Ann Rehabil Med.
2017 Apr;41(2):299-305. 10.5535/arm.2017.41.2.299.
Maximal Inspiratory Pressure and Maximal Expiratory Pressure in Healthy Korean Children
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Pusan National University Hospital, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Busan, Korea. drshinmj@gmail.com
- 2Biomedical Research Institute, Pusan National University, Busan, Korea.
- 3Research Institute for Convergence of Biomedical Science and Technology, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Yangsan, Korea.
- 4Department of Pediatrics, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- 5Department of Statistics, Pusan National University, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 2389489
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2017.41.2.299
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To evaluate respiratory muscle strength in healthy Korean children in order to establish the criteria for normal reference values for future applications. In contrast with the other parameters for testing pulmonary function, normal values for respiratory muscle strength in healthy Korean children have not been assessed to date.
METHODS
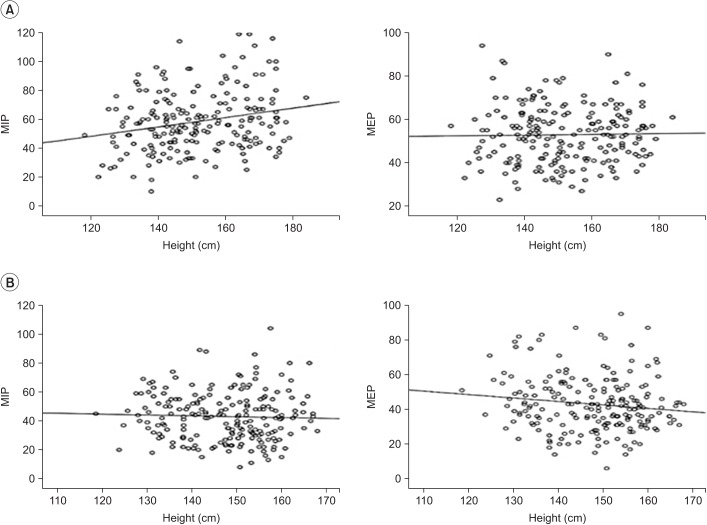
We conducted a complete survey of 263 students at Sinmyung Elementary School in Yangsan, Gyeongsangnam-do, and measured their height and body weight, performed pulmonary function tests, and evaluated maximal inspiratory pressure (MIP) and maximal expiratory pressure (MEP) as measures of respiratory muscle strength. We excluded the subjects with respiratory or cardiovascular diseases that could affect the results. The subjects were children aged 8-12 years, and they consisted of 124 boys and 139 girls.
RESULTS
The MIP and MEP values (mean±standard deviation) for the entire subject group were 48.46±18.1 cmHâ‚‚O and 47.95±16 cmHâ‚‚O, respectively. Boys showed higher mean values for MIP and MEP in every age group. Korean children showed lower mean values for MIP and MEP compared to those in previous studies conducted in other countries (Brazil and USA).
CONCLUSION
Our results showed that boys generally have greater respiratory muscle strength than girls. We found a significant difference between the results of our study and those of previous studies from other countries. We speculate that this may be attributed to differences in ethnicity, nutrition, or daily activities.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Phillips MF, Quinlivan RC, Edwards RH, Calverley PM. Changes in spirometry over time as a prognostic marker in patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001; 164:2191–2194. PMID: 11751186.
Article2. Inkley SR, Oldenburg FC, Vignos PJ Jr. Pulmonary function in Duchenne muscular dystrophy related to stage of disease. Am J Med. 1974; 56:297–306. PMID: 4813648.
Article3. Aslan GK, Gurses HN, Issever H, Kiyan E. Effects of respiratory muscle training on pulmonary functions in patients with slowly progressive neuromuscular disease: a randomized controlled trial. Clin Rehabil. 2014; 28:573–581. PMID: 24275453.
