J Dent Rehabil Appl Sci.
2017 Jun;33(2):106-113. 10.14368/jdras.2017.33.2.106.
Interaction of Hydroxyethylidene bisphosphonate (HEBP) with other endodontic irrigants on tissue dissolving capacity and antimicrobial effect
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Conservative Dentistry, Veterans Health Service Medical Center, Seoul, Republic of Korea. endo95@naver.com
- KMID: 2388016
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14368/jdras.2017.33.2.106
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The purpose of this study was to evaluate tissue dissolving capacity, antimicrobial effect of Hydroxyethylidene bisphosphonate (HEBP) interacting with sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl), Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) as conventional endodontic irrigants and to determine tissue dissolving efficacy depended on temperature.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
A total of 80 bovine muscles were randomly distributed into 8 groups (n = 10). After their initial weights determined on a precision scale, the specimens in each group were immersed in the solutions for 5, 10 and 15 min and reweighted at each time period. Agar diffusion test inoculated with Enterococcus faecalis was performed for antimicrobial effect of each endodontic irrigants.
RESULTS
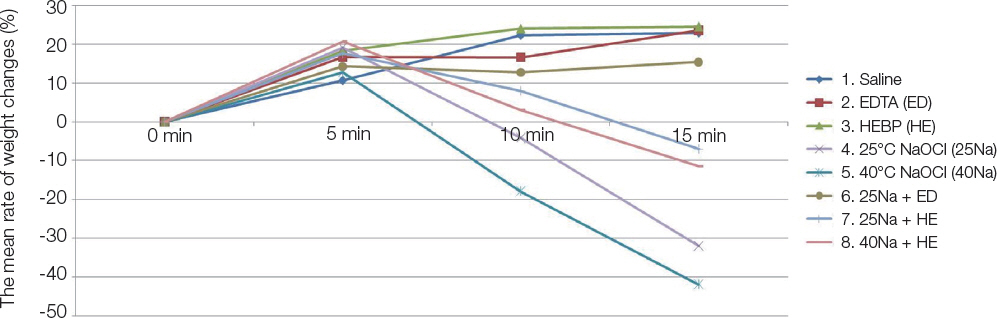
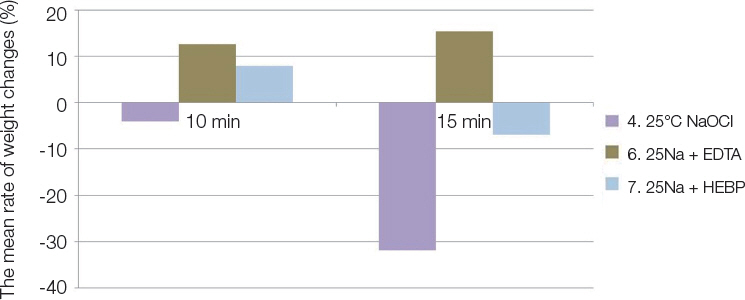
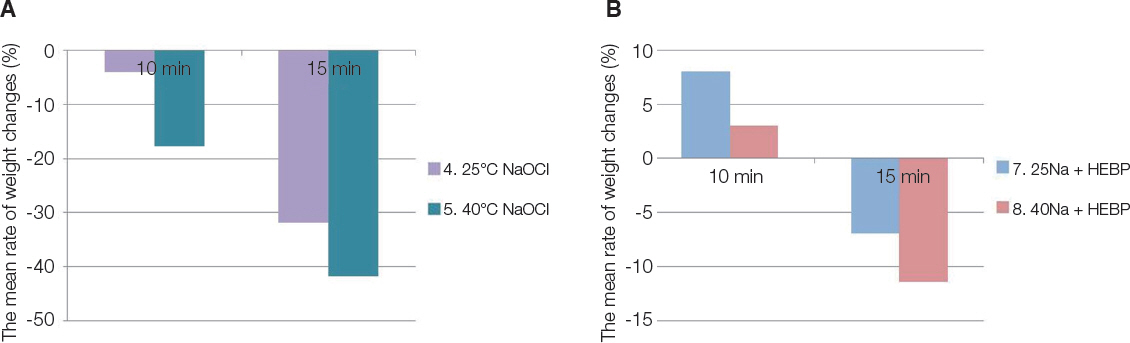
The ability to dissolve organic matter was greater in NaOCl group following NaOCl and HEBP mixture. Heated NaOCl (40℃) and NaOCl/HEBP mixture was greater tissue dissolving efficacy than room temperature (25℃). Antimicrobial effect was greater and significant in the following order EDTA > EDTA + 1% NaOCl > 1% NaOCl ≥ 1% NaOCl + HEBP.
