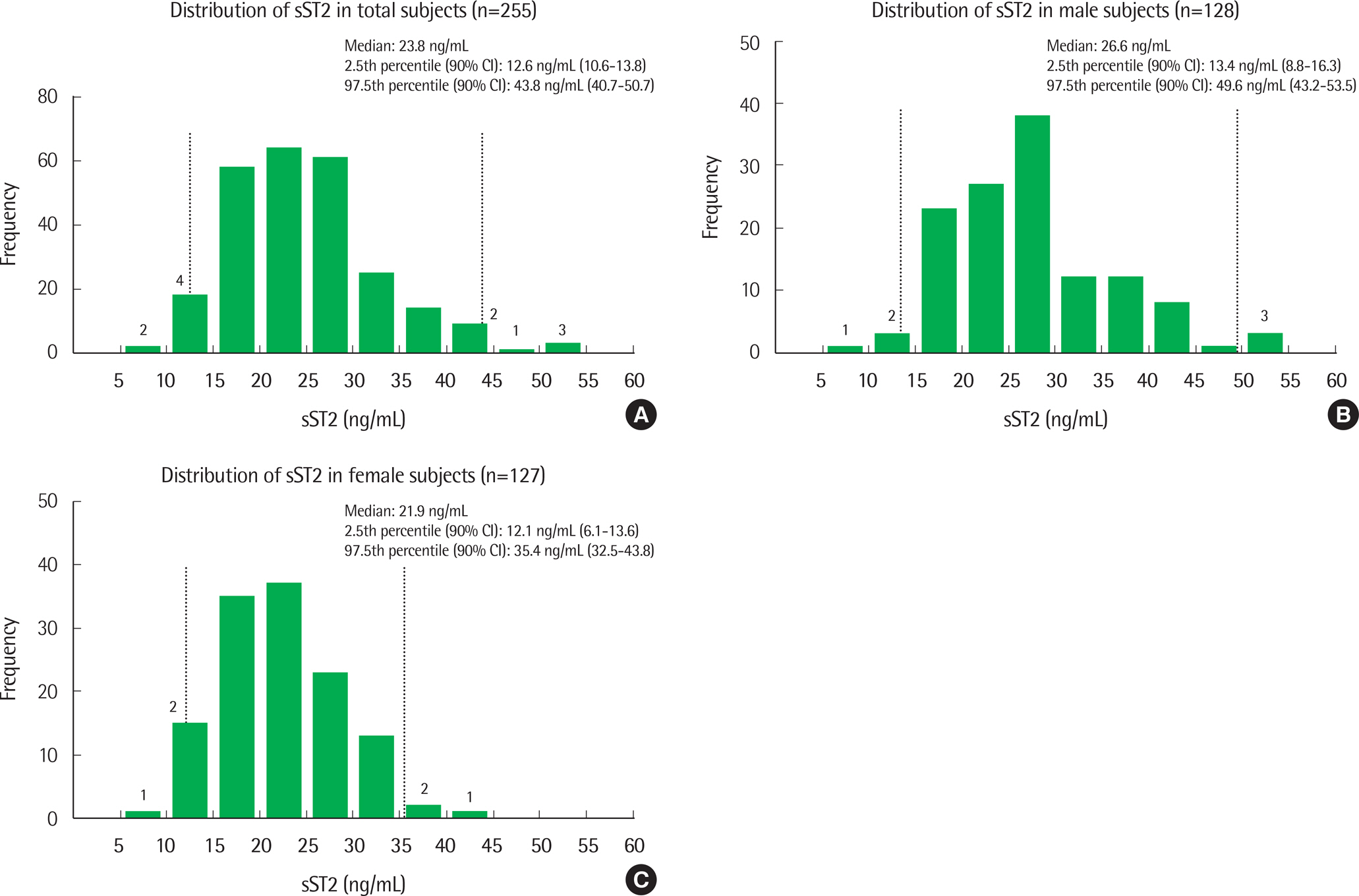
From March to May 2014, sST2 levels were assayed in serum samples of 255 cardio-healthy Koreans (128 men and 127 women) using the Presage ST2 ELISA kit (Critical Diagnostics, USA). The reference interval for sST2 was defined using the nonparametric percentile method according to the CLSI EP28-A3c guideline.
RESULTS
The median sST2 concentrations were 23.8 ng/mL (interquartile range (IQR), 19.0-28.7), 26.6 ng/mL (IQR, 21.0-30.9), and 21.9 ng/mL (IQR, 17.3-26.5) for the entire cohort, men, and women, respectively. sST2 levels were significantly higher in men than in women (P<0.0001). The 97.5th percentile upper reference limits for sST2 were 43.8 ng/mL, 49.6 ng/mL, and 35.4 ng/mL for the cohort, men, and women, respectively. Gender-specific upper reference limits were similar to limits reported by other studies.
