Ann Dermatol.
2011 Nov;23(4):544-547.
Sibutramine (Reductil(R))-Induced Cutaneous Leukocytoclastic Vasculitis: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, School of Medicine, Ewha Womans University, Seoul, Korea. hychoi@ewha.ac.kr
Abstract
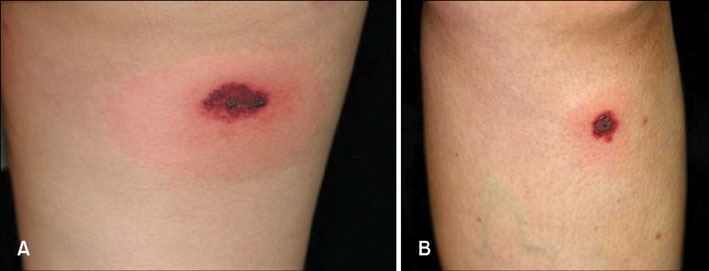
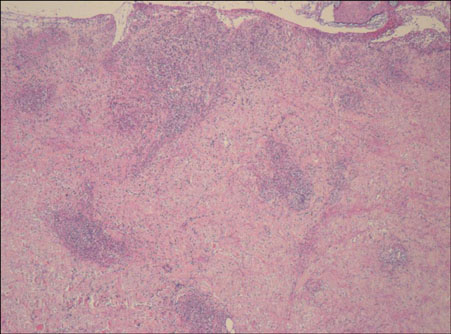
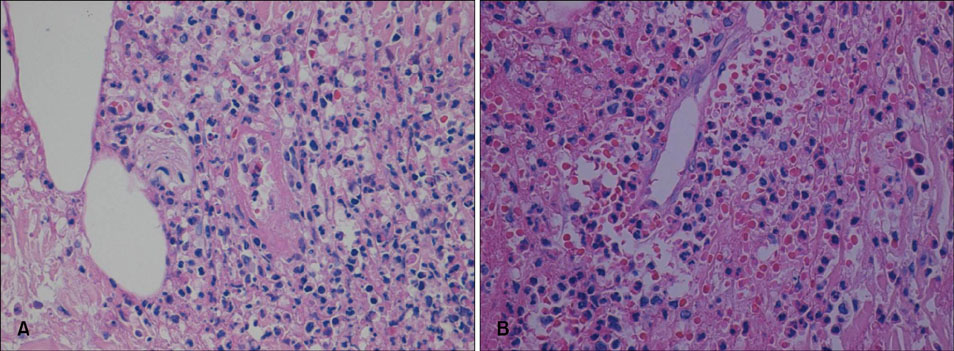
- A 24-year old woman presented with hemorrhagic vesicles on her legs. She had taken sibutramine (Reductil(R), Abbott Labs., Seoul, South Korea) for 3 months and developed skin lesions the week before. A skin biopsy showed leukocytoclastic vasculitis with conspicuous eosinophilic infiltration of the tissue. These lesions showed improvement after discontinuation of sibutramine. However, 3 months later the skin lesions recurred on other sites on the lower extremities when the patient was rechallenged with the same drug for 2 weeks. Herein, we report the first case of necrotizing vasculitis induced by sibutramine.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Florentin M, Liberopoulos EN, Elisaf MS. Sibutramine-associated adverse effects: a practical guide for its safe use. Obes Rev. 2008. 9:378–387.
Article2. McNeely W, Goa KL. Sibutramine. A review of its contribution to the management of obesity. Drugs. 1998. 56:1093–1124.3. Goh BK, Ng PP, Giam YC. Severe bullous drug eruption due to sibutramine (Reductil). Br J Dermatol. 2003. 149:215–216.
Article4. Carlson JA, Ng BT, Chen KR. Cutaneous vasculitis update: diagnostic criteria, classification, epidemiology, etiology, pathogenesis, evaluation and prognosis. Am J Dermatopathol. 2005. 27:504–528.
Article5. Sanchez NP, Van Hale HM, Su WP. Clinical and histopathologic spectrum of necrotizing vasculitis. Report of findings in 101 cases. Arch Dermatol. 1985. 121:220–224.
Article6. Shear NH, Knowles SR, Shapiro L. Woff K, Goldsmith LA, Katz SI, Gilchrest BA, Paller AS, Leffell DJ, editors. Cutaneous reactions to drugs. Fitzpatrick's dermatology in general medicine. 2007. 7th ed. New York: McGraw Hill;360–361.7. Bahrami S, Malone JC, Webb KG, Callen JP. Tissue eosinophilia as an indicator of drug-induced cutaneous small-vessel vasculitis. Arch Dermatol. 2006. 142:155–161.
Article8. Soter NA, Jose L, Perez D. Woff K, Goldsmith LA, Katz SI, Gilchrest BA, Paller AS, Leffell DJ, editors. Cutaneous necrotizing venulitis. Fitzpatrick's dermatology in general medicine. 2007. 7th ed. New York: McGraw Hill;1599–1606.9. Roger D, Rollé F, Mausset J, Lavignac C, Bonnetblanc JM. Urticarial vasculitis induced by fluoxetine. Dermatology. 1995. 191:164.
Article10. Welsh JP, Cusack CA, Ko C. Urticarial vasculitis secondary to paroxetine. J Drugs Dermatol. 2006. 5:1012–1014.11. Flores-Suárez LF, Vega-Memije ME, Chanussot-Deprez C. Cutaneous vasculitis during selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor therapy. Am J Med. 2006. 119:e1–e3.
Article12. Margolese HC, Chouinard G, Beauclair L, Rubino M. Cutaneous vasculitis induced by paroxetine. Am J Psychiatry. 2001. 158:497.
Article13. Krasowska D, Szymanek M, Schwartz RA, Myśliński W. Cutaneous effects of the most commonly used antidepressant medication, the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2007. 56:848–853.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Warfarin-induced Leukocytoclastic Vasculitis
- A Case of Leukocytoclastic Vasculitis Following COVID-19 Vaccination
- A Case of Leukocytoclastic Vasculitis Associated with Pulmonary Tuberculosis
- A Case of Leukocytoclastic Vasculitis Associated with Antiphospholipid Antibody Syndorme
- Leukocytoclastic Vasulitis Induced by Methoxy Polyethylene Glycol-Epoetin Beta