Article4. Arnall DA, Nelson AG, Owens B, Cebria i, Sokell GA, Kanuho V, et al. Maximal respiratory pressure reference values for Navajo children ages 6-14. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2013; 48:804–808. PMID: 23661611.
Article5. Lynn DJ, Woda RP, Mendell JR. Respiratory dysfunction in muscular dystrophy and other myopathies. Clin Chest Med. 1994; 15:661–674. PMID: 7867281.
Article6. Nam SY, Kim KH, Hong YM, Kim GH. Normal predicted values of pulmonary function test in healthy Korean children. J Korean Pediatr Soc. 1998; 41:338–345.7. Dimitriadis Z, Kapreli E, Konstantinidou I, Oldham J, Strimpakos N. Test/retest reliability of maximum mouth pressure measurements with the MicroRPM in healthy volunteers. Respir Care. 2011; 56:776–782. PMID: 21310113.
Article8. Brooke MH, Fenichel GM, Griggs RC, Mendell JR, Moxley RT 3rd, Miller JP, et al. Clinical investigation of Duchenne muscular dystrophy: interesting results in a trial of prednisone. Arch Neurol. 1987; 44:812–817. PMID: 3632393.9. McDonald CM, Abresch RT, Carter GT, Fowler WM Jr, Johnson ER, Kilmer DD, et al. Profiles of neuromuscular diseases: Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 1995; 74(5 Suppl):S70–S92. PMID: 7576424.10. Kreitzer SM, Saunders NA, Tyler HR, Ingram RH Jr. Respiratory muscle function in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1978; 117:437–447. PMID: 629478.
Article11. McCool FD, Tzelepis GE. Inspiratory muscle training in the patient with neuromuscular disease. Phys Ther. 1995; 75:1006–1014. PMID: 7480122.
Article12. Choi JK, Paek D, Lee JO. Normal predictive values of spirometry in Korean population. Tuberc Respir Dis. 2005; 58:230–242.
Article13. Heinzmann-Filho JP, Vasconcellos Vidal PC, Jones MH, Donadio MV. Normal values for respiratory muscle strength in healthy preschoolers and school children. Respir Med. 2012; 106:1639–1646. PMID: 22974829.
Article14. Wilson SH, Cooke NT, Edwards RH, Spiro SG. Predicted normal values for maximal respiratory pressures in Caucasian adults and children. Thorax. 1984; 39:535–538. PMID: 6463933.
Article15. American Thoracic Society. Lung function testing: selection of reference values and interpretative strategies. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1991; 144:1202–1218. PMID: 1952453.16. Dassios T, Katelari A, Doudounakis S, Dimitriou G. Comparison of two methods of measurement of maximal respiratory pressures in health and cystic fibrosis. J Biomed Sci Eng. 2013; 6:43–48.
Article17. Lyall RA, Donaldson N, Fleming T, Wood C, Newsom-Davis I, Polkey MI, et al. A prospective study of quality of life in ALS patients treated with noninvasive ventilation. Neurology. 2001; 57:153–156. PMID: 11445650.
Article18. Polkey MI, Green M, Moxham J. Measurement of respiratory muscle strength. Thorax. 1995; 50:1131–1135. PMID: 8553266.
Article19. Khalil M, Wagih K, Mahmoud O. Evaluation of maximum inspiratory and expiratory pressure in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Egypt J Chest Dis Tuberc. 2014; 63:329–335.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effects of Lower Rib Expansion Limitation on Maximal Respiratory Pressure and Abdominal Muscle Activity During Maximal Breathing in Healthy Subjects
- Maximal Expiratory and Inspiratory Mouth Pressures in Korean Normal Adults
- Respiratory Muscle Strength and Cough Capacity in Patients with Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
- Reference Range of Respiratory Muscle Strength and Its Clinical Application in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: A Single-Center Study
- A Comparison of Stress Leak-Point Pressure and Maximal Urethral Closure Pressure in Patients with Genuine Stress Incontinence