J Clin Neurol.
2016 Jul;12(3):361-367. 10.3988/jcn.2016.12.3.361.
Reference Range of Respiratory Muscle Strength and Its Clinical Application in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: A Single-Center Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Gyeongsang National University Hospital, Jinju, Korea.
- 2Regional Cardiocerebrovascular Center, Gyeongsang National University Hospital, Jinju, Korea.
- 3Department of Neurology, Gil Medical Center, Gachon University, Incheon, Korea.
- 4Department of Neurology, Jeju National University School of Medicine, Jeju, Korea.
- 5Department of Neurology, Korea Cancer Center Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 6Department of Neurology, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 7Department of Neurology, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jjsaint@snu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2354125
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3988/jcn.2016.12.3.361
Abstract
- BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE
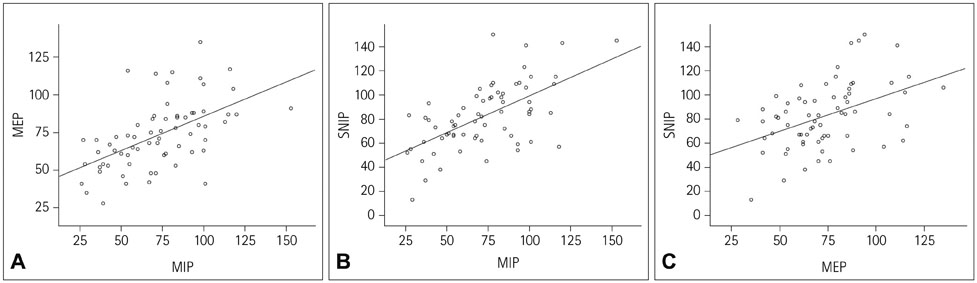
Evaluating respiratory function is important in neuromuscular diseases. This study explored the reference ranges of the maximal inspiratory pressure (MIP), maximal expiratory pressure (MEP), and sniff nasal inspiratory pressure (SNIP) in healthy adults, and applied them to amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) patients.
METHODS
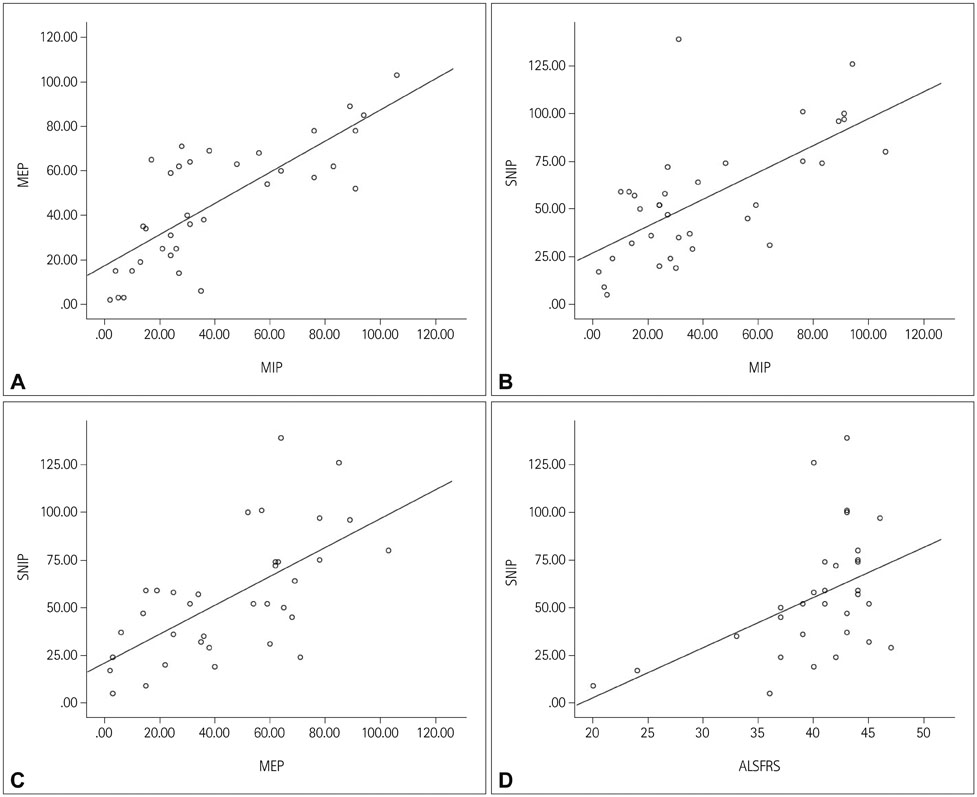
MIP, MEP, and SNIP were measured in 67 healthy volunteers aged from 21 to 82 years. Reference ranges were evaluated by multivariate regression analysis using the generalized additive modeling of location, scale, and shape method. Thirty-six ALS patients were reviewed retrospectively, and abnormal values of MIP, MEP, and SNIP were determined according to the reference ranges.
RESULTS
MIP, MEP, and SNIP were abnormal in 57.1%, 51.4%, and 25.7% of the ALS patients, respectively. MIP and SNIP were significantly correlated with the degree of restrictive pattern and respiratory symptoms. The ALS Functional Rating Scale-Revised score was correlated with SNIP.
CONCLUSIONS
This study has provided the reference range of respiratory muscle strength in healthy adults. This range is suitable for evaluating respiratory function in ALS patients.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Gelinas DF. Pulmonary function screening. Semin Neurol. 2003; 23:89–96.
