Clin Endosc.
2015 Nov;48(6):466-475. 10.5946/ce.2015.48.6.466.
The Past, Present, and Future of Image-Enhanced Endoscopy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Internal Medicine, Kyung Hee University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jyjang@khu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2380402
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2015.48.6.466
Abstract
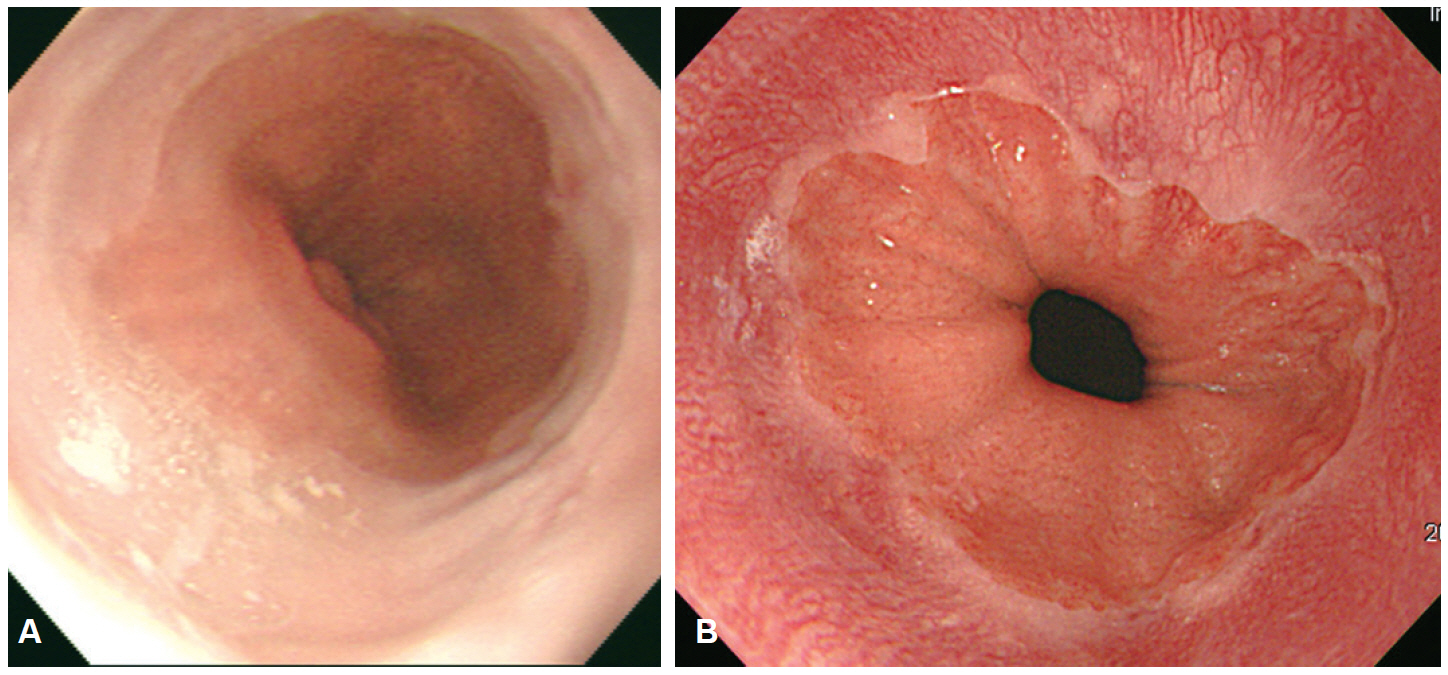
