Nat Prod Sci.
2017 Jun;23(2):132-138. 10.20307/nps.2017.23.2.132.
Synergetic Hepatoprotective Effects of Korean Red Ginseng and Pueraria Radix on the Liver Damaged-Induced by Carbon Tetrachloride (CClâ‚„) in Mice
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Food Science and Nutrition, Hallym University, 1 Hallymdeahak-gil, Chuncheon 24252, Republic of Korea. limss@hallym.ac.kr
- 2Institute of Korean Nutrition, Hallym University, 1 Hallymdeahak-gil, Chuncheon 24252, Republic of Korea.
- 3Institute of Natural Medicine, Hallym University, 1 Hallymdeahak-gil, Chuncheon 24252, Republic of Korea.
- KMID: 2387064
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.20307/nps.2017.23.2.132
Abstract
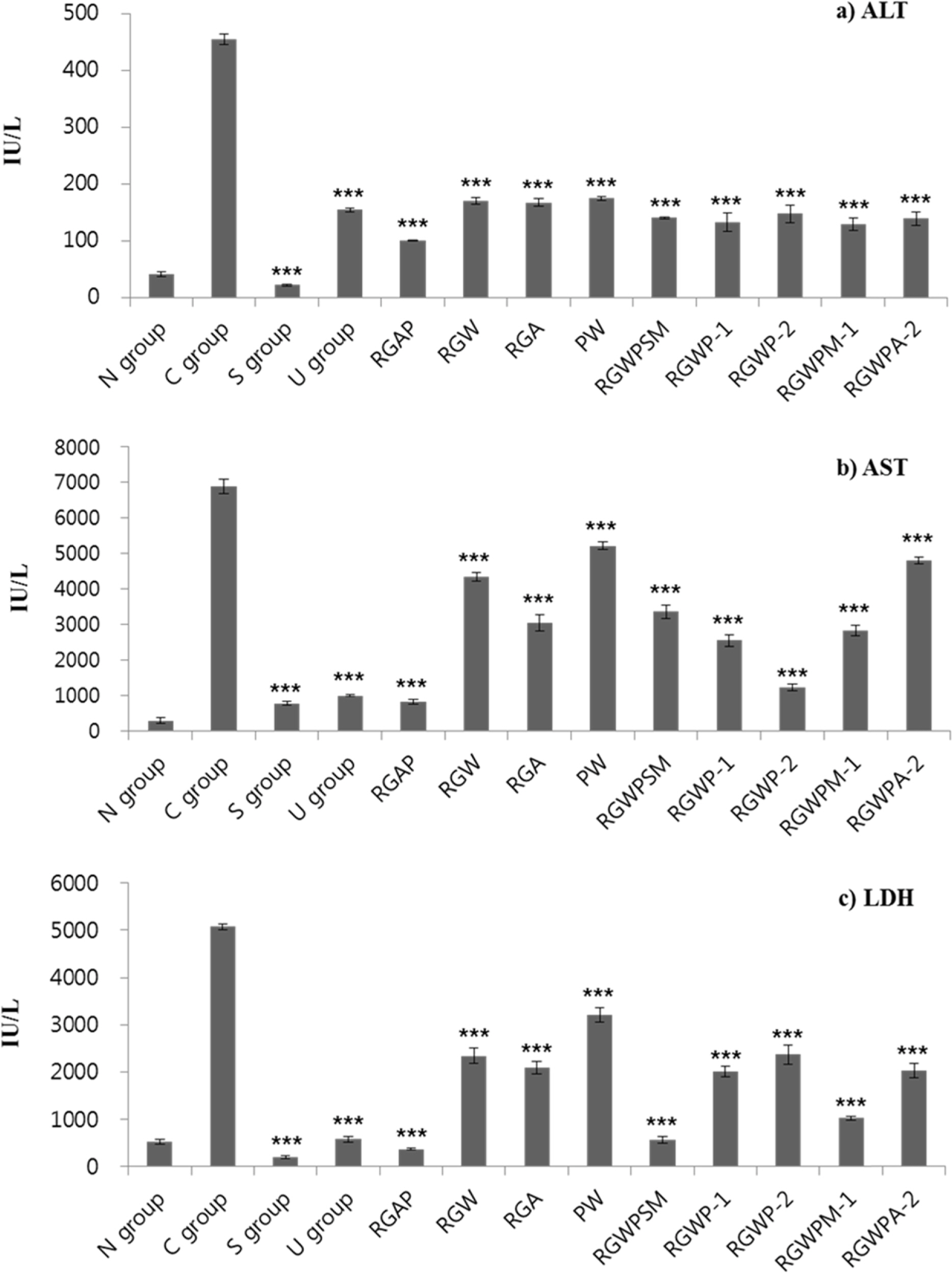
- This study was designed to investigate the synergetic hepatoprotective effects from a mixture of Korean Red Ginseng and Pueraria Radix on carbon tetrachloride (CClâ‚„)-induced hepatotoxicity in mice. Liver toxicity was induced by intraperitoneal administration of CClâ‚„ (0.6 mg/kg) in 12 groups of ICR mice. The negative control group was given CClâ‚„ without test samples and the normal group was given no treatment. Among treatment groups, the RGAP treatment (Korean Red ginseng acetic acid extract : Pueraria Radix water extract, w/w, 38.4:57.6) decreased CClâ‚„-elevated ALT (101.60 IU/L), AST (833.89 IU/L), and LDH (365.02 IU/L) levels in the serum, and increased the SOD (11.03 unit/mg protein) and CAT (0.37 unit/mg protein) levels and the LPO levels (59.09 µM/g tissue) more than that in the mice group with CClâ‚„-induced control group hepatotoxicity. These results suggest that administration of a mixture of Korean Red ginseng and Pueraria Radix decreases CClâ‚„-induced liver damage and enhances antioxidant activity in mice and imply that administration of the mixture in a certain ratio is more effective than single administration of either Korean Red ginseng or Pueraria Radix alone.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
(1). Lee C. K.., Han Y. N.., Kim N. Y.., Choi J. W. J.Ginseng Res. 2003. 27:11–16.(2). Kim H. J.., Lee J. W.., Ji Y. J.., Yu M. H.., Park J. H.., Lee K. D.., Lee I. S. J.Korean Soc. Food Sci. Nutr. 2007. 36:521–526.(3). Campos R.., Garrido A.., Guerra R.., Valenzula A.Planta Med. 1989. 55:417–419.(4). Han J. Y.., Lee S. K.., Yang J. H.., Kim S. J.., Sim J. H.., Kim M. G.., Jeong T. C.., Ku S. K.., Cho I. J.., Kim S. H. J.Ginseng Res. 2015. 39:105–115.(5). Han B. H.., Park M. W.., Han Y. N.Arch. Pharm. Res. 1981. 4:53–58.(6). Lee F. C.., Park J. K.., Kim E. K.., Ko J. K.., Lee J. S.., Kim K. Y.Proc 4th Int Ginseng Symp. 1984. 21–26.(7). Ha T. Y.., Lee J. H.., Kim S. H. J.Korea Soc. Microbiol. 1986. 21:133–144.(8). Lee S. E.., Lee S. W.., Bang J. K.., Yu Y. J.., Seong N. S.Korean J. Medicinal Crop Sci. 2004. 12:237–242.(9). Shin H. R.., Kim J. Y.., Yun T. K.., Morgan G.., Vainio H.Cancer Causes Control. 2000. 11:565–576.
