Lab Med Online.
2013 Oct;3(4):242-252.
Evaluation of the Performance of an Adiponectin ELISA-based Test and Establishing Serum Adiponectin Reference Intervals for Korean Population
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. kimhs54@yuhs.ac
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Adiponectin is a plasma protein secreted by adipose tissues and low serum adiponectin concentration has been reported to be associated with insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome (MS). We evaluated the performance of an ELISA-based assay for measuring serum adiponectin levels and established reference intervals of adiponectin for Korean population.
METHODS
Laboratory performance, including precision and linearity, of the AdipoMark Human Adiponectin ELISA kit (Mesdia Co., Korea) was assessed. Reference intervals of adiponectin concentration were determined after evaluation of 1200 subjects with no history of MS. Adiponectin was also measured in 100 patients with MS.
RESULTS
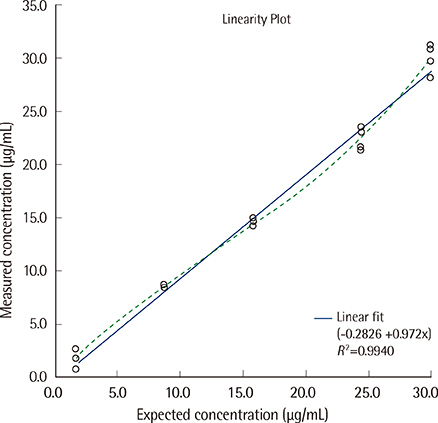
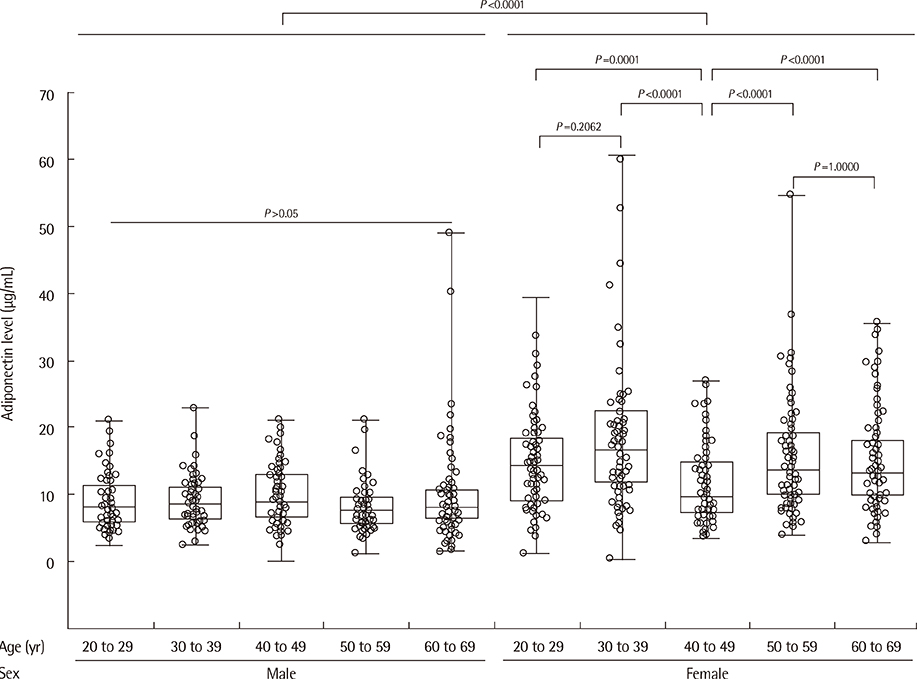
The mean concentrations of serum samples tested for precision evaluation were 6.66, 12.61, and 23.42 microg/mL: the ELISA showed total imprecision of 13.6%, 9.3%, and 10.5% CV for the respective concentrations. The assay demonstrated linear responses in the range of 1.8-29.9 microg/mL serum adiponectin levels. The 95% reference intervals for Korean population were 3.6-19.2 microg/mL for men and 4.5-34.2 microg/mL for women. ROC-area under the curve values of adiponectin for the diagnosis of MS were 0.85 for men and 0.83 for women. Low adiponectin level was independently associated with MS in the multivariate analysis.
CONCLUSIONS
The adiponectin quantitation assay evaluated in this study showed acceptable laboratory and clinical performances in an ELISA platform. To meet the ever-increasing demand for a reliable assay for measuring adiponectin levels in the study of various metabolic diseases, this assay could be further improved by the automation of the platform.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Maeda K, Okubo K, Shimomura I, Funahashi T, Matsuzawa Y, Matsubara K. cDNA cloning and expression of a novel adipose specific collagen-like factor, apM1 (AdiPose Most abundant Gene transcript 1). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1996; 221:286–289.
Article2. Arita Y, Kihara S, Ouchi N, Takahashi M, Maeda K, Miyagawa J, et al. Paradoxical decrease of an adipose-specific protein, adiponectin, in obesity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1999; 257:79–83.
Article3. Ouchi N, Kihara S, Arita Y, Maeda K, Kuriyama H, Okamoto Y, et al. Novel modulator for endothelial adhesion molecules: adipocyte-derived plasma protein adiponectin. Circulation. 1999; 100:2473–2476.4. Okamoto Y, Arita Y, Nishida M, Muraguchi M, Ouchi N, Takahashi M, et al. An adipocyte-derived plasma protein, adiponectin, adheres to injured vascular walls. Horm Metab Res. 2000; 32:47–50.