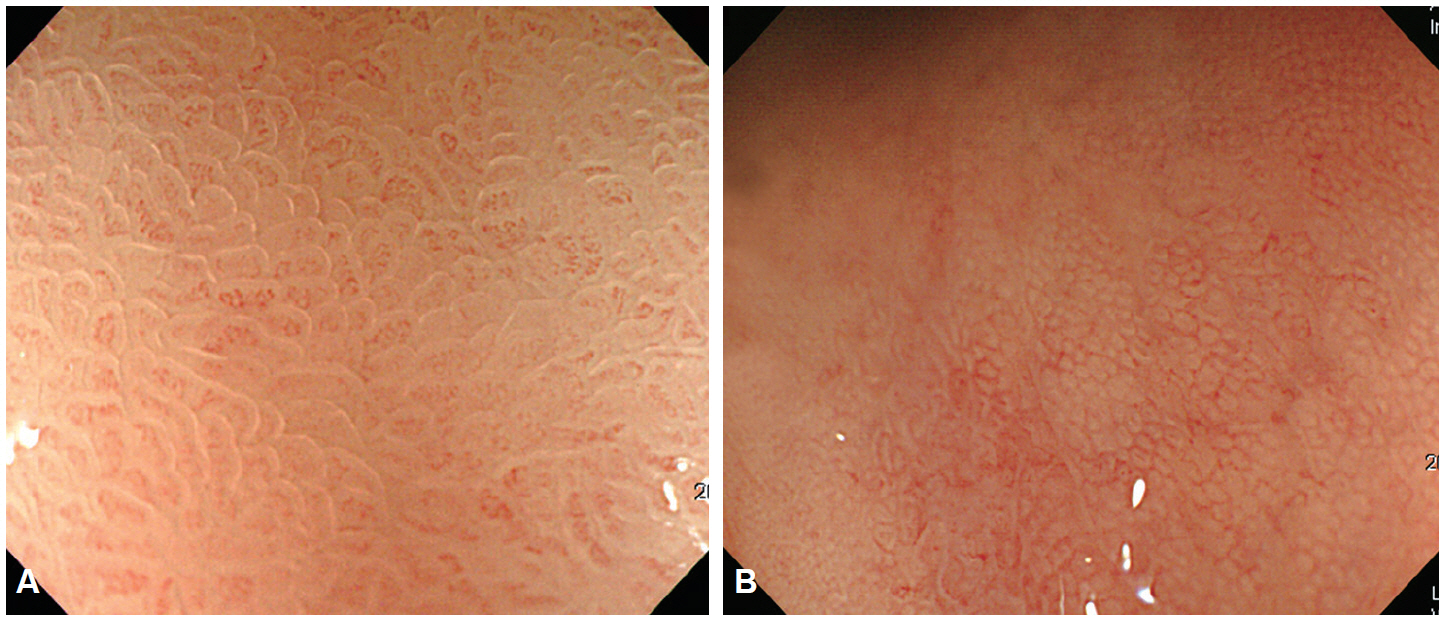
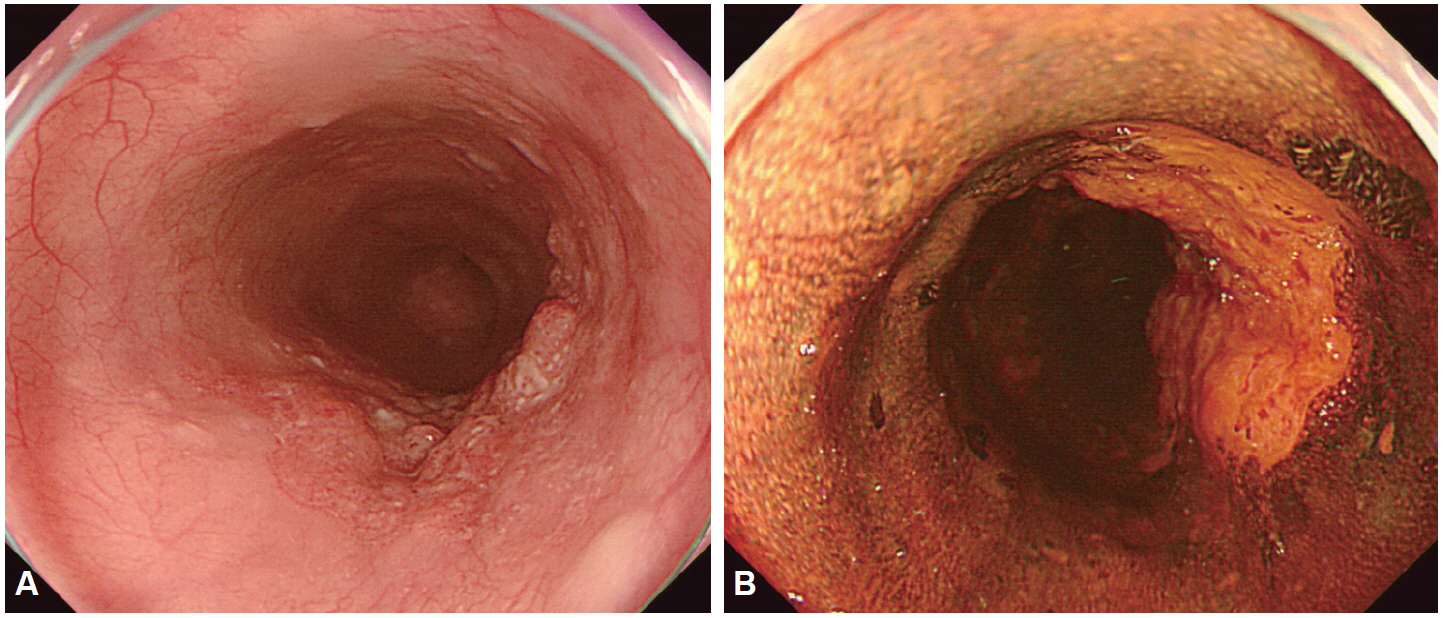
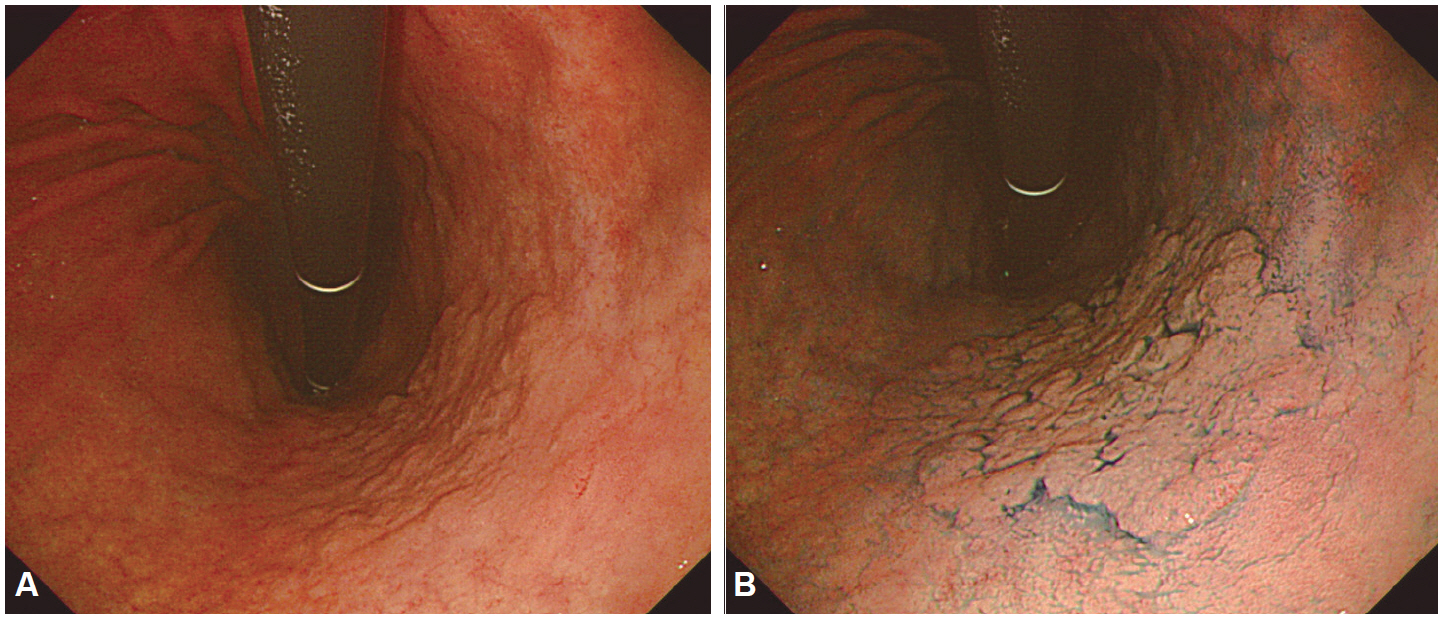
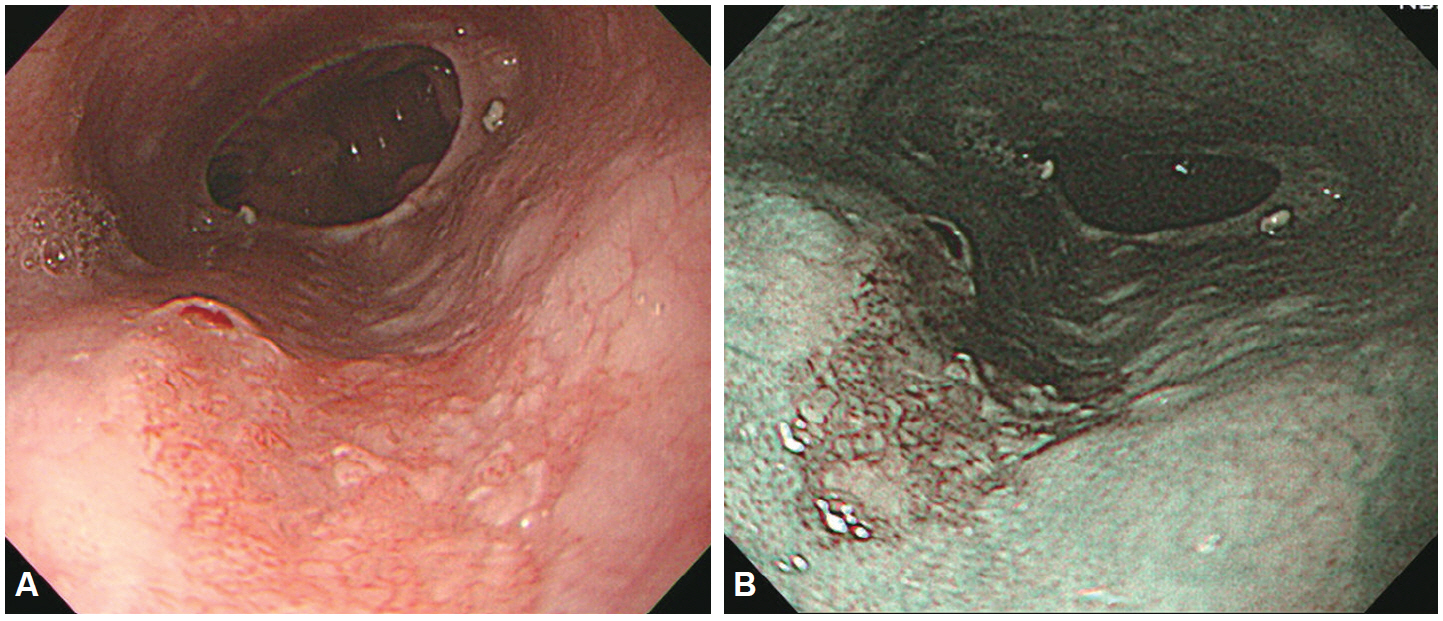
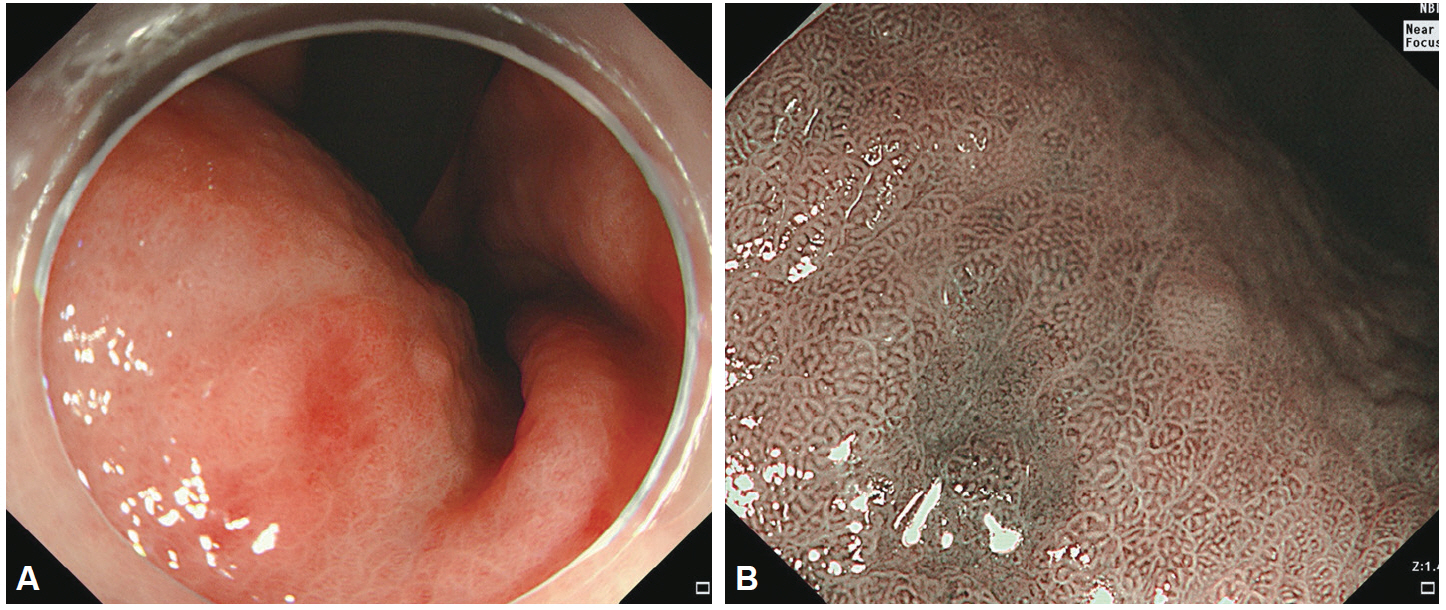
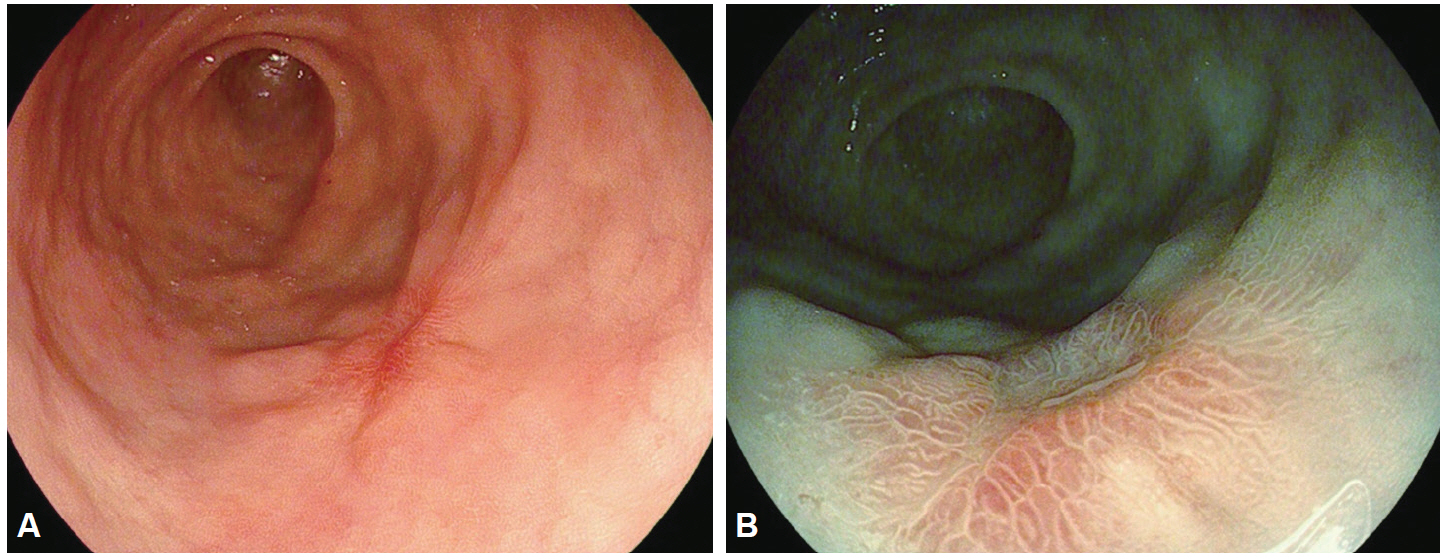
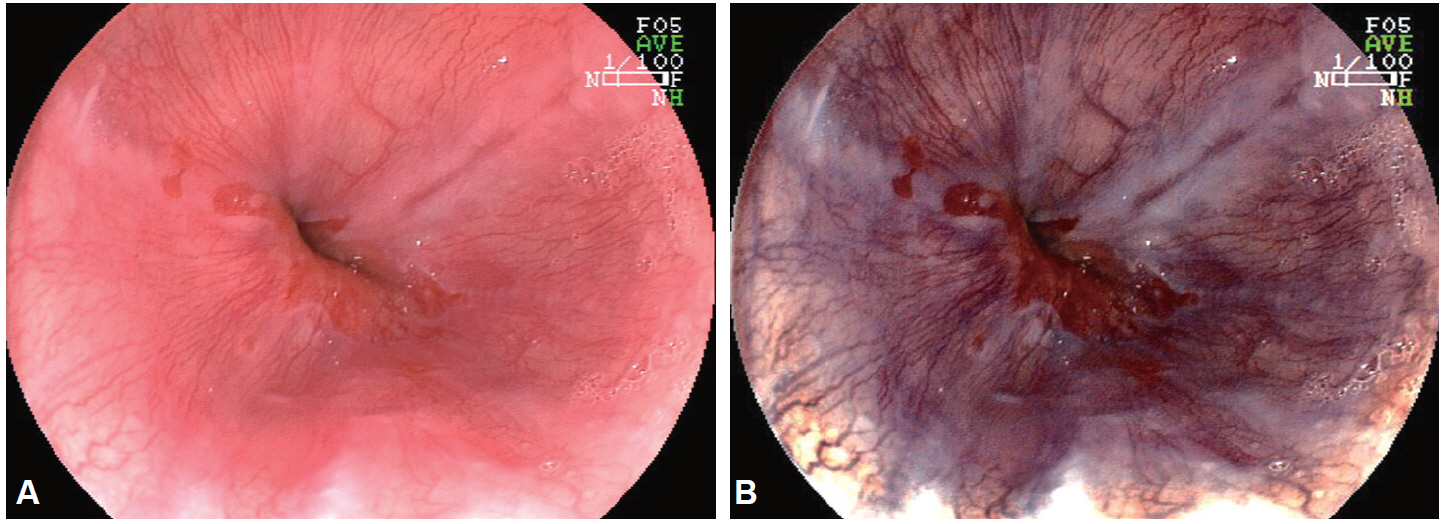
- Despite the remarkable progress recently made to enhance the resolution of white-light endoscopy, detection, and diagnosis