Korean J healthc assoc Infect Control Prev.
2019 Dec;24(2):97-102. 10.14192/kjicp.2019.24.2.97.
Comparison of Blood Culture Contamination Rate Before and After Improving Skin Antisepsis Methods in Blood Culture
- Affiliations
-
- 1Infection Control Office, Ajou University Hospital, Suwon, Korea.
- 2Department of Nursing, Ajou University Hospital, Suwon, Korea. comun@nate.com
- KMID: 2467909
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14192/kjicp.2019.24.2.97
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
This study aims to investigate blood culture contamination rates before and after improving the skin antisepsis methods used in blood cultures, and to compare the differences observed.
METHODS
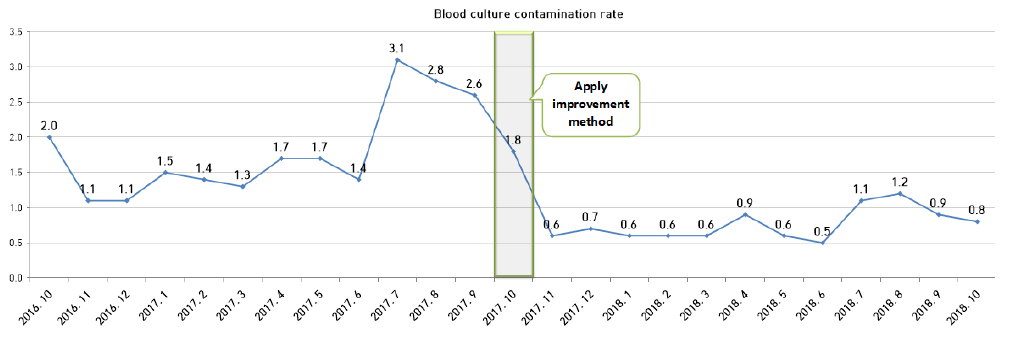
This is a retrospective investigation study comparing the blood culture contamination rates before and after applying the skin disinfection method for blood cultures at a tertiary hospital. Blood culture tests were conducted for 25 months, from October 2016 to October 2018. We measured the blood culture contamination rates monthly, for one year each, before and after the improvement of activities applied in October 2017. The analyses were carried out using the Mann-Whitney U test, a non-parametric statistical method of the SPSS 25 statistical program.
RESULTS
The mean blood culture contamination rate was 1.8% before the improvement of skin antisepsis methods for blood cultures and 0.8% after improvements in skin antisepsis methods for blood cultures. The difference in the mean rates of blood culture contamination was statistically significant (P < .001).
CONCLUSION
00 This study confirmed the reduction of blood culture contamination rates after adhering to the improved method of applying skin antisepsis. Therefore, these results may be meaningful in that they can provide basic data for the preparation of clinical guidelines that aim to reduce culture contamination rates.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Jung MY, Son OS, Hong YR, Oh CE. Clinical characteristics associated with blood culture contamination in neonates. Pediatr Infect Vaccine. 2015; 22:147–153.
Article2. Lee YS, Won HK, Chun HK, Kim MR, Lee MS, Son JS. Reduction of blood contamination rate by improving electronic medical record program. J Korean Soc Qual Assur Health Care. 2009; 3:714–715.3. Wilson ML. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. M47-A: principles and procedures for blood cultures: approved guideline. 6th ed. Wayne: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;2007. p. 795–796.4. Hall KK. Updated review of blood culture contamination. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2006; 19:788–802.
Article5. Youssef D, Shams W, Bailey B, O'Neil TJ, Al-Abbadi MA. Effective strategy for decreasing blood culture contamination rates: the experience of a Veterans Affairs Medical Centre. J Hosp Infect. 2012; 81:288–291.
Article6. Dawson S. Blood culture contaminants. J Hosp Infect. 2014; 87:1–10.7. Kim NH, Kim M, Lee S, Yun NR, Kim KH, Park SW, et al. Effect of routine sterile gloving on contamination rates in blood culture: a cluster randomized trial. Ann Intern Med. 2011; 154:145–151.
Article8. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Collecting Cultures: a Clinician Guide - Blood cultures. Medical Director Infection Prevention and Epidemiology. Updated on December 2015. https://www.cdc.gov/antibiotic-use/core-elements/collecting-cultures.Html.9. Johns Hopkins Medicine. Johns Hopkins hospital medical microbiology specimen collection guidelines. Johns Hopkins Medicine Pathology. Updated on June 2015. http://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/microbiology/specimen/Specimen%20Collection%20Guidelines%20_11_2015.pdf.10. Kim SH. Comparison of blood culture contamination rate of three methods using different disinfectants. Korean Clin Lab Microbiol. 2015; P11:162.11. Maiwald M. The forgotten role of alcohol: a systematic review and meta-analysis of the clinical efficacy and perceived role of chlorhexidine in skin antisepsis. PLoS One. 2012; 7:e44277.
Article12. Kiyoyama T, Tokuda Y, Shiiki S, Hachiman T, Shimasaki T, Endo K. Isopropyl alcohol compared with isopropyl alcohol plus povidone-iodine as skin preparation for prevention of blood culture contamination. J Clin Microbiol. 2009; 47:54–58.
Article13. Jeong HR. Effects of multimodal interventions to reduce blood bulture contamination rates at the emergency deoartment of tertiary care hospital [MD dissertation]. Ulsan: Ulsan University;2015. 6–7.14. Baron EJ, Weinstein MP, Dunne M, Yagupsky P, Welch DF, Wilson DM, et al. Blood Cultures IV: cumitech: cumulative techniques and procedures in clinical microbiology, 1C. Washington: American Society of Microbiology;2005. p. 2–7.15. Stonecypher K. Creating a patient education tool. J Contin Educ Nurs. 2009; 40:462–467.
Article16. Park WB, Myung SJ, Oh MD, Lee J, Kim NJ, Kim EC, et al. Educational intervention as an effective step for reducing blood culture contamination: a prospective cohort study. J Hosp Infect. 2015; 91:111–116.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of Chlorhexidine-Alcohol and Povidone-Iodine for Skin Antisepsis and the Effect of Increased Blood Volume in Blood Culture
- Blood Cultures: Principles and Practices
- Clinical Characteristics Associated with Blood Culture Contamination in Neonates
- Ureaplasma Contamination Rate in Donated Cord Blood Units
- Nationwide Survey of Blood Culture Performance Regarding Skin Disinfection, Blood Collection and Laboratory Procedures