CONCLUSIONS
We suggest that gender-specific reference intervals should be used for the Korean population, as application of a single cut-off value of 35 ng/mL may be overcautious of the possibility of false positivity, especially in men.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Dieplinger B, Mueller T. Soluble ST2 in heart failure. Clin Chim Acta. 2015; 443:57–70.
Article2. Mueller T, Jaffe AS. Soluble ST2-analytical considerations. Am J Cardiol. 2015; 115:8B–21B.
Article3. Yoo B-S. Biomarkers in heart failure: focus on B-type natriuretic peptide. Korean J Med. 2012; 82:647–50.
Article4. Lu J, Snider JV, Grenache DG. Establishment of reference intervals for soluble ST2 from a United State population. Clin Chim Acta. 2010; 411:1825–6.5. Critical diagnostics. Use of ST2 in Conjunction with Traditional clinical evaluations. http://www.criticaldiagnostics.com/US/products/pdfs/Presage_ELISA_Indication_For_Use.pdf. (Updated on July 2017).6. US Food and Drug Administration. 510(k) Premarket Notifcation. http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/cdrh_docs/reviews/k111452.pdf. (Updated on July 2017).7. Felker GM, Fiuzat M, Thompson V, Shaw LK, Neely ML, Adams KF, et al. Soluble ST2 in ambulatory patients with heart failure: association with functional capacity and longterm outcomes. Circ Heart Fail. 2013; 6:1172–9.8. Dieplinger B, Januzzi JL, Steinmair M, Gabriel C, Poelz W, Haltmayer M, et al. Analytical and clinical evaluation of a novel high-sensitivity assay for measurement of soluble ST2 in human plasma–the Presage ST2 assay. Clin Chim Acta. 2009; 409:33–40.9. Coglianese EE, Larson MG, Vasan RS, Ho JE, Ghorbani A, McCabe EL, et al. Distribution and Clinical Correlates of the Interleukin Receptor Family Member Soluble ST2 in the Framingham Heart Study. Clin Chem. 2012; 58:1673–81.
Article10. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Defning, establishig, and verifying reference intervals in Clinical laboratory; Approved guideline-Third edition. CLSI document EP28-A3C. Wayne PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. 2010.11. McMurray JJ, Adamopoulos S, Anker SD, Auricchio A, Böhm M, Dick-stein K, et al. ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure 2012: The Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute and Chronic Heart Failure 2012 of the European Society of Cardiology. Developed in collaboration with the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur J Heart Fail. 2012; 14:803–69.12. Gillett MJ. International Expert Committee report on the role of the A1C assay in the diagnosis of diabetes, Diabetes Care. 2009; 32:1327–1334. Clin Biochem Rev 2009;30: 197-200.13. Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) CKD Work Group. KDIGO 2012 clinical practice guideline for the evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease. http://kdigo.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/KDIGO_2012_CKD_GL.pdf. (Updated on July 2017).14. Levey AS, Goresh J, Greene T, Stevens LA, Zhang YL, Hendriksen S, et al. Using standardized serum creatinine values in the modifcation of diet in renal disease study equation for estimating glomerular fltration rate. Ann Intern Med. 2006; 145:247–54.15. Reed AH, Henry RJ, Mason WB. Infuence of statistical method used on the resulting estimate of normal range, Clin Chem. 1971; 17:275–84.16. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Preliminary evaluation of quantitative clinical laboratory measurement procedures; Approved guideline-third edition. CLSI document EP10-A3-AMD. Wayne PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. 2014.17. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Evaluation of the linearity of quantitative measurement procedures: a statistical approach; Approved guideline. CLSI document EP06-A. Wayne PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. 2003.18. Dieplinger B, Egger M, Poelz W, Gabriel C, Haltmayer M, Mueller T. Soluble ST2 is not independently associated with androgen and estrogen status in healthy males and females. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2011; 49:1515–8.
Article19. Wu AH, Wians F, Jaffe A. Biological variation of galectin-3 and soluble ST2 for chronic heart failure: implication on interpretation of test results. Am Heart J. 2013; 165:995–9.
Article20. Mueller T, Dieplinger B. Soluble ST2 and Galectin-3: What We Know and Don't Know Analytically. EJIFCC. 2016; 27:224–37.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Establishment of Reference Intervals for Soluble Suppression of Tumorigenicity 2 in the Elderly South Korean Population
- Elevated levels of soluble ST2 but not galectin-3 are associated with increased risk of mortality in hemodialysis patients
- Evaluation of the Performance of an Adiponectin ELISA-based Test and Establishing Serum Adiponectin Reference Intervals for Korean Population
- Establishment of Trimester-Specific Reference Intervals for Thyroid Hormones in Korean Pregnant Women
- Establishing Reference Intervals for Sex Hormones on the Analytical Platforms Advia Centaur and Immulite 2000XP