Tuberc Respir Dis.
2017 Jul;80(3):270-276. 10.4046/trd.2017.80.3.270.
Frequency and Type of Disputed rpoB Mutations in Mycobacterium tuberculosis Isolates from South Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. shimts@amc.seoul.kr
- 2YD R&D Center, YD Diagnostics, Yongin, Korea.
- 3Department of Laboratory Medicine, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2385042
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4046/trd.2017.80.3.270
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
A disputed rpoB mutation is a specific type of rpoB mutation that can cause low-level resistances to rifampin (RIF). Here, we aimed to assess the frequency and types of disputed rpoB mutations in Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates from South Korea.
METHODS
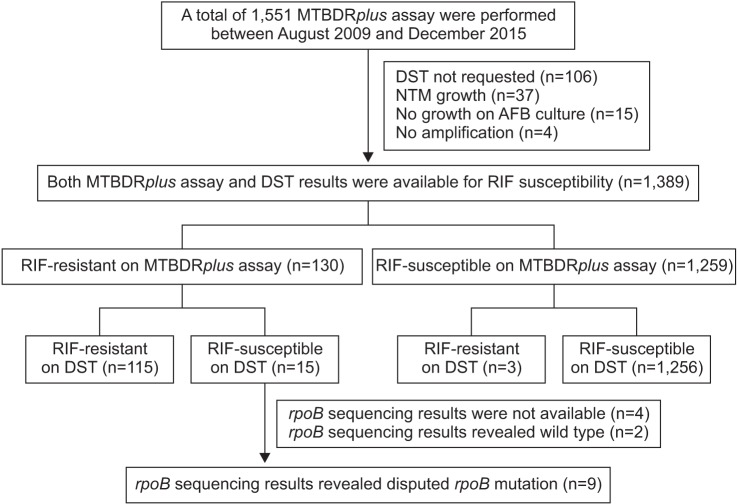
Between August 2009 and December 2015, 130 patients exhibited RIF resistance on the MTBDRplus assay at Asan Medical Center. Among these cases, we identified the strains with disputed rpoB mutation by rpoB sequencing analysis, as well as among the M. tuberculosis strains from the International Tuberculosis Research Center (ITRC).
RESULTS
Among our cases, disputed rpoB mutations led to RIF resistance in at least 6.9% (9/130) of the strains that also exhibited RIF resistance on the MTBDRplus assay. Moreover, at the ITRC, sequencing of the rpoB gene of 170 strains with the rpoB mutation indicated that 23 strains (13.5%) had the disputed mutations. By combining the findings from the 32 strains from our center and the ITRC, we identified the type of disputed rpoB mutation as follows: CTG511CCG (L511P, n=8), GAC516TAC (D516Y, n=8), CTG533CCG (L533P, n=8), CAC526CTC (H526L, n=4), CAC526AAC (H526N, n=3), and ATG515GTG (M515V, n=1).
CONCLUSION
Disputed rpoB mutations do not seem to be rare among the strains exhibiting RIF resistance in South Korea.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Park JS. Issues related to the updated 2014 Korean guidelines for tuberculosis. Tuberc Respir Dis. 2016; 79:1–4.
Article2. Zhang Y, Yew WW. Mechanisms of drug resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis: update 2015. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2015; 19:1276–1289. PMID: 26467578.3. Telenti A, Imboden P, Marchesi F, Lowrie D, Cole S, Colston MJ, et al. Detection of rifampicin-resistance mutations in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Lancet. 1993; 341:647–650. PMID: 8095569.4. Ocheretina O, Escuyer VE, Mabou MM, Royal-Mardi G, Collins S, Vilbrun SC, et al. Correlation between genotypic and phenotypic testing for resistance to rifampin in Mycobacterium tuberculosis clinical isolates in Haiti: investigation of cases with discrepant susceptibility results. PLoS One. 2014; 9:e90569. PMID: 24599230.5. Ho J, Jelfs P, Sintchencko V. Phenotypically occult multidrug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis: dilemmas in diagnosis and treatment. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2013; 68:2915–2920. PMID: 23838950.6. van Ingen J, Aarnoutse R, de Vries G, Boeree MJ, van Soolingen D. Low-level rifampicin-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis strains raise a new therapeutic challenge. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2011; 15:990–992. PMID: 21682979.7. Van Deun A, Aung KJ, Hossain A, de Rijk P, Gumusboga M, Rigouts L, et al. Disputed rpoB mutations can frequently cause important rifampicin resistance among new tuberculosis patients. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2015; 19:185–190. PMID: 25574917.8. Huitric E, Werngren J, Jureen P, Hoffner S. Resistance levels and rpoB gene mutations among in vitro-selected rifampin-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis mutants. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006; 50:2860–2862. PMID: 16870787.9. Cavusoglu C, Turhan A, Akinci P, Soyler I. Evaluation of the genotype MTBDR assay for rapid detection of rifampin and isoniazid resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates. J Clin Microbiol. 2006; 44:2338–2342. PMID: 16825346.10. Ramaswamy S, Musser JM. Molecular genetic basis of antimicrobial agent resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis: 1998 update. Tuber Lung Dis. 1998; 79:3–29. PMID: 10645439.11. Jeon D. Medical management of drug-resistant tuberculosis. Tuberc Respir Dis. 2015; 78:168–174.