of premalignant lesions, such as adenomas and subtle early-stage cancers, remains a great challenge. As for example, although chromoendoscopy, such as endoscopy using indigo carmine, is useful for the early diagnosis of subtle lesions, the technique presents various disadvantages ranging from the time required for spray application of the dye and suctioning of excess dye to the increased difficulty in identifying lesions in the presence of severe inflammation and obstruction of visual field due to the pooling of solution in depressed-type lesions. To overcome these diagnostic problems associated with chromoendoscopy, research has focused on the development of endoscopes based on new optical technologies. Several types of image-enhanced endoscopy methods have recently been presented. In particular, image-enhanced endoscopy has emerged as a new paradigm for the diagnosis of gastrointestinal disorders. Image-enhanced endoscopes provide high-contrast images of lesions by means of optical or electronic technologies, including the contrast enhancement of the mucosal surface and of blood vessels. Chromoendoscopy, narrow-band imaging, i-SCAN, and flexible spectral imaging color enhancement are representative examples of image-enhanced endoscopy discussed in this paper.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
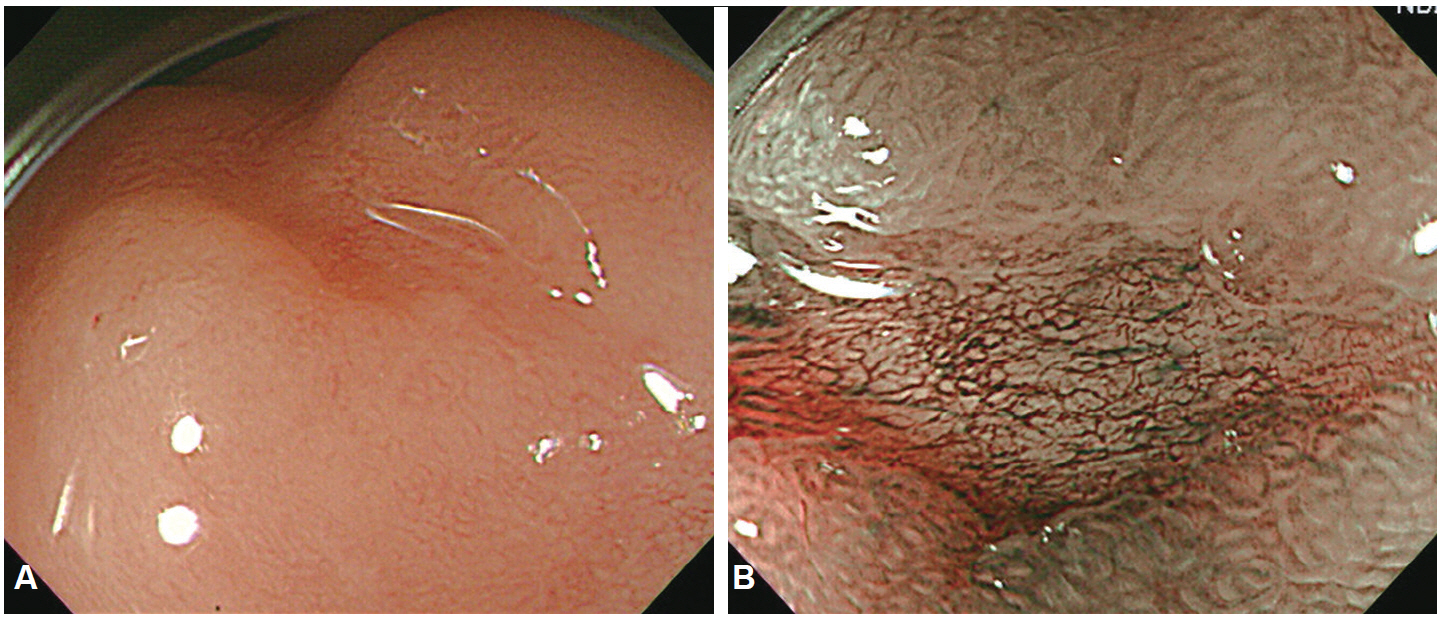
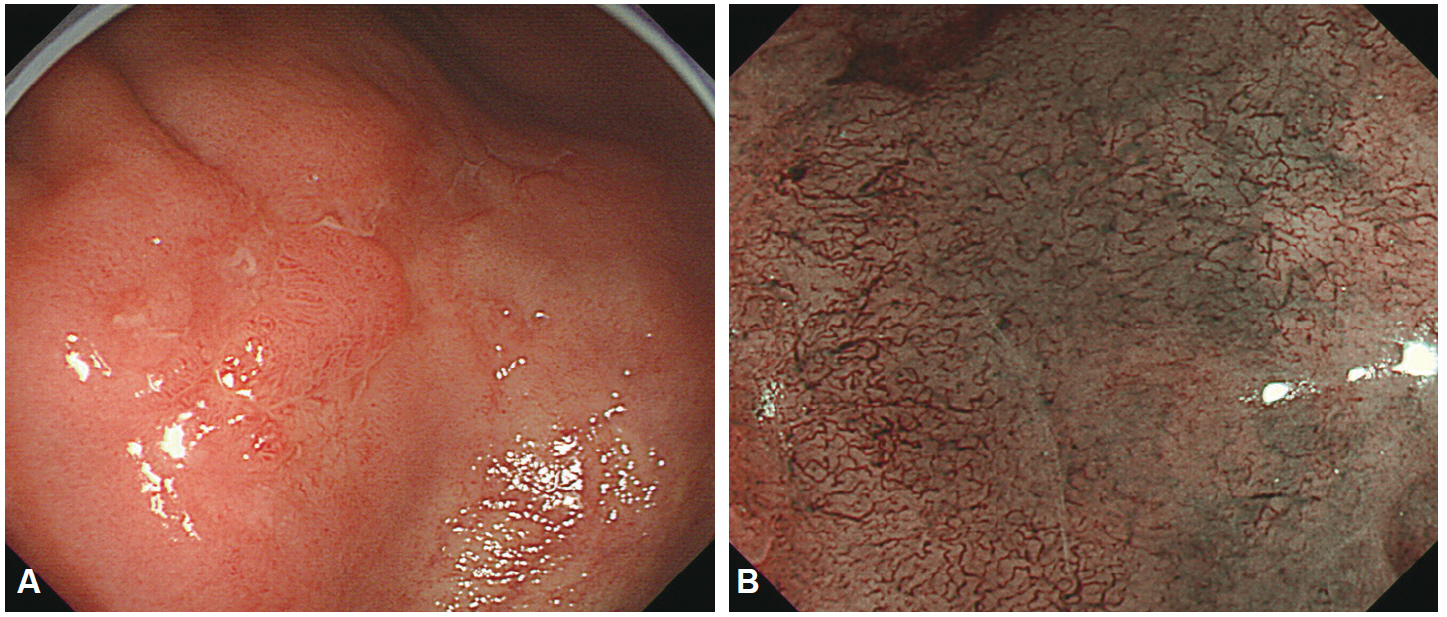
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Application of Current Image-Enhanced Endoscopy in Gastric Diseases
Wansik Lee
Clin Endosc. 2021;54(4):477-487. doi: 10.5946/ce.2021.160.The Role of Dual Red Imaging in Gastric Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection
In Kyung Yoo, Joo Young Cho
Clin Endosc. 2020;53(1):1-2. doi: 10.5946/ce.2020.018.Usefulness of Narrow-Band Imaging in Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection of the Stomach
Jung-Wook Kim
Clin Endosc. 2018;51(6):527-533. doi: 10.5946/ce.2018.186.
Reference
-
1. Subramanian V, Ragunath K. Advanced endoscopic imaging: a review of commercially available technologies. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014; 12:368.e1–376.e1.
