Ann Dermatol.
2011 Nov;23(4):501-503.
Nicolau Syndrome in Patient Following Diclofenac Administration: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Konyang University College of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea. ajouos@hanmail.net
Abstract
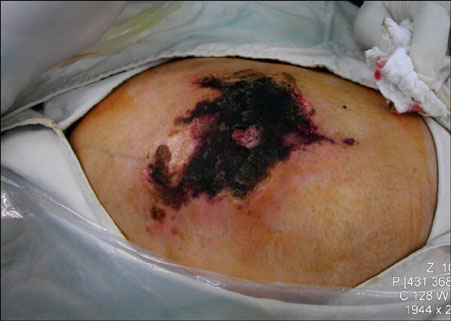
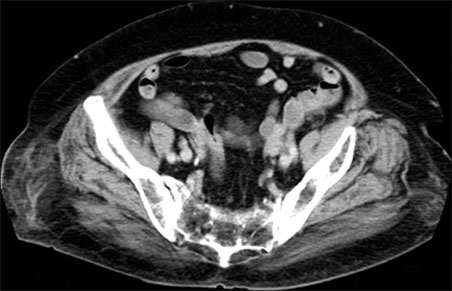
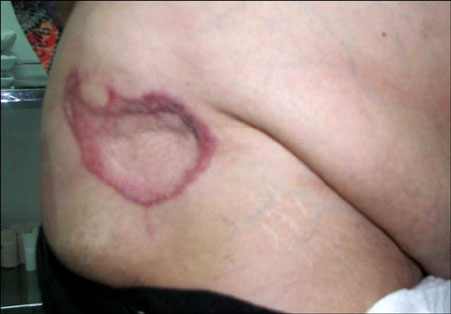
- Nicolau syndrome is a rare adverse reaction to a variety of intra-muscular drug preparations. The typical presentation is pain around the injection site soon after injection, followed by erythema, livedoid patch, hemorrhagic patch, and finally, necrosis of skin, subcutaneous fat, and muscle tissue. The phenomenon has been related to the administration of a variety of drugs, including non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, corticosteroids, and penicillin. We report a case with typical features associated with diclofenac injection for pain control in a patient who had undergone bilateral total knee arthroplasty.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Faucher L, Marcoux D. What syndrome is this? Nicolau syndrome. Pediatr Dermatol. 1995. 12:187–190.2. Köhler LD, Schwedler S, Worret WI. Embolia cutis medicamentosa. Int J Dermatol. 1997. 36:197.
Article3. Hamilton B, Fowler P, Galloway H, Popovic N. Nicolau syndrome in an athlete following intra-muscular diclofenac injection. Acta Orthop Belg. 2008. 74:860–864.4. Ruffieux PH, Salomón D, Saurat JH. Livedo-like dermatitis (Nicolau's syndrome): a review of three cases. Dermatology. 1996. 193:368–371.
Article5. Lie C, Leung F, Chow SP. Nicolau syndrome following intramuscular diclofenac administration: a case report. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2006. 14:104–107.
Article6. Cockshott WP, Thompson GT, Howlett LJ, Seeley ET. Intramuscular or intralipomatous injections? N Engl J Med. 1982. 307:356–358.
Article7. Okan G, Canter HI. Nicolau syndrome and perforator vessels: a new viewpoint for an old problem. Cutan Ocul Toxicol. 2010. 29:70–72.
Article