J Korean Acad Nurs Adm.
2019 Jun;25(3):157-166. 10.11111/jkana.2019.25.3.157.
Relationship between Organizational Culture and Job Satisfaction among Korean Nurses: A Meta-Analysis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Graduate School, College of Nursing, Catholic University of Korea, Korea.
- 2College of Nursing, Catholic University of Korea, Korea. shahn@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 2451692
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.11111/jkana.2019.25.3.157
Abstract
- PURPOSE
This study was undertaken to understand the determinants of job satisfaction for hospital nurses in Korea. Organization culture is deemed as a strong factor which contributes to overall job satisfaction.
METHODS
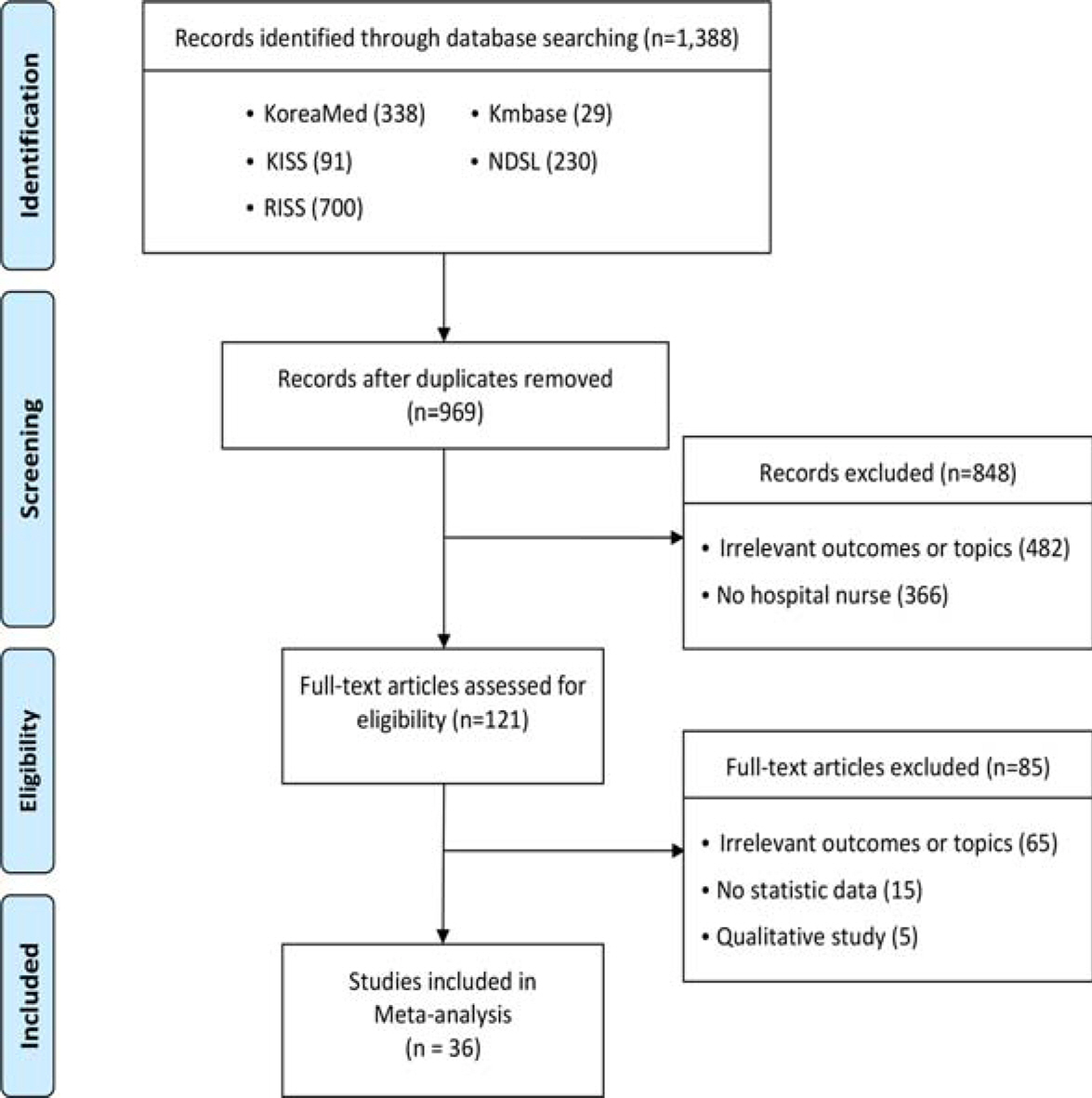
A systematic review was conducted using five electronic databases to identify Korean studies for the years 1998 to 2017. The Comprehensive Meta-Analysis Software Ver 2.0 was then utilized in data analysis.
