Ann Clin Microbiol.
2017 Jun;20(2):35-41. 10.5145/ACM.2017.20.2.35.
Analysis of Blood Culture Data at a Tertiary University Hospital, 2006-2015
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Gachon University Gil Medical Center, Incheon, Korea. seoyh@gilhospital.com
- KMID: 2383229
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5145/ACM.2017.20.2.35
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Cumulative blood culture data provide clinicians with important information in the selection of empiric therapy for blood stream infections.
METHODS
We retrospectively analyzed blood culture data from a university hospital during the period from 2006 to 2015. Only the initial isolates of a given species for each patient were included.
RESULTS
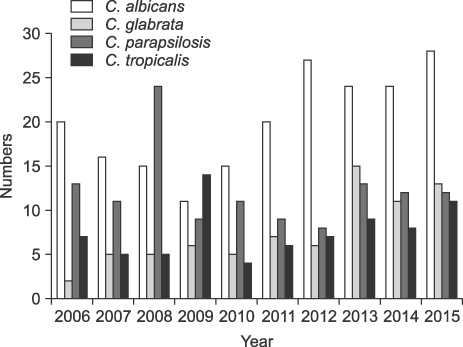
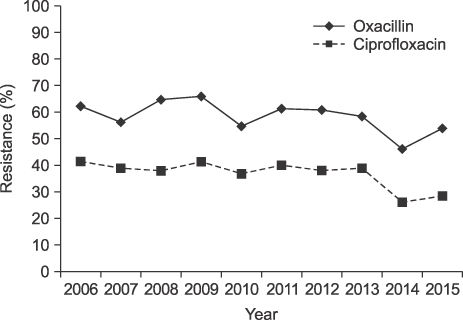
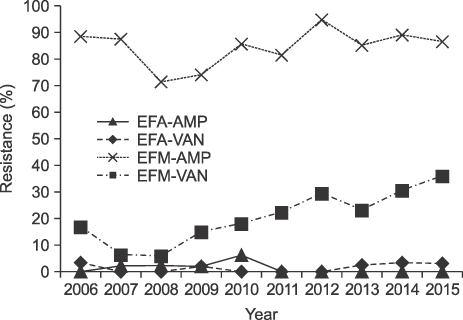
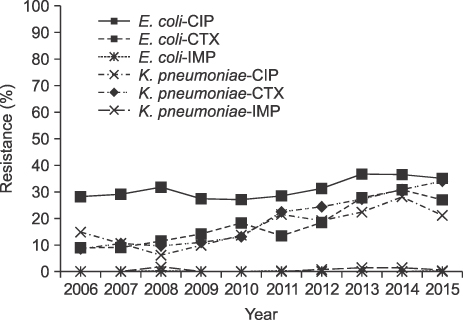
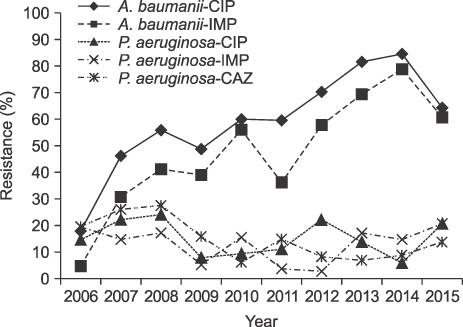
The number of blood cultures per 1,000 inpatient-days increased from 64 in 2006 to 117 in 2015. The ratio of significant pathogens to total isolates was 0.56-0.63. The most common organisms were Escherichia coli in 2006-2010 but changed to coagulase-negative staphylococci (CoNS) in 2011. The proportion of Staphylococci aureus was decreased during the study period, but Klebsiella pneumoniae was increased. Enterococci were increased, especially E. faecium, which was more frequently isolated than E. faecalis in 2015. Pseudomonas aeruginosa was decreased during the study, but Acinetobacter baumannii was increased. The prevalence of methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) changed from 62.2% to 53.9%, while vancomycin-resistant E. faecium increased to 35.8%. Extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL)-producing E. coli and K. pneumoniae increased to 25% and 34%, respectively, in 2015. Starting in 2008, three E. coli and 11 K. pneumoniae isolates were carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae (CRE), and three were carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae (CPE). The prevalence of imipenem-resistant A. baumannii rapidly increased during the study period.