Article12. Song T, Park Y, Shamputa IC, Seo S, Lee SY, Jeon HS, et al. Fitness costs of rifampicin resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis are amplified under conditions of nutrient starvation and compensated by mutation in the beta' subunit of RNA polymerase. Mol Microbiol. 2014; 91:1106–1119. PMID: 24417450.13. Hain Lifescience. Genotype MTBDRplus ver 2.0 [Internet]. Nehren: Hain Lifescience;2017. cited 2017 Jan 2. Available from: http://www.hain-lifescience.de/en/products/microbiology/mycobacteria/tuberculosis/genotype-mtbdrplus.html.14. Definitions and reporting framework for tuberculosis: 2013 revision [Internet]. Geneva: World Health Organization;2017. cited 2017 Jan 2. Available from: http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/79199/1/9789241505345_eng.pdf.15. Van Deun A, Aung KJ, Bola V, Lebeke R, Hossain MA, de Rijk WB, et al. Rifampin drug resistance tests for tuberculosis: challenging the gold standard. J Clin Microbiol. 2013; 51:2633–2640. PMID: 23761144.
Article16. Andres S, Hillemann D, Rusch-Gerdes S, Richter E. Occurrence of rpoB mutations in isoniazid-resistant but rifampin-susceptible Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates from Germany. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014; 58:590–592. PMID: 24145520.17. Kambli P, Ajbani K, Sadani M, Nikam C, Shetty A, Udwadia Z, et al. Defining multidrug-resistant tuberculosis: correlating GenoType MTBDRplus assay results with minimum inhibitory concentrations. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2015; 82:49–53. PMID: 25749461.18. Williams DL, Spring L, Collins L, Miller LP, Heifets LB, Gangadharam PR, et al. Contribution of rpoB mutations to development of rifamycin cross-resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1998; 42:1853–1857. PMID: 9661035.19. Yakrus MA, Driscoll J, Lentz AJ, Sikes D, Hartline D, Metchock B, et al. Concordance between molecular and phenotypic testing of Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex isolates for resistance to rifampin and isoniazid in the United States. J Clin Microbiol. 2014; 52:1932–1937. PMID: 24648563.20. WHO treatment guidelines for drug-resistant tuberculosis, 2016 update [Internet]. Geneva: World Health Organization;2016. cited 2017 Jan 2. Available from: http://www.who.int/tb/MDRTBguidelines2016.pdf.21. van Ingen J, Aarnoutse RE, Donald PR, Diacon AH, Dawson R, Plemper van Balen G, et al. Why do we use 600 mg of rifampicin in tuberculosis treatment? Clin Infect Dis. 2011; 52:e194–e199. PMID: 21467012.
Article22. Jindani A, Borgulya G, de Patino IW, Gonzales T, de Fernandes RA, Shrestha B, et al. A randomised Phase II trial to evaluate the toxicity of high-dose rifampicin to treat pulmonary tuberculosis. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2016; 20:832–838. PMID: 27155189.
Article23. Williamson DA, Roberts SA, Bower JE, Vaughan R, Newton S, Lowe O, et al. Clinical failures associated with rpoB mutations in phenotypically occult multidrug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2012; 16:216–220. PMID: 22137551.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Rifabutin susceptibility and rpoB gene mutations in multi-drug resistant mycobacterium tuberculosis
- Detection of rpoB Gene Mutation in Rifampin-Resistant M. Tuberculosis by Oligonucleotide Chip
- The Proportion of Rifabutin-susceptible Strains among Rifampicin- resistant Isolates and Its Specific rpoB Mutations
- Molecular Taxonomic Survey of Mycobacteria Clinical Isolates from Patients in Jeju Island by rpoB Gene Based Molecular Biological Methods
- Patterns of rpoC Mutations in Drug-Resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis Isolated from Patients in South Korea