Article(10). Yun T. K.Lancet Oncol. 2001. 2:49–55.(11). Nakamoto H.., Iwasaki Y.., Kizu H.Yakugaku Zasshi. 1977. 97:103–105.(12). Miura K.., Takeda R.., Nakamoto H.., Saito H. J.Appl. Pharmacol. 1971. 5:247–252.(13). Fan L. L.., Zeng G. Y.., Zhou Y. P.., Zhang L. Y.., Cheng Y. S.Chin. Med. J. 1982. 95:145–150.(14). Jha H. C.., von Recklinghausen G.., Zilliken F.Biochem. Pharmacol. 1985. 34:1367–1369.(15). Lin R. C.., Guthrie S.., Xie C. Y.., Mai K.., Lee, D. Y, Lumeng L.., Li T. K.Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 1996. 20:659–663.(16). Lee C. H.., Han S. H.., Kim J. B.., Min S. G. J.Korean Soc. Food Sci. Nutr. 1995. 24:713–719.(17). Reitman S.., Frankel S.Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1957. 28:56–63.(18). King J.Clin Chem. 1972. 18:1443.(19). Cropo J. D.., McCord J. M.., Fridovich I.Methods. Enzymol. 1978. 53:382–393.(20). Lee E.., Shin C. O.Korean J. Plant Res. 2007. 20:475–480.(21). Ohkawa H.., Ohishi N.., Yagi K.Anal. Biochem. 1979. 95:351–358.(22). Uchida T.., Kao H.., Quispe-Sjogen M.., Peters R. L.Gastroenterology. 1983. 84:683–692.(23). Davies P.., Maloney A. J. F.Lancet. 1976. 2:1403–1407.(24). Kim Y. S.Korean J. Ginseng Sci. 1995. 19:108–113.(25). Lee J. S.., Kim E. S.., Kim S. W. J.Korean Soc. Food Sci. Nutr. 1999. 28:901–906.(26). Lee Y. K. J.East Asian Soc. Diet. Life. 1994. 4:59–67.(27). Seong G. S.., Chun S. G.., Chang C. C. J.Ginseng Res. 2005. 29:131–137.(28). Sung K. S.., Chun C.., Kwon Y. H.., Chang C. C. J.Ginseng Res. 2000. 24:176–182.(29). Nam K. Y.., Choi J. E.., Park J. D.Korean J. Medicinal Crop Sci. 2013. 21:401–414.(30). Kong Y. H.., Rho J. H.., Cho C. W.., Kim M. H.., Lee Y. C.., Kim S. S.., Lee P. J.., Choi S. Y. J.Ginseng Res. 2009. 33:194–198.(31). Bae E. A.., Han M. J.., Kim E. J.., Kim D. H.Arch. Pharm. Res. 2004. 27:61–67.(32). Kim M. H.., Hong H. D.., Kim Y. C.., Rhee Y. K.., Kim K. T.., Rho J. H. J.Ginseng Res. 2010. 34:93–97.(33). Hong H. D.., Sim E. M.., Kim K.., Rho J.., Rhee Y. K.., Cho C. W.Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2009. 18:565–569.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Hepaprotective Effect of Standardized Ecklonia stolonifera Formulation on CClâ‚„-Induced Liver Injury in Sprague-Dawley Rats
- Swertiamarin ameliorates carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatic apoptosis via blocking the PI3K/Akt pathway in rats
- Effect of sodium selenite on the hepatotoxicity induced with carbon tetrachloride
- Morphologic Change of Rat Liver Induced by Repeated Administration of Carbon Tetrachloride and Dimethylnitrosamine
- Carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)-induced hepatic fibrosis in the rat