CONCLUSION
About 60% of all blood isolates were significant pathogens. The most common isolates changed from E. coli to CoNS in 2011. ESBL-producing E. coli and K. pneumoniae, vancomycin-resistant E. faecium, and imipenem-resistant A. baumannii were increased during the study, while the proportion of MRSA tended to decrease slightly. Of the total isolates, 14 were CRE, and 3 were CPE.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
The Infinity War: How to Cope with Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae
Jin-Hong Yoo
J Korean Med Sci. 2018;33(40):. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2018.33.e255.Carbapenem-resistant
Enterobacteriaceae : recent updates and treatment strategies
Hyo-Jin Lee, Dong-Gun Lee
J Korean Med Assoc. 2018;61(4):281-289. doi: 10.5124/jkma.2018.61.4.281.Trends in Bloodstream Infections and Antimicrobial Susceptibilities at a University Hospital in Korea Between 2007 and 2016
Sangeun Lim, Joon-Sup Yeom, Eun-Jeong Joo, Hae Suk Cheong, Kyunghoon Lee, Hee-Yeon Woo, Hyosoon Park, Min-Jung Kwon
Lab Med Online. 2019;9(2):63-72. doi: 10.3343/lmo.2019.9.2.63.
Reference
-
1. Lark RL, Chenoweth C, Saint S, Zemencuk JK, Lipsky BA, Plorde JJ. Four year prospective evaluation of nosocomial bacteremia: epidemiology, microbiology, and patient outcome. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2000; 38:131–140.2. Rodríguez-Créixems M, Alcalá L, Muñoz P, Cercenado E, Vicente T, Bouza E. Bloodstream infections: evolution and trends in the microbiology workload, incidence, and etiology, 1985-2006. Medicine (Baltimore). 2008; 87:234–249.3. Oh TS, Nam YS, Kim YJ, Yang HS, Lee MY, Gu HJ, et al. Trends in bloodstream infections at a Korean University Hospital between 2008 and 2013. Ann Clin Microbiol. 2015; 18:14–19.4. Wisplinghoff H, Bischoff T, Tallent SM, Seifert H, Wenzel RP, Edmond MB. Nosocomial bloodstream infections in US hospitals: analysis of 24,179 cases from a prospective nationwide surveillance study. Clin Infect Dis. 2004; 39:309–317.5. Song W, Hong SG, Yong D, Jeong SH, Kim HS, Kim HS, et al. Combined use of the modified Hodge test and carbapenemase inhibition test for detection of carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae and metallo-β-lactamase-producing Pseudomonas spp. Ann Lab Med. 2015; 35:212–219.6. Poirel L, Walsh TR, Cuvillier V, Nordmann P. Multiplex PCR for detection of acquired carbapenemase genes. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2011; 70:119–123.7. Baron EJ, Weinstein MP, Dunne WM, Yagupsky P, Welch DF, Wilson DM. Cumitech 1c: blood cultures IV. Washington, D.C.: American Society of Microbiology Press;2005.8. Kim EC, Shin JH, Kim S, Lee NY, Cho JH, Koo SH, et al. Number of blood cultures per 1,000 patient days at university-affiliated hospitals in Korea. Korean J Clin Microbiol. 2012; 15:67–69.9. Pien BC, Sundaram P, Raoof N, Costa SF, Mirrett S, Woods CW, et al. The clinical and prognostic importance of positive blood cultures in adults. Am J Med. 2010; 123:819–828.10. Kim NH, Hwang JH, Song KH, Choe PG, Park WB, Kim ES, et al. Changes in antimicrobial susceptibility of blood isolates in a university hospital in South Korea, 1998-2010. Infect Chemother. 2012; 44:275–281.11. Koh EM, Lee SG, Kim CK, Kim M, Yong D, Lee K, et al. Microorganisms isolated from blood cultures and their antimicrobial susceptibility patterns at a university hospital during 1994-2003. Korean J Lab Med. 2007; 27:265–275.12. Kim SY, Lim G, Kim MJ, Suh JT, Lee HJ. Trends in five-year blood cultures of patients at a university hospital (2003~2007). Korean J Clin Microbiol. 2009; 12:163–168.13. Al Wohoush I, Rivera J, Cairo J, Hachem R, Raad I. Comparing clinical and microbiological methods for the diagnosis of true bacteraemia among patients with multiple blood cultures positive for coagulase-negative staphylococci. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2011; 17:569–571.14. Finkelstein R, Fusman R, Oren I, Kassis I, Hashman N. Clinical and epidemiologic significance of coagulase-negative staphylococci bacteremia in a tertiary care university Israeli hospital. Am J Infect Control. 2002; 30:21–25.15. Beekmann SE, Diekema DJ, Doern GV. Determining the clinical significance of coagulase-negative staphylococci isolated from blood cultures. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2005; 26:559–566.16. Hall KK, Lyman JA. Updated review of blood culture contamination. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2006; 19:788–802.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of Blood Culture Contamination Rate Before and After Improving Skin Antisepsis Methods in Blood Culture
- Effects of Work Environment and Nursing Organizational Culture on Tertiary Hospital Nurses’ Turnover Intention
- Relationship between Organizational Culture and Job Satisfaction among Korean Nurses: A Meta-Analysis
- The Usefulness of Blood Culture in Febrile Immunocompetent Patients at Emergency Department
- Nurses' Safety Control according to Patient Safety Culture and Perceived Teamwork