CONCLUSION
HEBP as soft chelating agent does not disturb antimicrobial effect and less affected tissue dissolving efficacy as inherent properties of NaOCl. In the heated NaOCl/HEBP mixture analyzed, it dissolved more the organic matter than room temperature.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Peters OA, Laib A, Göhring TN, Barbakow F. Changes in root canal geometry after preparation assessed by high-resolution computed tomography. J Endod. 2001; 27:1–6. DOI: 10.1097/00004770-200101000-00001. PMID: 11487156.2. Zehnder M, Kosicki D, Luder H, Sener B, Waltimo T. Tissue-dissolving capacity and antibacterial effect of buffered and unbuffered hypochlorite solutions. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2002; 94:756–62. DOI: 10.1067/moe.2002.128961. PMID: 12464903.3. Sirtes G, Waltimo T, Schaetzle M, Zehnder M. The effects of temperature on sodium hypochlorite short-term stability, pulp dissolution capacity, and antimicrobial efficacy. J Endod. 2005; 31:669–71. DOI: 10.1097/01.don.0000153846.62144.d2. PMID: 16123703.4. Wang Z, Shen Y, Haapasalo M. Effect of smear layer against disinfection protocols on Enterococcus faecalis-infected dentin. J Endod. 2013; 39:1395400. DOI: 10.1016/j.joen.2013.05.007. PMID: 24139261.5. Grawehr M, Sener B, Waltimo T, Zehnder M. Interactions of ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid with sodium hypochlorite in aqueous solutions. Int Endod J. 2003; 36:411–7. DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2591.2003.00670.x. PMID: 12801288.6. Zehnder M, Schmidlin P, Sener B, Waltimo T. Chelation in root canal therapy reconsidered. J Endod. 2005; 31:817–20. DOI: 10.1097/01.don.0000158233.59316.fe. PMID: 16249726.7. Russell RG, Rogers MJ. Bisphosphonates:from the laboratory to the clinic and back again. Bone. 1999; 25:97–106. DOI: 10.1016/S8756-3282(99)00116-7.8. Kuruvilla A, Jaganath BM, Krishnegowda SC, Ramachandra PK, Johns DA, Abraham A. A comparative evaluation of smear layer removal by using edta, etidronic acid, and maleic acid as root canal irrigants:an in vitro scanning electron microscopic study. J Conserv Dent. 2015; 18:247–51. DOI: 10.4103/0972-0707.157266. PMID: 26069414. PMCID: PMC4450534.9. Lottanti S, Gautschi H, Sener B, Zehnder M. Effects of ethylenediaminetetraacetic, etidronic and peracetic acid irrigation on human root dentine and the smear layer. Int Endod J. 2009; 42:335–43. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2591.2008.01514.x. PMID: 19220516.10. Dineshkumar MK, Vinothkumar TS, Arathi G, Shanthisree P, Kandaswamy D. Effect of ethylene diamine tetra-acetic acid, MTADTM, and HEBP as a final rinse on the microhardness of root dentin. J Conserv Dent. 2012; 15:170–3. DOI: 10.4103/0972-0707.94587. PMID: 22557818. PMCID: PMC3339014.11. Schwartz RS. Adhesive dentistry and endodontics. Part 2:bonding in the root canal system-the promise and the problems:a review. J Endod. 2006; 32:1125–34. DOI: 10.1016/j.joen.2006.08.003. PMID: 17174666.12. Cunningham WT, Balekjian AY. Effect of temperature on collagen-dissolving ability of sodium hypochlorite endodontic irrigant. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1980; 49:175–7. DOI: 10.1016/0030-4220(80)90313-8.13. Dychdala GR. Chlorine and chlorine compounds. Block SS, editor. Disinfection, sterilization and preservation. Philadelphia: Lea & Febiger;1991. p. 131–51.14. Siqueira JF Jr, Batista MM, Fraga RC, de Uzeda M. Antibacterial effects of endodontic irrigants on black-pigmented gram-negative anaerobes and facultative bacteria. J Endod. 1998; 24:414–6. DOI: 10.1016/S0099-2399(98)80023-X.15. Heling I, Chandler NP. Antimicrobial effect of irrigant combinations within dentinal tubules. Int Endod J. 1998; 31:8–14. DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2591.1998.t01-1-00124.x. PMID: 9823123.16. Moorer WR, Wesselink PR. Factors promoting the tissue dissolving capability of sodium hypochlorite. Int Endo J. 1982; 15:187–96. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2591.1982.tb01277.x.17. Zapata RO, Bramante CM, de Moraes IG, Bernardineli N, Gasparoto TH, Graeff MS, Campanelli AP, Garcia RB. Confocal laser scanning microscopy is appropriate to detect viability of Enterococcus faecalis in infected dentin. J Endod. 2008; 34:1198201. DOI: 10.1016/j.joen.2008.07.001. PMID: 18793919.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Chemically induced osteomyelitis in the mandible: A case report
- Antimicrobial effect of calcium hydroxide as an intracanal medicament in root canal treatment: a literature review - Part I. In vitro studies
- A new phantom to evaluate the tissue dissolution ability of endodontic irrigants and activating devices
- Evaluation of time-dependent antimicrobial effect of sodium dichloroisocyanurate (NaDCC) on Enterococcus faecalis in the root canal
- Accuracy of Root ZX in teeth with simulated root perforation in the presence of gel or liquid type endodontic irrigant