RESULTS
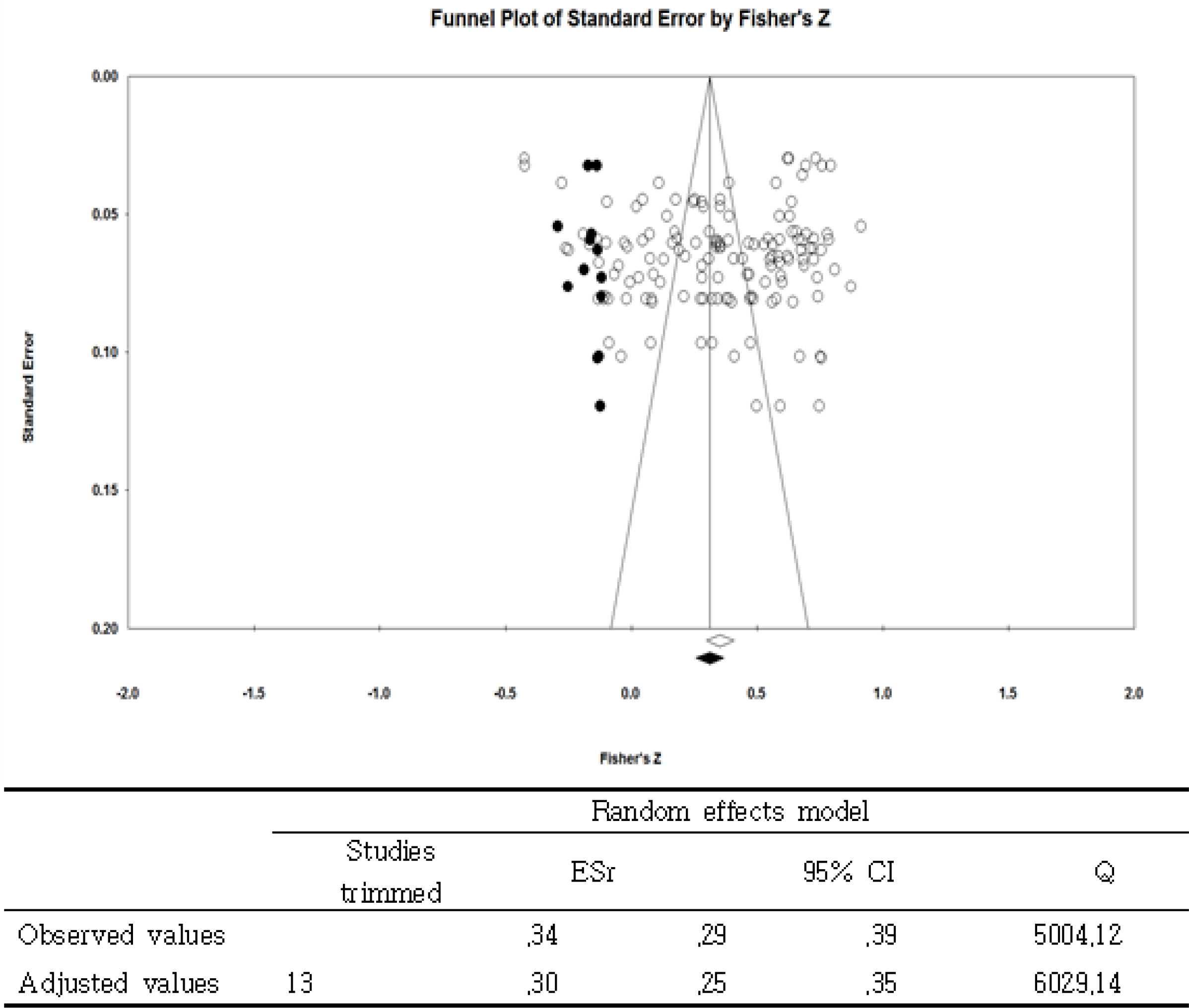
A meta-analysis of data from 36 studies indicated that the overall effect size of correlation between organizational culture and job satisfaction was moderate (ESr=.36), and publication year was negatively associated with these factors in the meta-regression model. In addition, the magnitude of the types of organizational culture and job satisfaction varied according to size of the hospitals: innovation-oriented culture for secondary hospitals (ESr=.49) and relation-oriented culture for tertiary hospitals (ESr=.46). Lastly, of four different organizational cultures, innovation-oriented culture showed the strongest correlation with job satisfaction (ESr=.50), followed by relation-oriented culture (ESr=.49), and task-oriented culture (ESr=.30).