Article2. ASGE Technology Committee, Kwon RS, Adler DG, et al. High-resolution and high-magnification endoscopes. Gastrointest Endosc. 2009; 69(3 Pt 1):399–407.
Article3. Bruno MJ. Magnification endoscopy, high resolution endoscopy, and chromoscopy; towards a better optical diagnosis. Gut. 2003; 52 Suppl 4:iv7–iv11.
Article4. Peitz U, Malfertheiner P. Chromoendoscopy: from a research tool to clinical progress. Dig Dis. 2002; 20:111–119.
Article5. Woolf GM, Riddell RH, Irvine EJ, Hunt RH. A study to examine agreement between endoscopy and histology for the diagnosis of columnar lined (Barrett’s) esophagus. Gastrointest Endosc. 1989; 35:541–544.
Article6. Inoue H, Rey JF, Lightdale C. Lugol chromoendoscopy for esophageal squamous cell cancer. Endoscopy. 2001; 33:75–79.7. Kida M, Kobayashi K, Saigenji K. Routine chromoendoscopy for gastrointestinal diseases: indications revised. Endoscopy. 2003; 35:590–596.
Article8. Canto MI, Setrakian S, Petras RE, Blades E, Chak A, Sivak MV Jr. Methylene blue selectively stains intestinal metaplasia in Barrett’s esophagus. Gastrointest Endosc. 1996; 44:1–7.
Article9. Stevens PD, Lightdale CJ, Green PH, Siegel LM, Garcia-Carrasquillo RJ, Rotterdam H. Combined magnification endoscopy with chromoendoscopy for the evaluation of Barrett’s esophagus. Gastrointest Endosc. 1994; 40:747–749.
Article10. Siegel LM, Stevens PD, Lightdale CJ, et al. Combined magnification endoscopy with chromoendoscopy in the evaluation of patients with suspected malabsorption. Gastrointest Endosc. 1997; 46:226–230.
Article11. Axelrad AM, Fleischer DE, Geller AJ, et al. High-resolution chromoendoscopy for the diagnosis of diminutive colon polyps: implications for colon cancer screening. Gastroenterology. 1996; 110:1253–1258.
Article12. Sano Y, Muto M, Tajiri H, Ohtsu A, Yoshida S. Optical/digital chromoendoscopy during colonoscopy using narrow-band imaging system. Dig Endosc. 2005; 17 Suppl 1:S43–S48.
Article13. Muto M, Katada C, Sano Y, Yoshida S. Narrow band imaging: a new diagnostic approach to visualize angiogenesis in superficial neoplasia. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2005; 3(7 Suppl 1):S16–S20.
Article14. Cho WY, Jang JY, Lee DH; Endoscopic Technology and Investigation Study Group. Recent advances in image-enhanced endoscopy. Clin Endosc. 2011; 44:65–75.
Article15. Tajiri H, Matsuda K, Fujisaki J. What can we see with the endoscope? Present status and future perspectives. Dig Endosc. 2002; 14:131–137.
Article16. Kodashima S, Fujishiro M. Novel image-enhanced endoscopy with i-scan technology. World J Gastroenterol. 2010; 16:1043–1049.
Article17. Lee BI. EPK-i Endoscopy. Korean J Gastrointest Endosc. 2009; 39(Suppl 1):184–186.18. Yoshizawa M, Osawa H, Yamamoto H, et al. Diagnosis of elevated-type early gastric cancers by the optimal band imaging system. Gastrointest Endosc. 2009; 69:19–28.
Article19. Osawa H, Yoshizawa M, Yamamoto H, et al. Optimal band imaging system can facilitate detection of changes in depressed-type early gastric cancer. Gastrointest Endosc. 2008; 67:226–234.
Article20. ASGE Technology Committee, Manfredi MA, Abu Dayyeh BK, et al. Electronic chromoendoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2015; 81:249–261.
Article21. Osawa H, Yamamoto H. Present and future status of flexible spectral imaging color enhancement and blue laser imaging technology. Dig Endosc. 2014; 26 Suppl 1:105–115.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Is Image-Enhanced Endoscopy Useful for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Gastrointestinal Tumor?
- Past, Present, and Future of the Korea-Japan Joint Symposium on Gastrointestinal Endoscopy
- Application of Current Image-Enhanced Endoscopy in Gastric Diseases
- Quality Improvement of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy in Korea: Past, Present, and Future
- Role of Image-Enhanced Endoscopy in Pancreatobiliary Diseases