Article5. Ouchi N, Kihara S, Arita Y, Nishida M, Matsuyama A, Okamoto Y, et al. Adipocyte-derived plasma protein, adiponectin, suppresses lipid accumulation and class A scavenger receptor expression in human monocyte-derived macrophages. Circulation. 2001; 103:1057–1063.
Article6. Hotta K, Funahashi T, Arita Y, Takahashi M, Matsuda M, Okamoto Y, et al. Plasma concentrations of a novel, adipose-specific protein, adiponectin, in type 2 diabetic patients. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2000; 20:1595–1599.
Article7. Yang WS, Lee WJ, Funahashi T, Tanaka S, Matsuzawa Y, Chao CL, et al. Weight reduction increases plasma levels of an adipose-derived anti-inflammatory protein, adiponectin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2001; 86:3815–3819.
Article8. Weyer C, Funahashi T, Tanaka S, Hotta K, Matsuzawa Y, Pratley RE, et al. Hypoadiponectinemia in obesity and type 2 diabetes: close association with insulin resistance and hyperinsulinemia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2001; 86:1930–1935.
Article9. Hotta K, Funahashi T, Bodkin NL, Ortmeyer HK, Arita Y, Hansen BC, et al. Circulating concentrations of the adipocyte protein adiponectin are decreased in parallel with reduced insulin sensitivity during the progression to type 2 diabetes in rhesus monkeys. Diabetes. 2001; 50:1126–1133.
Article10. Rasmussen-Torvik LJ, Wassel CL, Ding J, Carr J, Cushman M, Jenny N, et al. Associations of body mass index and insulin resistance with leptin, adiponectin, and the leptin-to-adiponectin ratio across ethnic groups: the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA). Ann Epidemiol. 2012; 22:705–709.
Article11. Liu Q, Yuan B, Lo KA, Patterson HC, Sun Y, Lodish HF. Adiponectin regulates expression of hepatic genes critical for glucose and lipid metabolism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012; 109:14568–14573.
Article12. Behnes M, Brueckmann M, Lang S, Putensen C, Saur J, Borggrefe M, et al. Alterations of adiponectin in the course of inflammation and severe sepsis. Shock. 2012; 38:243–248.
Article13. Dalamaga M, Diakopoulos KN, Mantzoros CS. The role of adiponectin in cancer: a review of current evidence. Endocr Rev. 2012; 33:547–594.
Article14. Martos-Moreno GÁ, Burgos-Ramos E, Canelles S, Argente J, Barrios V. Evaluation of a multiplex assay for adipokine concentrations in obese children. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2010; 48:1439–1446.
Article15. Loo BM, Marniemi J, Jula A. Evaluation of multiplex immunoassays, used for determination of adiponectin, resistin, leptin, and ghrelin from human blood samples, in comparison to ELISA assays. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 2011; 71:221–226.
Article16. Cangemi G, Di Iorgi N, Barco S, Reggiardo G, Maghnie M, Melioli G. Plasma total adiponectin levels in pediatrics: reference intervals calculated as a continuous variable of age. Clin Biochem. 2012; 45:1703–1705.
Article17. Gavrila A, Peng CK, Chan JL, Mietus JE, Goldberger AL, Mantzoros CS. Diurnal and ultradian dynamics of serum adiponectin in healthy men: comparison with leptin, circulating soluble leptin receptor, and cortisol patterns. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2003; 88:2838–2843.
Article18. Shand B, Elder P, Scott R, Frampton C, Willis J. Biovariability of plasma adiponectin. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2006; 44:1264–1268.
Article19. Pischon T, Hotamisligil GS, Rimm EB. Adiponectin: stability in plasma over 36 hours and within-person variation over 1 year. Clin Chem. 2003; 49:650–652.
Article20. Wildman RP, Wang D, Fernandez I, Mancuso P, Santoro N, Scherer PE, et al. Associations of testosterone and sex hormone binding globulin with adipose tissue hormones in midlife women. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2013.
Article21. Riestra P, García-Anguita A, Lasunción MA, Cano B, de Oya M, Garcés C. Relationship of adiponectin with metabolic syndrome components in pubertal children. Atherosclerosis. 2011; 216:467–470.
Article22. Yoon SJ, Lee HS, Lee SW, Yun JE, Kim SY, Cho ER, et al. The association between adiponectin and diabetes in the Korean population. Metabolism. 2008; 57:853–857.
Article23. Kotani K, Sakane N. Leptin:adiponectin ratio and metabolic syndrome in the general Japanese population. Korean J Lab Med. 2011; 31:162–166.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Development of ELISA-kit of Quantitative Analysis for Adiponectin and Their Correlation with Cardiovascular Risk Factors
- The Role of Plasma Adiponectin and Polymorphism of Adiponectin Gene in the Development of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Changes of Serum Adiponectin Levels in Murine Experimental Sparganosis
- Correlations between umbilical and maternal serum adiponectin levels and neonatal birthweight
- Adiponectin and Resistin