CONCLUSION
Results indicate that nursing organization culture plays a significant role in Korean nurses' job satisfaction. The implication of the study is that creating an innovation-oriented and relation-oriented culture in hospitals may effectively promote nurses' job satisfaction more than hierarchy-oriented culture.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kang SJ. Mediating effects of empowerment, job stress, and organizational commitment in relation-oriented nursing organization culture and turnover intention of clinical nurses. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration. 2013; 19(3):372–381. https://doi.org/10.11111/jkana.2013.19.3.372.
Article2. Yom YH, Noh SM, Kim KH. Clinical nurses' experience of positive organizational culture. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration. 2014; 20(5):469–480. https://doi.org/10.11111/jkana.2014.20.5.469.
Article3. Fisher CJ, Alford RJ. Consulting on culture: A new bottom line. Consulting Psychology Journal: Practice and Research. 2000; 52(3):206–217. https://doi.org/10.1037/1061-4087.52.3.206.
Article4. Firth-Cozens J. Cultures for improving patient safety through learning: The role of teamwork. Quality in Health Care. 2001; 10(Suppl 2):26–31. https://doi.org/10.1136/qhc.0100026.
Article5. Speroff T, Nwosu S, Greevy R, Weinger MB, Talbot TR, Wall RJ, et al. Organisational culture: Variation across hospitals and connection to patient safety climate. Quality & Safety in Health Care. 2010; 19(6):592–596. https://doi.org/10.1136/qshc.2009.039511.
Article6. An JY, Yom YH, Ruggiero JS. Organizational culture, quality of work life, and organizational effectiveness in Korean university hospitals. Journal of Transcultural Nursing. 2011; 22(1):22–30. https://doi.org/10.1177/1043659609360849.
Article7. Park KO, Park SH, Yu M. Review of research on nursing organizational culture in Korea. The Journal of the Korea Contents Association. 2014; 14(2):387–395. https://doi.org/10.5392/JKCA.2014.14.02.387.
Article8. Quinn RE, Rohrbaugh J. A spatial model of effectiveness criteria: Towards a competing values approach to organizational analysis. Management Science. 1983; 29(3):363–377. https://doi.org/10.1287/mnsc.29.3.363.
Article9. Jang IS, Park SM. A comparative study on nurses' organizational culture and job satisfaction according to the hospital size differences. Korean Journal of Occupational Health Nursing. 2011; 20(1):1–13.
Article10. Park JS. The effect of organizational culture types on job satisfaction and intension of turnover perceived by national hospital employees. Korean Journal of Hospital Management. 2005; 10:1–24.11. Yoo SY, Kim IS. A study on the relationship between nursing organizational culture of military hospital and organizational performance. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration. 2005; 11(2):129–145.12. Lee EJ, Han JY, Kim MY. Effects of the organizational culture on the job satisfaction and organization commitment. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration. 2008; 14(1):5–12.13. Hulin CL, Judge TA. Job attitudes. Weiner IB, editor. Handbook of psychology. New York: Wiley;2003. p. 255.
Article14. Abdullah Al Maqbali M. Factors that influence nurses' job satisfaction: a literature review. Nursing Management. 2015; 22(2):30–37. https://doi.org/10.7748/nm.22.2.30.e1297.