Article2. Evans JA, Whitelaw WA. The assessment of maximal respiratory mouth pressures in adults. Respir Care. 2009; 54:1348–1359.3. Morgan RK, McNally S, Alexander M, Conroy R, Hardiman O, Costello RW. Use of Sniff nasal-inspiratory force to predict survival in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2005; 171:269–274.
Article4. Choi JK, Paek D, Lee JO. Normal predictive values of spirometry in Korean population. Tuberc Respir Dis. 2005; 58:230–242.
Article5. Kamide N, Ogino M, Yamashina N, Fukuda M. Sniff nasal inspiratory pressure in healthy Japanese subjects: mean values and lower limits of normal. Respiration. 2009; 77:58–62.
Article6. Brooks BR, Miller RG, Swash M, Munsat TL. World Federation of Neurology Research Group on Motor Neuron Diseases. El Escorial revisited: revised criteria for the diagnosis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Amyotroph Lateral Scler Other Motor Neuron Disord. 2000; 1:293–299.
Article7. Gordon PH, Miller RG, Moore DH. ALSFRS-R. Amyotroph Lateral Scler Other Motor Neuron Disord. 2004; 5:Suppl 1. 90–93.
Article8. Rigby RA, Stasinopoulos DM. Generalized additive models for location, scale and shape. J R Stat Soc: Serie C (Appl Stat). 2005; 54:507–554.9. Cole TJ, Stanojevic S, Stocks J, Coates AL, Hankinson JL, Wade AM. Age- and size-related reference ranges: a case study of spirometry through childhood and adulthood. Stat Med. 2009; 28:880–898.
Article10. Cedarbaum JM, Stambler N, Malta E, Fuller C, Hilt D, Thurmond B, et al. The ALSFRS-R: a revised ALS functional rating scale that incorporates assessments of respiratory function. BDNF ALS Study Group (Phase III). J Neurol Sci. 1999; 169:13–21.
Article11. Harik-Khan RI, Wise RA, Fozard JL. Determinants of maximal inspiratory pressure. The Baltimore Longitudinal Study of Aging. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998; 158(5 Pt 1):1459–1464.12. Pessoa IM, Houri Neto M, Montemezzo D, Silva LA, Andrade AD, Parreira VF. Predictive equations for respiratory muscle strength according to international and Brazilian guidelines. Braz J Phys Ther. 2014; 18:410–418.
Article13. Huang CH, Yang GG, Chen TW. Sniff nasal inspiratory pressure does not decrease in elderly subjects. J Phys Ther Sci. 2014; 26:1509–1513.
Article14. Beyerlein A, Fahrmeir L, Mansmann U, Toschke AM. Alternative regression models to assess increase in childhood BMI. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2008; 8:59.
Article15. Black LF, Hyatt RE. Maximal respiratory pressures: normal values and relationship to age and sex. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1969; 99:696–702.16. Charfi MR, Matran R, Regnard J, Richard MO, Champeau J, Dall'ava J, et al. [Maximal ventilatory pressure through the mouth in adults: normal values and explanatory variables]. Rev Mal Respir. 1991; 8:367–374.17. Sclauser Pessoa IM, Franco Parreira V, Fregonezi GA, Sheel AW, Chung F, Reid WD. Reference values for maximal inspiratory pressure: a systematic review. Can Respir J. 2014; 21:43–50.
Article18. Sachs MC, Enright PL, Hinckley Stukovsky KD, Jiang R, Barr RG. Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis Lung Study. Performance of maximum inspiratory pressure tests and maximum inspiratory pressure reference equations for 4 race/ethnic groups. Respir Care. 2009; 54:1321–1328.19. Heffernan C, Jenkinson C, Holmes T, Macleod H, Kinnear W, Oliver D, et al. Management of respiration in MND/ALS patients: an evidence based review. Amyotroph Lateral Scler. 2006; 7:5–15.
Article20. Hardiman O. Management of respiratory symptoms in ALS. J Neurol. 2011; 258:359–365.
Article21. Gregory SA. Evaluation and management of respiratory muscle dysfunction in ALS. NeuroRehabilitation. 2007; 22:435–443.
Article22. Schmidt EP, Drachman DB, Wiener CM, Clawson L, Kimball R, Lechtzin N. Pulmonary predictors of survival in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: use in clinical trial design. Muscle Nerve. 2006; 33:127–132.
Article23. Baumann F, Henderson RD, Morrison SC, Brown M, Hutchinson N, Douglas JA, et al. Use of respiratory function tests to predict survival in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Amyotroph Lateral Scler. 2010; 11:194–202.
Article24. Mendoza M, Gelinas DF, Moore DH, Miller RG. A comparison of maximal inspiratory pressure and forced vital capacity as potential criteria for initiating non-invasive ventilation in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Amyotroph Lateral Scler. 2007; 8:106–111.
Article25. Kaufmann P, Levy G, Thompson JL, Delbene ML, Battista V, Gordon PH, et al. The ALSFRSr predicts survival time in an ALS clinic population. Neurology. 2005; 64:38–43.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Use of Total Intravenous Anesthesia Without Muscle Relaxation in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Patient
- Anesthetic management with neuromuscular monitoring and bispectral index in an amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patient: A case report
- Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Associated With CADASIL
- Anesthetic Management of an Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Patient Undergoing Dental Care in Daysurgery Center
- Syndrome of Progressive Bulbar Palsy in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: A Case Report