Article15. Han JR, Ahn SH. The effects of nurses' satisfaction on hospital performance -Focused on the patient satisfaction and revisit intention, recommendation intention-. Journal of Digital Convergence. 2015; 13(9):419–430. https://doi.org/10.14400/JDC.2015.13.9.419.
Article16. Xue Y. Racial and ethnic minority nurses' job satisfaction in the U.S. International Journal of Nursing Studies. 2015; 52(1):280–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2014.10.007.
Article17. Kang H. Statistical considerations in meta-analysis. Hanyang Medical Reviews. 2015; 35(1):23–32. https://doi.org/10.7599/hmr.2015.35.1.23.
Article18. Cummings GG, MacGregor T, Davey M, Lee H, Wong CA, Lo E, et al. Leadership styles and outcome patterns for the nursing workforce and work environment: A systematic review. International Journal of Nursing Studies. 2010; 47(3):363–385. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2009.08.006.
Article19. Lambrou P, Merkouris A, Middleton N, Papastavrou E. Nurses' perceptions of their professional practice environment in relation to job satisfaction: A review of quantitative studies. Health Science. 2014; 8(3):298–317.20. Cummings G, Lee H, Macgregor T, Davey M, Wong C, Paul L, et al. Factors contributing to nursing leadership: A systematic review. Journal of Health Services Research & Policy. 2008; 13(4):240–248. https://doi.org/10.1258/jhsrp.2008.007154.
Article21. Simes RJ. Confronting publication bias: a cohort design for meta-analysis. Statistics in Medicine. 1987; 6(1):11–29. https://doi.org/10.1002/sim.4780060104.
Article22. Rothstein HR. Publication bias as a threat to the validity of meta-analytic results. Journal of Experimental Criminology. 2008; 4(1):61–81. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11292-007-9046-9.
Article23. Cohen J. Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences. 2nd ed.Hillsdale, N.J.: L. Erlbaum Associates;1988.24. Higgins JPT, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ (Clinical Research Ed.). 2003; 327(7414):557–560. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.327.7414.557.
Article25. Song F, Sheldon TA, Sutton AJ, Abrams KR, Jones DR. Methods for exploring heterogeneity in meta-analysis. Evaluation & the Health Professions. 2001; 24(2):126–151. https://doi.org/10.1177/016327870102400203.
Article26. Matt GE, Cook TD. Threats to the validity of generalized inferences. Cooper H, Hedges LV, Valentine JC, editors. The handbook of research synthesis and meta-analysis. 2nd ed. NewYork: Russell Sage Foundation;2009. p. 537–560.27. Shirey MR. Authentic leadership, organizational culture, and healthy work environments. Critical Care Nursing Quarterly. 2009; 32(3):189–198. https://doi.org/10.1097/CNQ.0b013e3181ab91db.
Article28. Fang YY. A meta-analysis of relationships between organizational culture, organizational climate, and nurse work outcomes [dissertation]. Baltimore: University of Maryland;2007.29. Tzeng HM, Ketefian S, Redman RW. Relationship of nurses' assessment of organizational culture, job satisfaction, and patient satisfaction with nursing care. International Journal of Nursing Studies. 2002; 39(1):79–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0020-7489(00)00121-8.
Article30. Shin HJ. Relationship between Organizational Cultures and Organizational Effectiveness in small to medium sized Hospitals [master's thesis]. Gwangju: University of Chonnam National University;2003.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effects of Organizational Culture, Self-Leadership and Empowerment on Job Satisfaction and Turnover Intention in General Hospital Nurses
- Effect of Nursing Wok Environment, Job Crafting and Organizational Commitment on Nurses’ Job Satisfaction
- Effects of Job Characteristics, Organizational Culture on Job Satisfaction and Turnover Intention in Public Institution Nurses
- Self-efficacy, Nursing Organizational Culture and Emotional Labor in Clinical Nurses
- A Study on the Influence of Job Characteristics Perceived by Nurses on Their Job Satisfaction and Organizational Commitment: Focusing on Moderating Effect of Individual Personality Characteristics